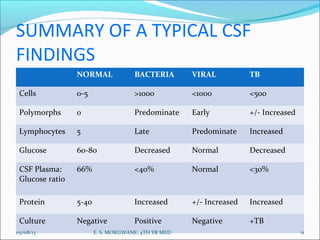
This document contains information about cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) characteristics, including normal values for components such as volume, color, transparency, pH, and electrolyte levels. It also describes abnormal CSF appearances such as being bright red, xanthochromic, or turbid that can indicate conditions like recent hemorrhage or bacterial infection. Common CSF analytes that are measured are discussed, such as total protein, glucose, and cell counts, and how their levels may be altered in different pathological states including infection, inflammation, and tumors. Overall, the document provides a review of typical CSF findings and how they can help to distinguish between normal, bacterial, viral, tuberculosis, and other neurological conditions.