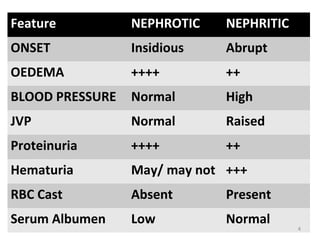
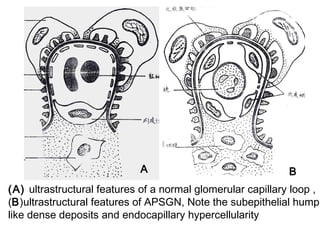
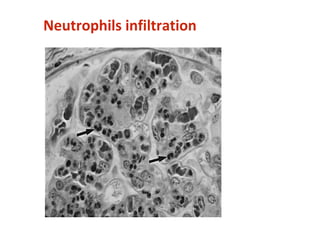
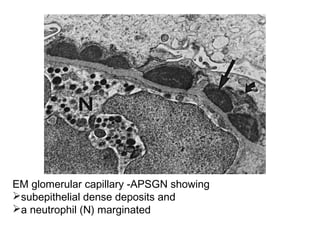
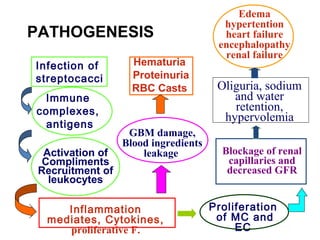
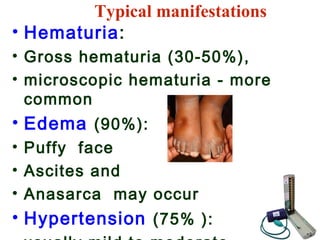
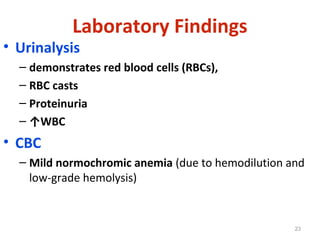
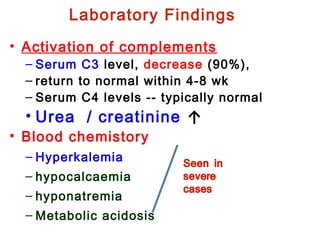
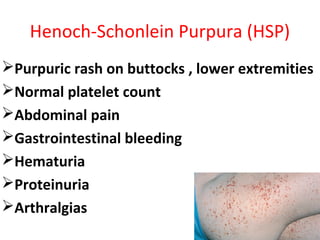
This document provides information about Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis (APSGN). It begins by describing the features of acute nephritic syndrome which is characterized by gross hematuria, edema, hypertension, and renal insufficiency. It then discusses the pathology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management of APSGN. APSGN is caused by a previous streptococcal infection and results in immune complex deposition in the glomeruli. It presents abruptly with hematuria, edema, hypertension, and sometimes renal insufficiency. Treatment focuses on supporting kidney function and controlling blood pressure while the patient recovers over 6-8 weeks. Prognosis is generally good with complete recovery in over 95