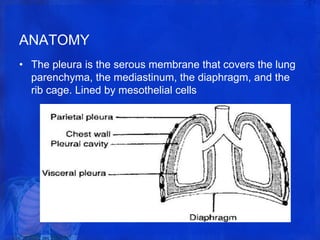
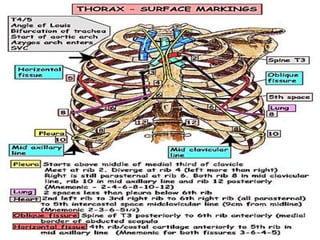
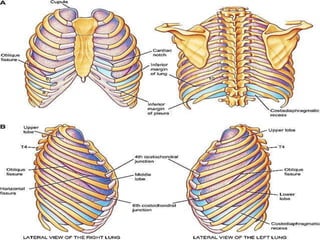
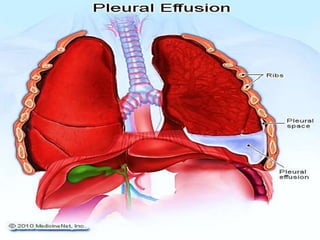
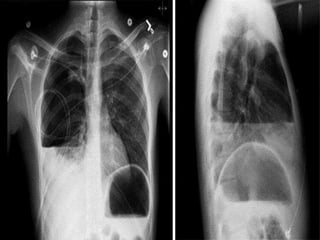
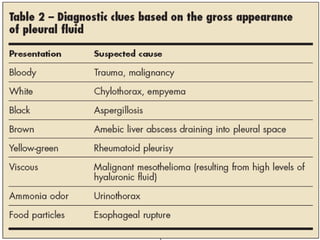
The pleura is a membrane that covers the lungs and lines the chest cavity. Pleural effusions occur when there is an imbalance between pleural fluid formation and absorption, causing excess fluid in the pleural space. Effusions can be transudative or exudative based on fluid characteristics. Common causes include heart failure, pneumonia, cancer, and cirrhosis. Symptoms range from none to chest pain and dyspnea. Diagnosis involves chest imaging, fluid analysis, and other tests. Treatment focuses on resolving the underlying cause and draining significant fluid accumulations.