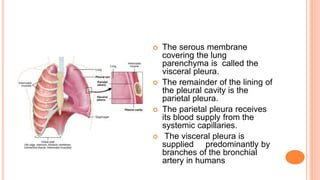
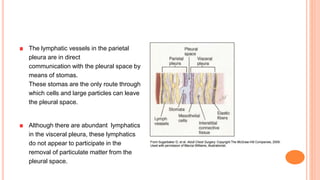
This document discusses pleural effusions, which occur when fluid accumulates in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. A small amount of fluid is normal but excess fluid can accumulate if the rate of fluid formation exceeds drainage by lymphatics. Effusions are classified as transudative or exudative based on their protein content and cell characteristics. Common causes of transudative effusions include heart failure and cirrhosis, while exudative effusions have infectious or inflammatory causes like pneumonia or cancer. Diagnosis involves physical exam, imaging like chest x-ray, and analyzing pleural fluid obtained via thoracentesis.