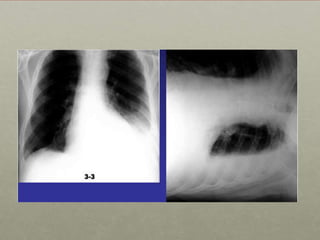
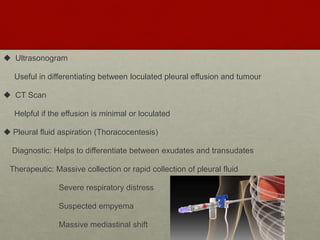
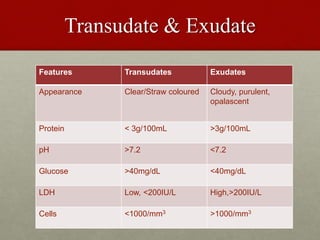
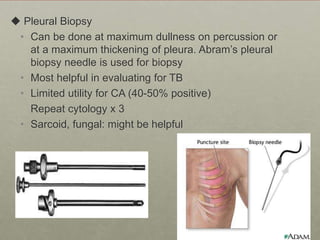
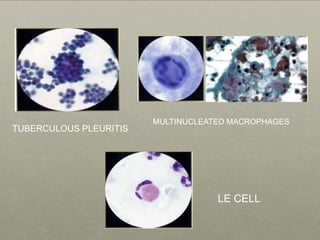
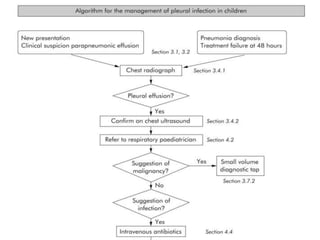
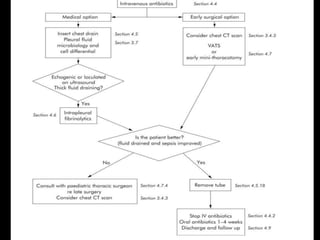
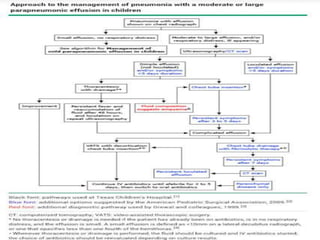
Pleural effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It can be caused by conditions that alter fluid pressure or permeability of the pleura. A pleural effusion is classified based on its location, mechanism, and fluid characteristics. Evaluation involves physical exam, chest x-ray, ultrasound, and thoracentesis to analyze the fluid. Management depends on treating the underlying cause, with antibiotics for infections, diuretics for heart failure, or drainage procedures for large or infected effusions.