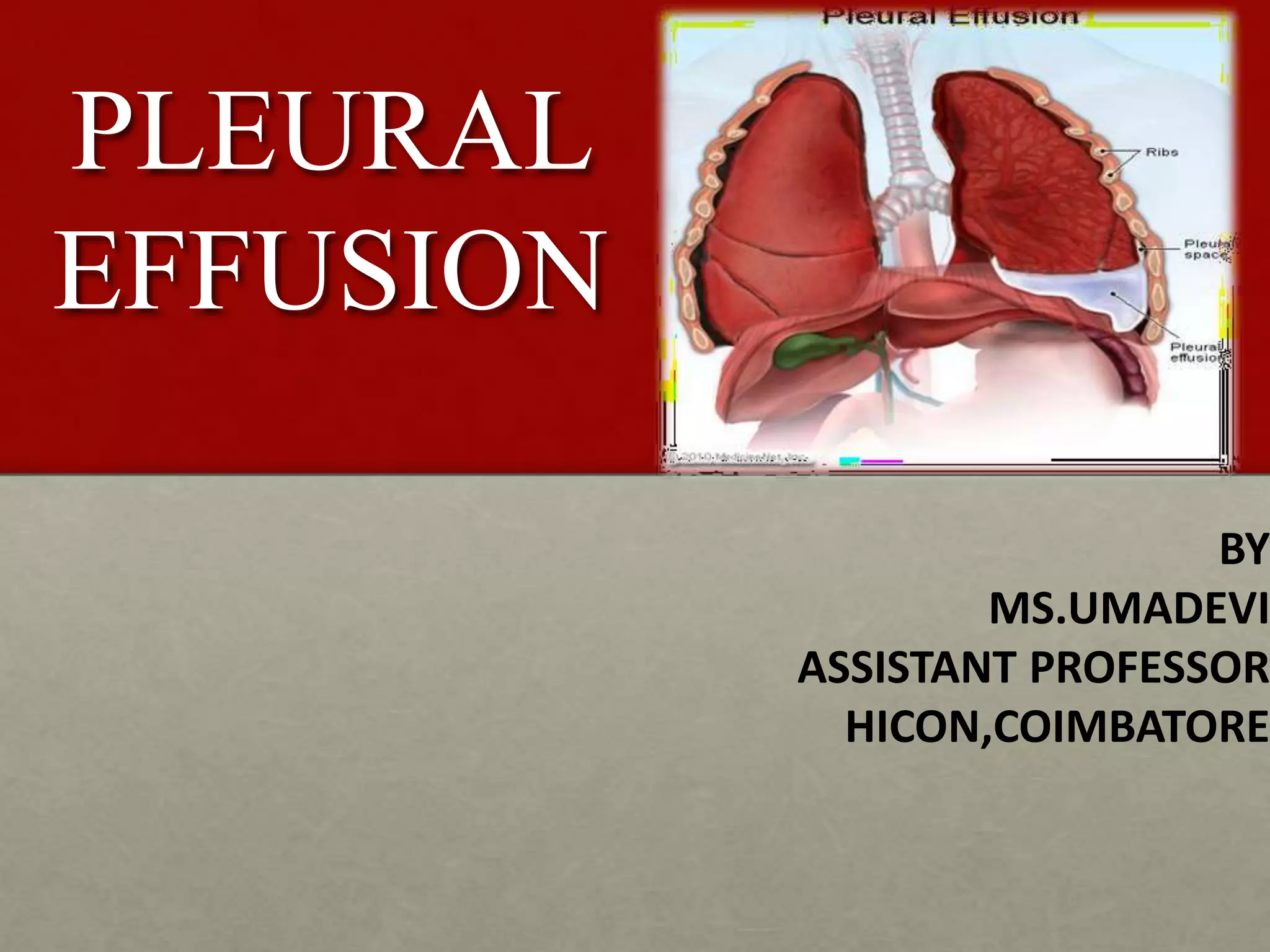
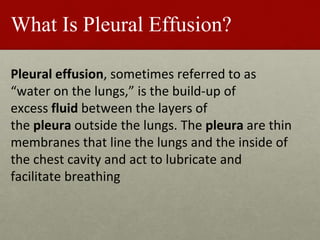
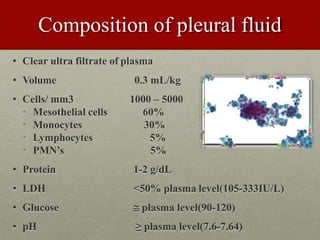
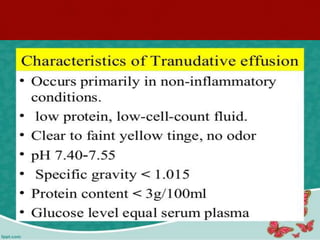
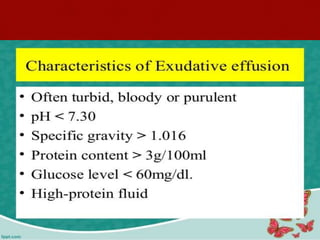
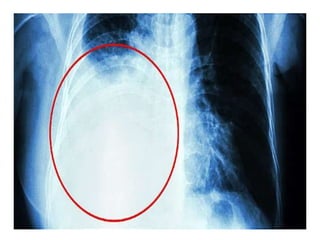
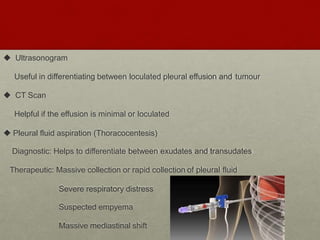
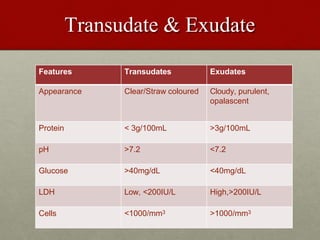
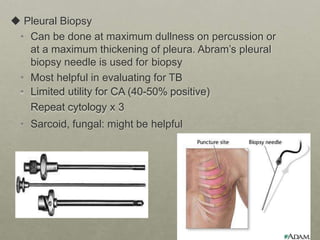
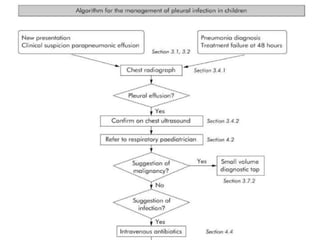
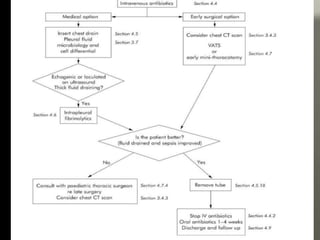
Pleural effusion is an accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It is usually secondary to other conditions that interfere with fluid drainage or secretion in the pleural space. Common causes include infections like pneumonia, congestive heart failure, cancers, and autoimmune diseases. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray, ultrasound, and thoracentesis to analyze pleural fluid characteristics. Management focuses on treating the underlying cause, relieving symptoms by removing fluid via thoracentesis or chest tube, and preventing further fluid buildup. Surgery may be needed for cases that do not improve with drainage or medication.