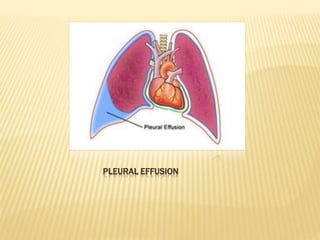
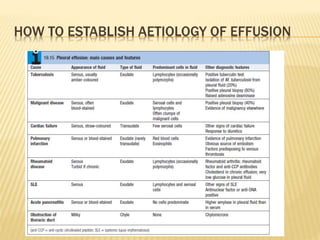
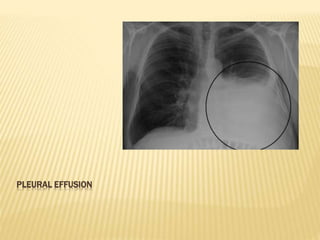
The document discusses pleural effusion, which is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Common causes include pneumonia, tuberculosis, pulmonary infarction, and malignant diseases. The fluid can be classified as a transudate or exudate based on biochemical analysis. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan to detect fluid levels. Diagnostic thoracentesis allows classification and identification of causative organisms if infected. Treatment focuses on draining large fluid volumes and addressing the underlying cause.