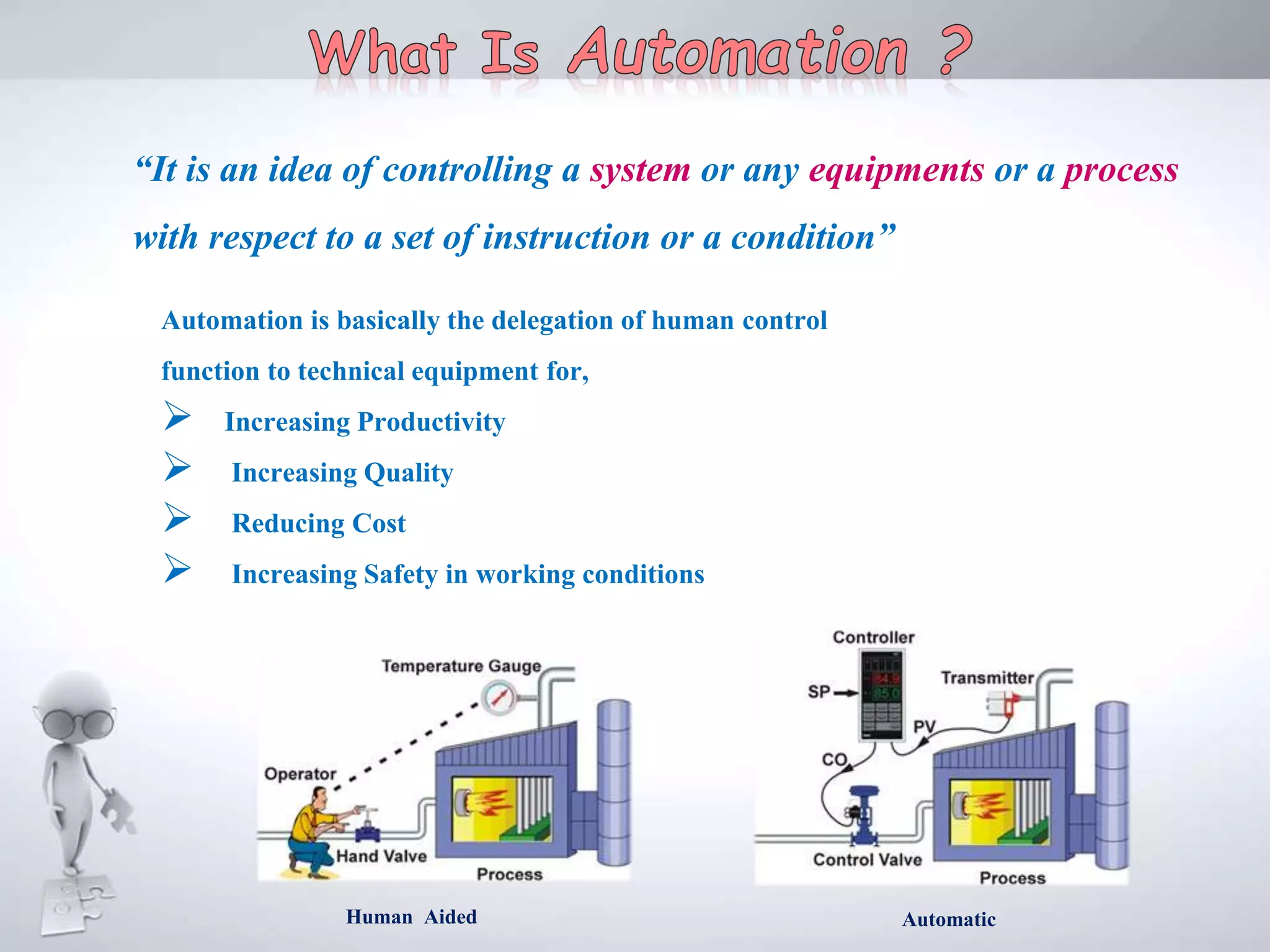
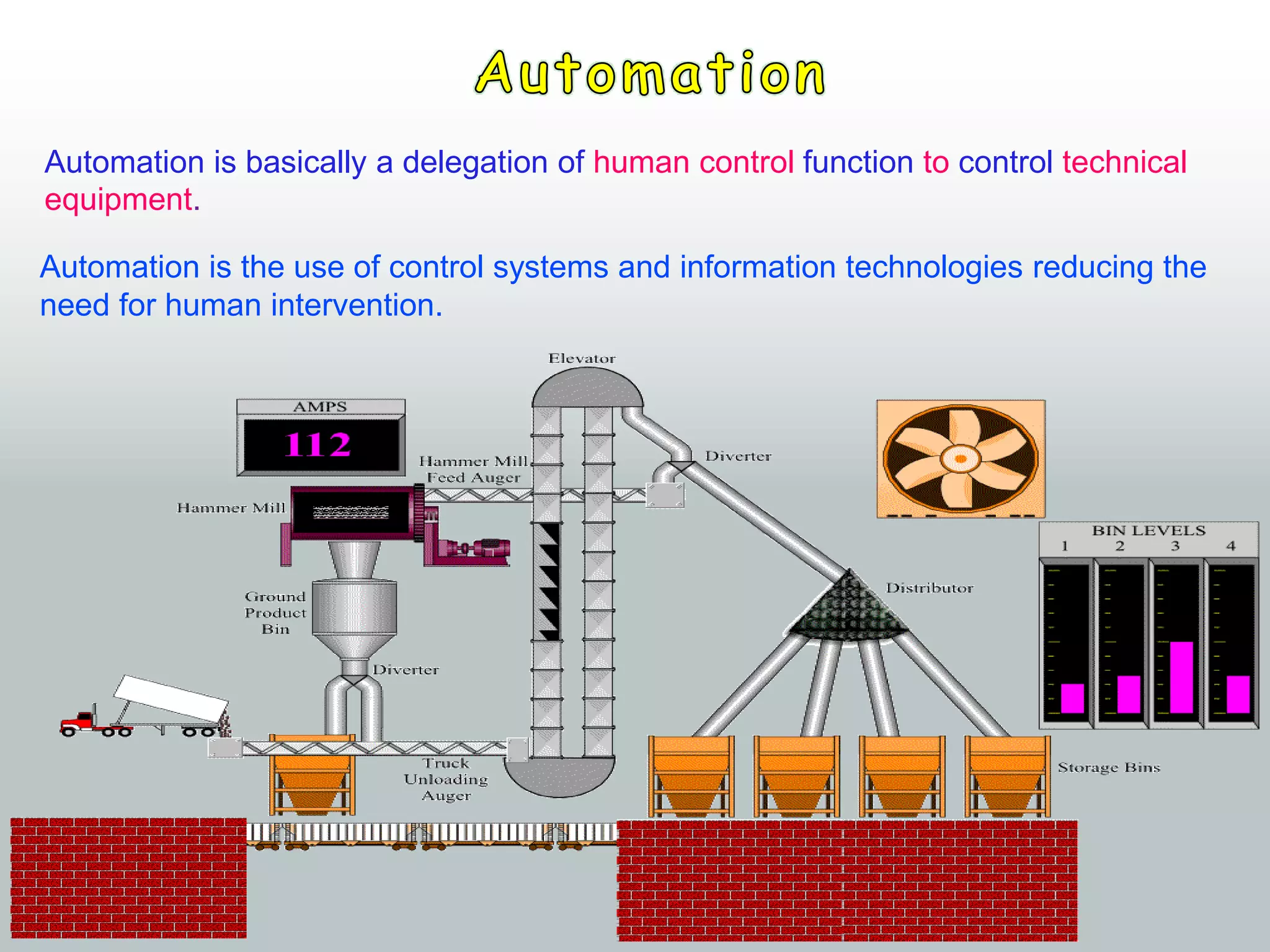
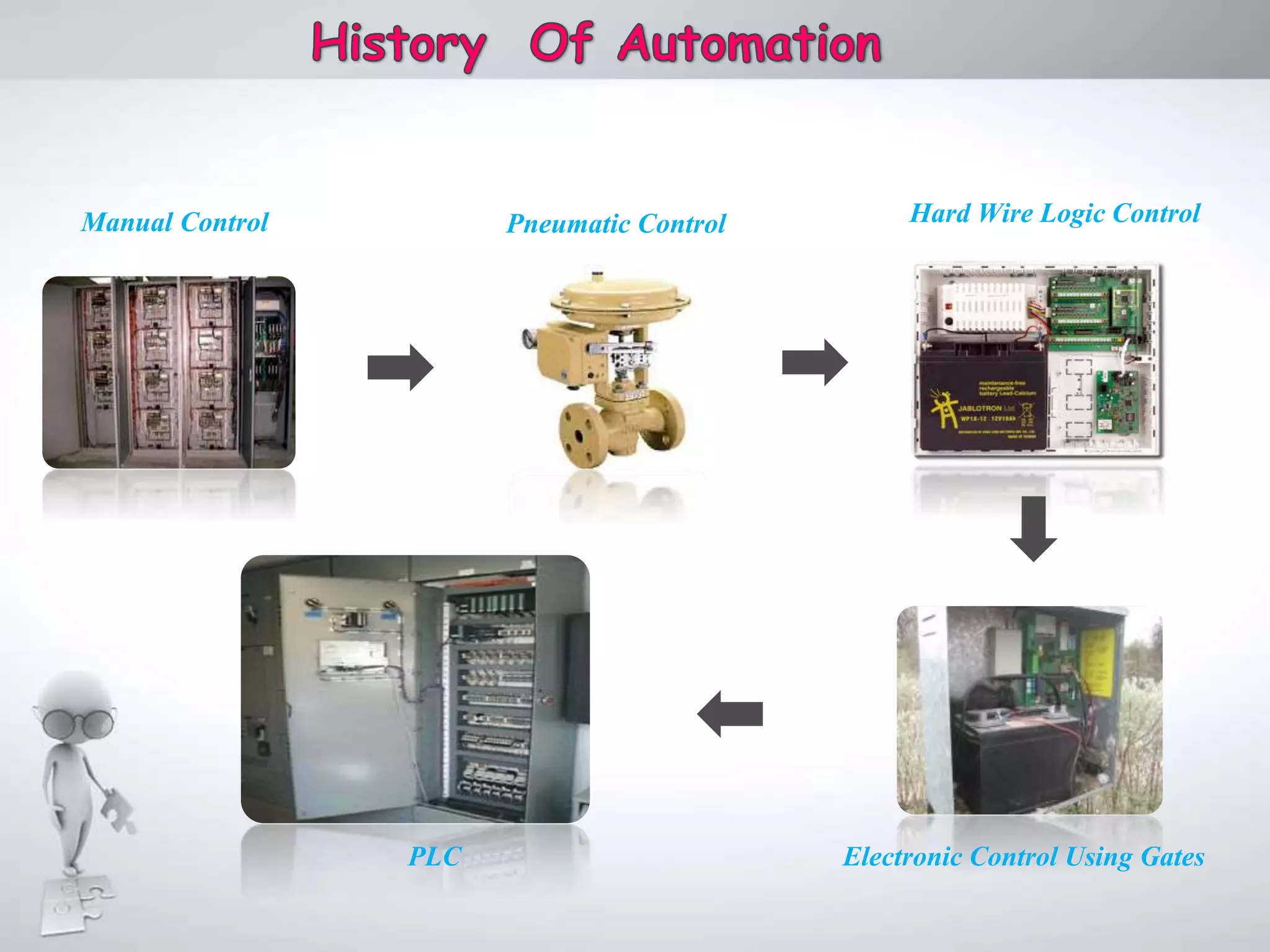
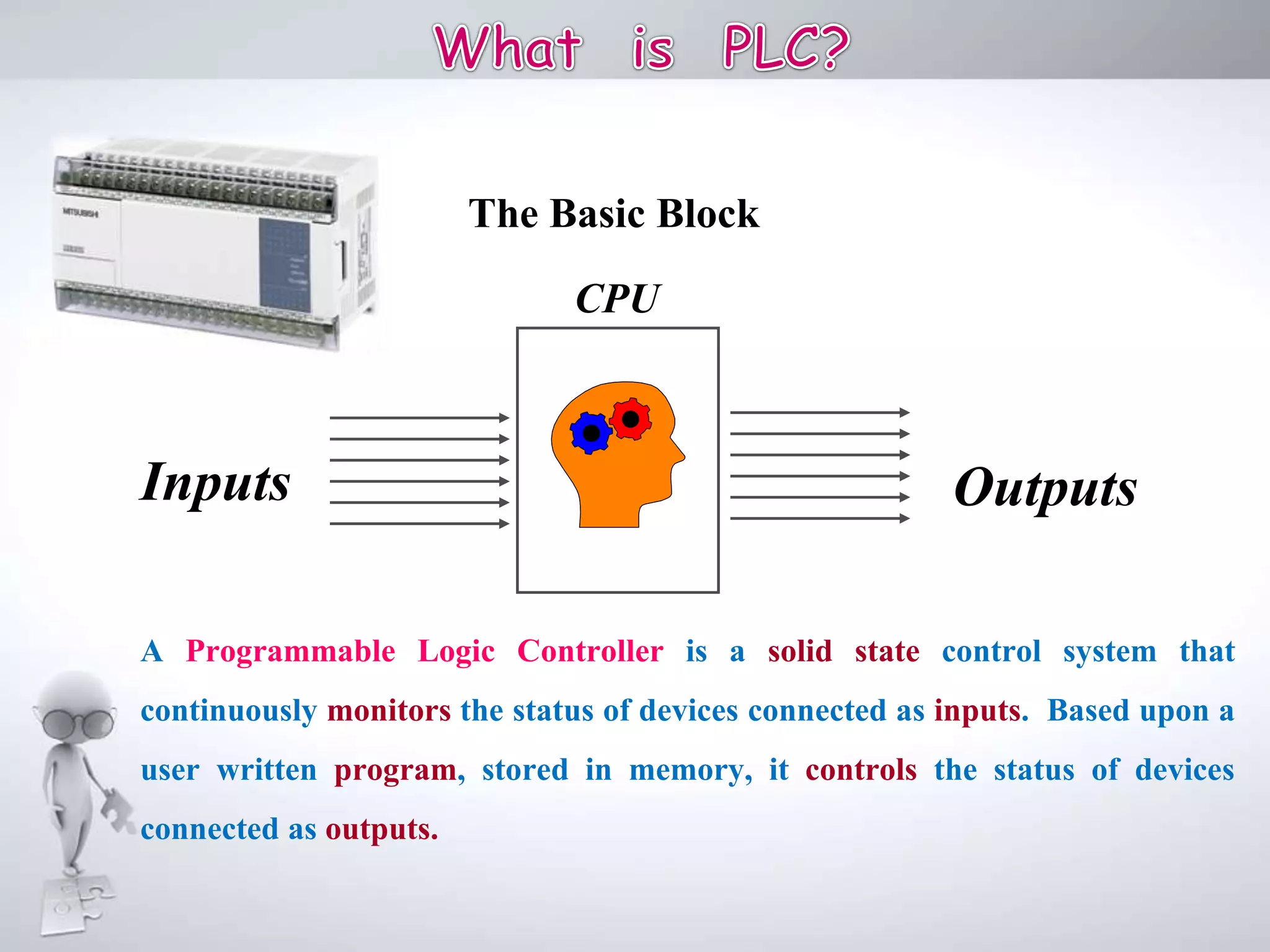
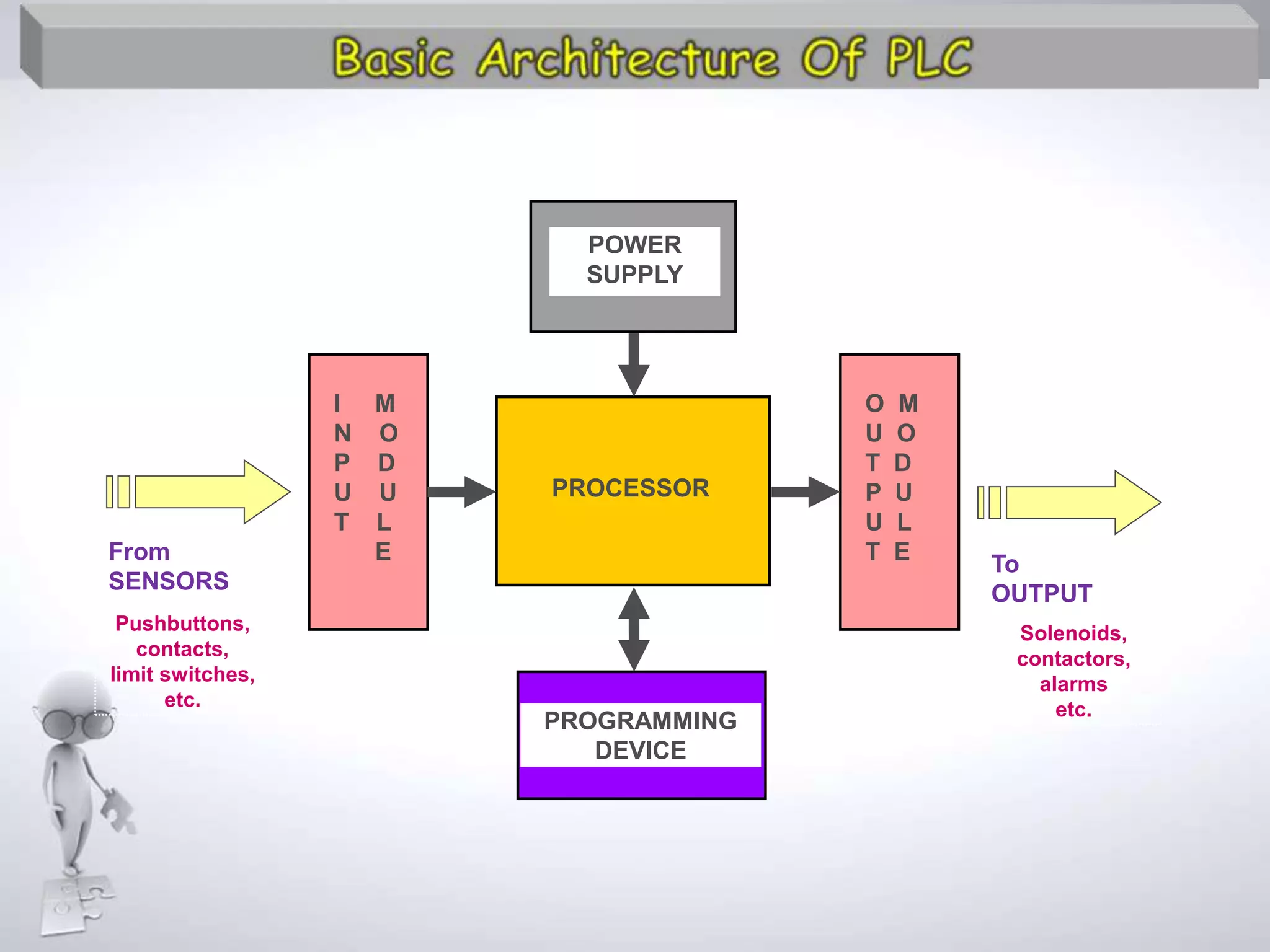
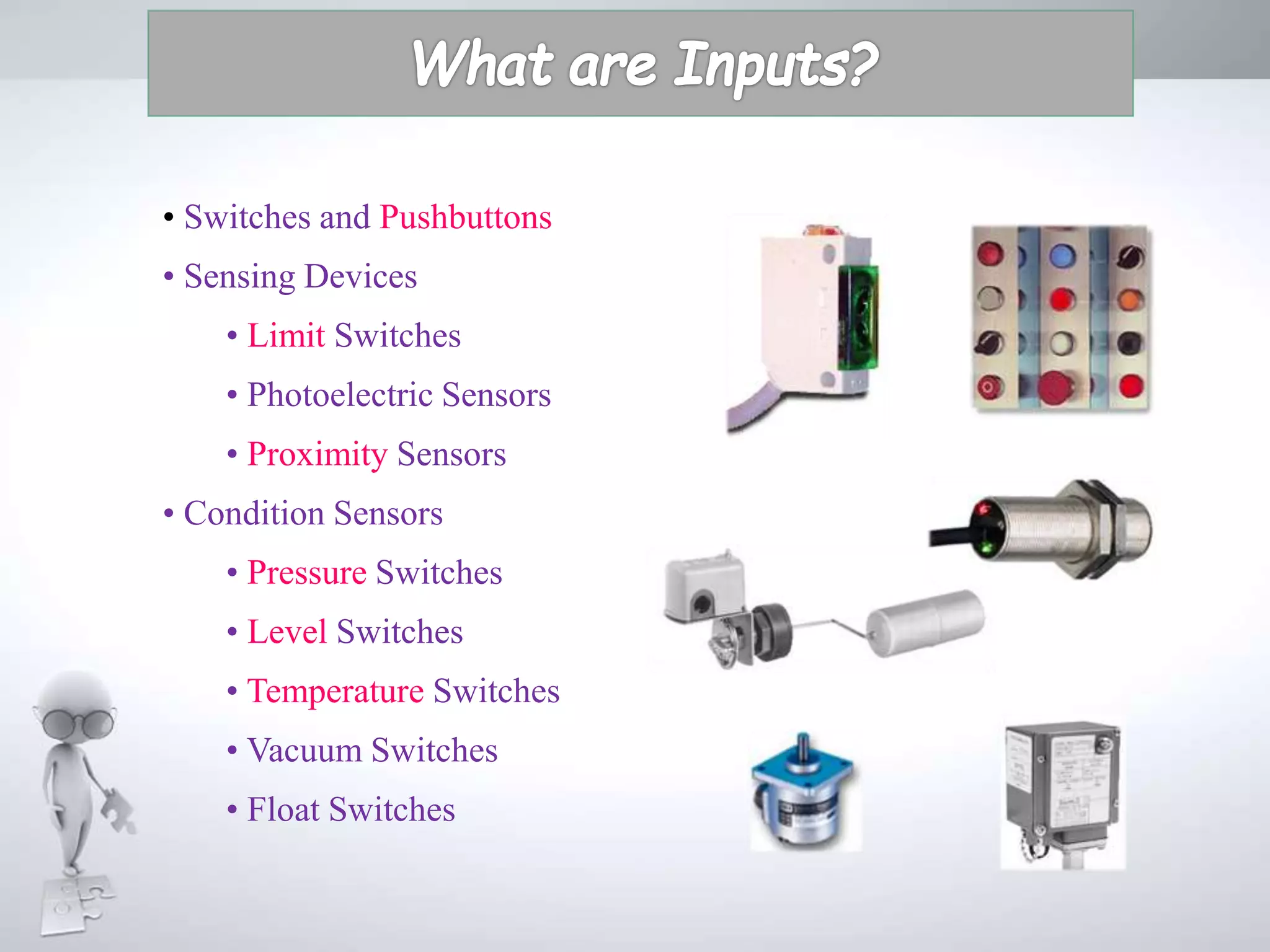
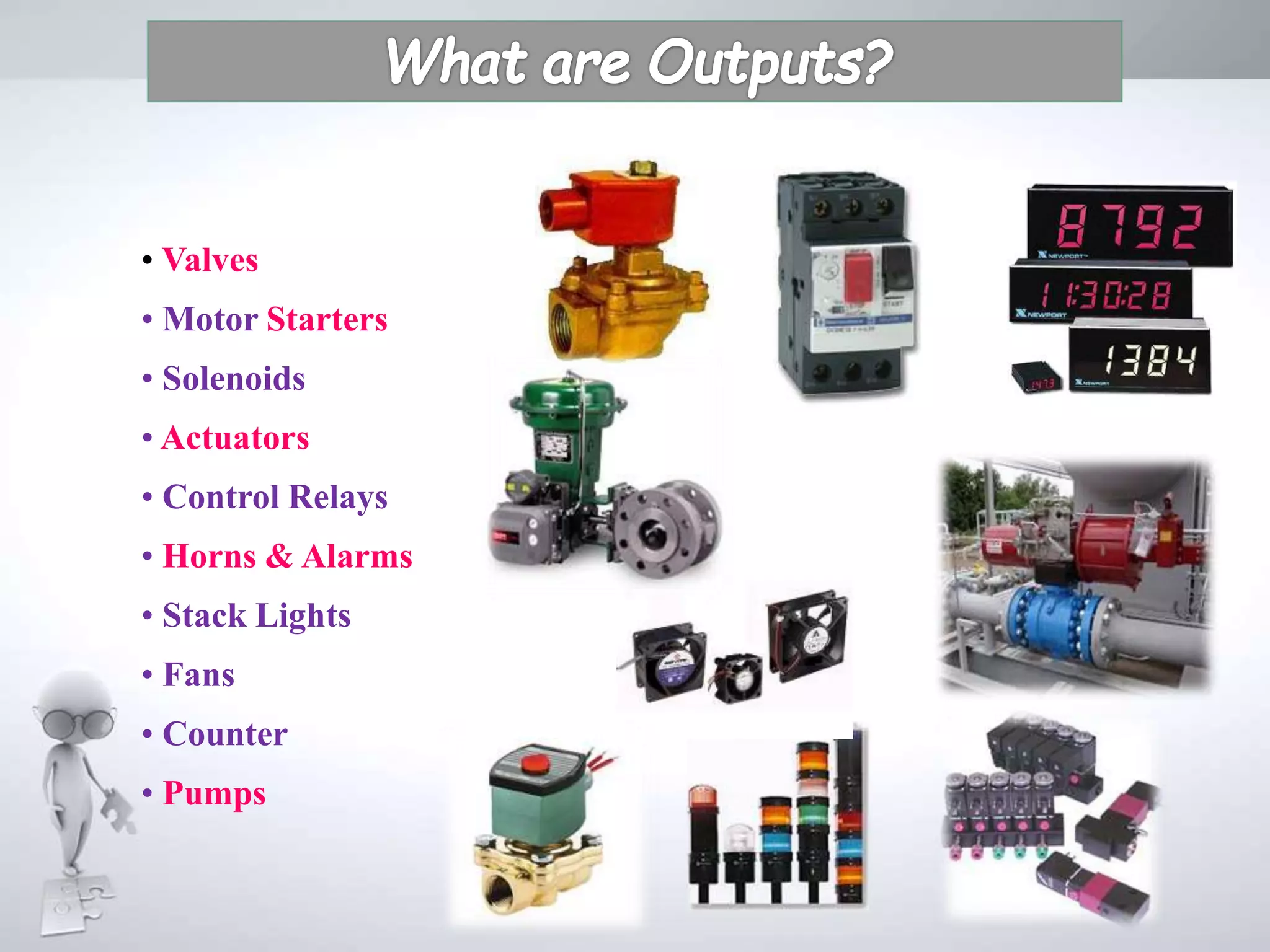
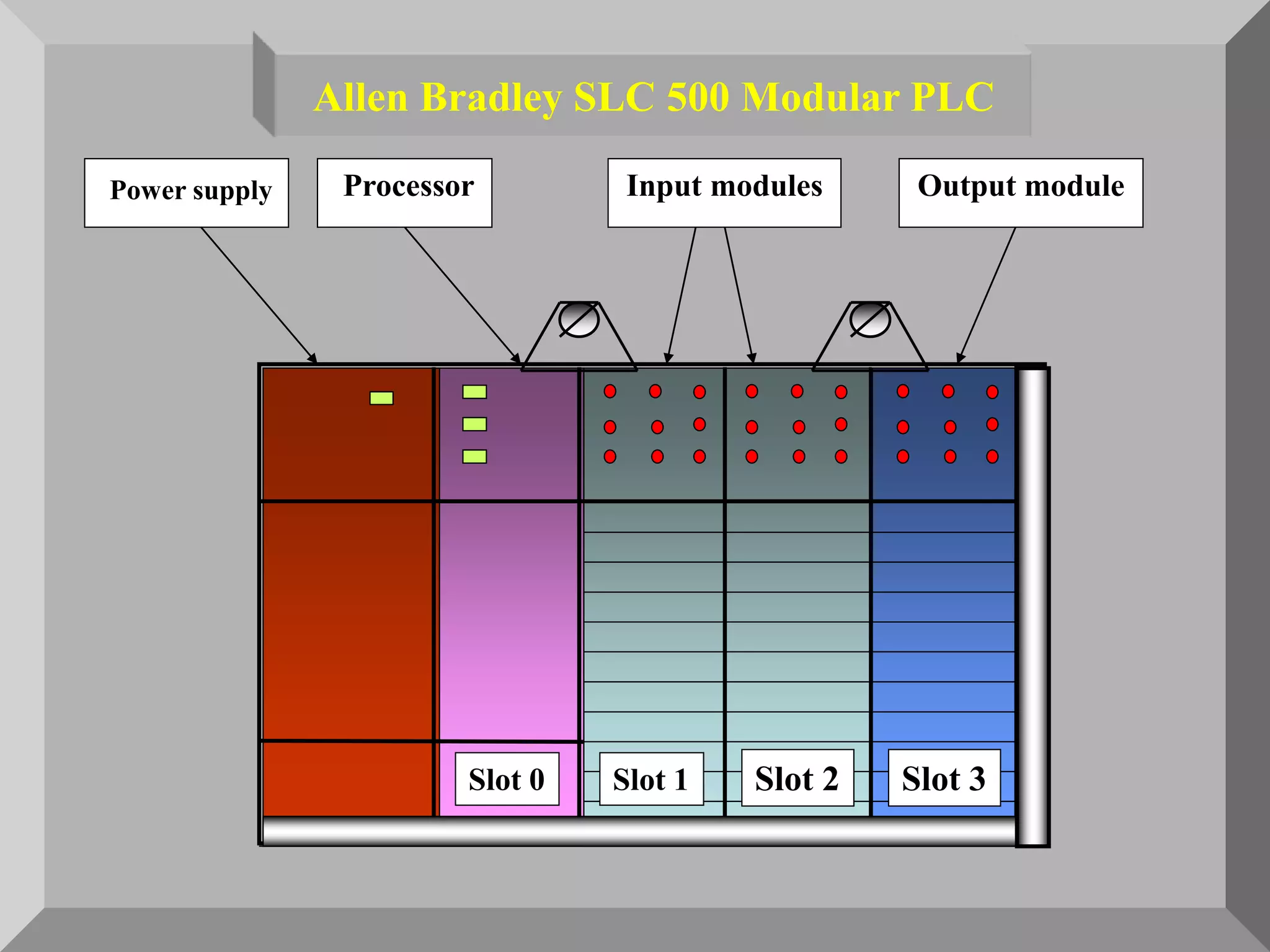
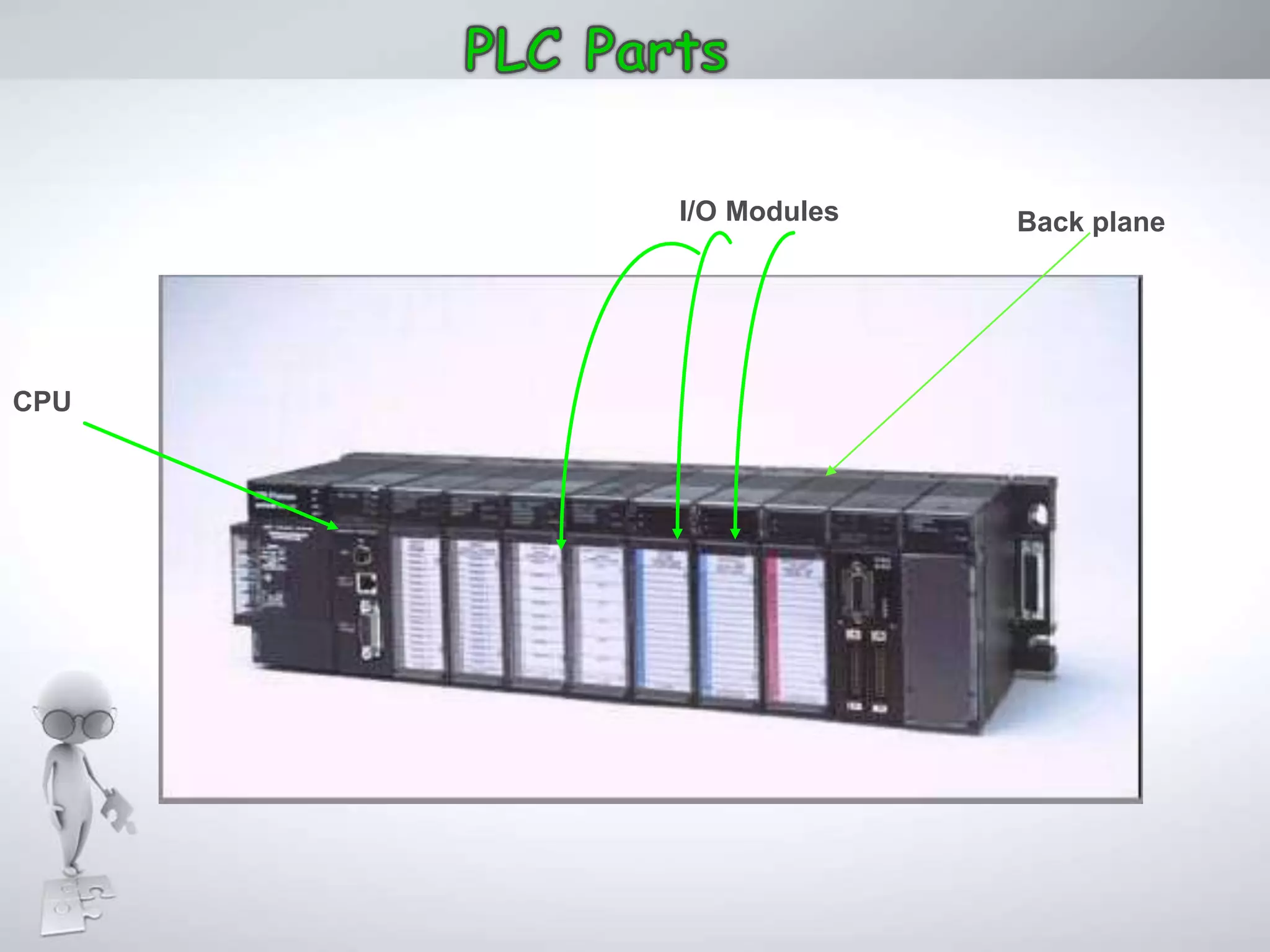
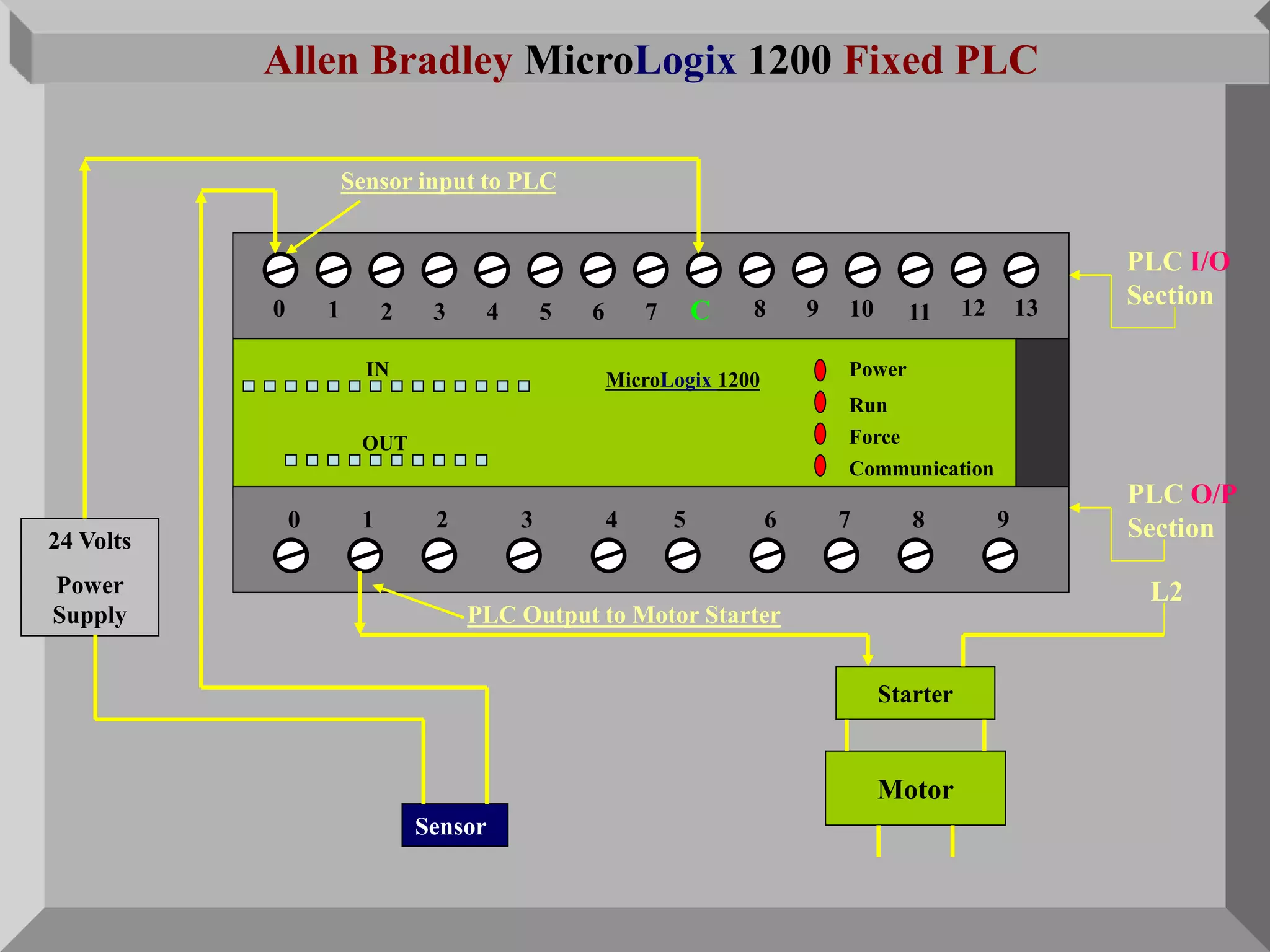
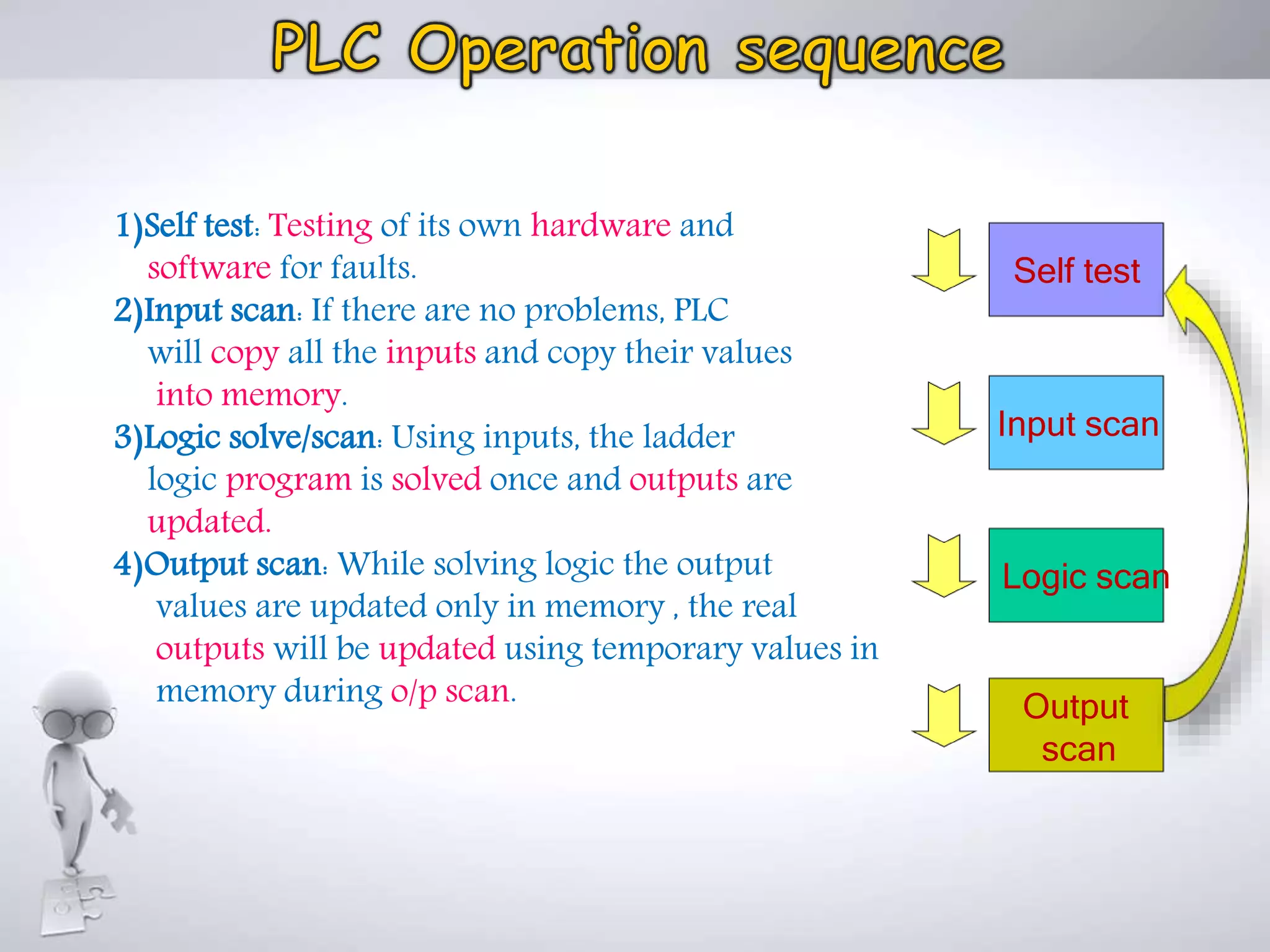
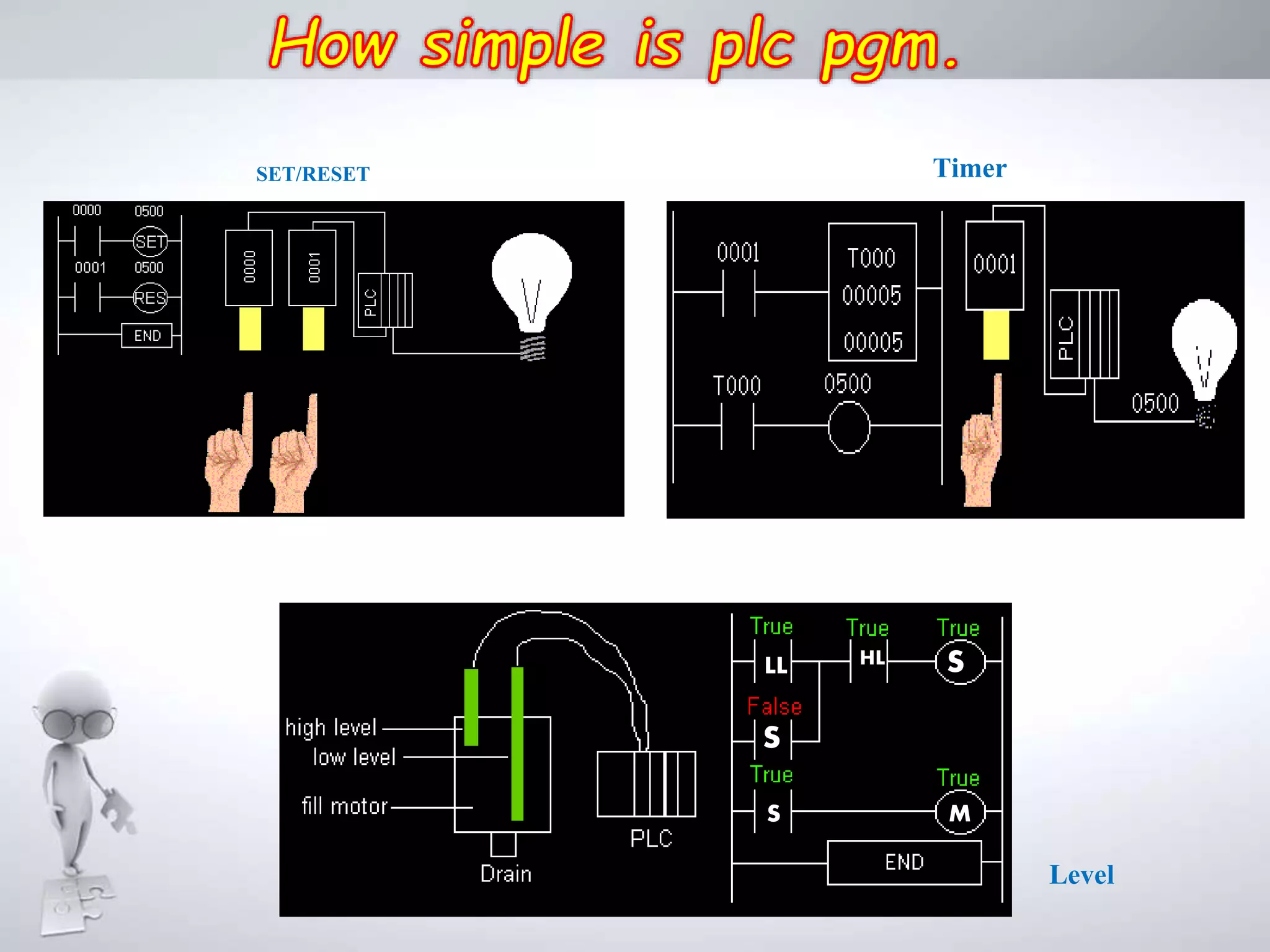
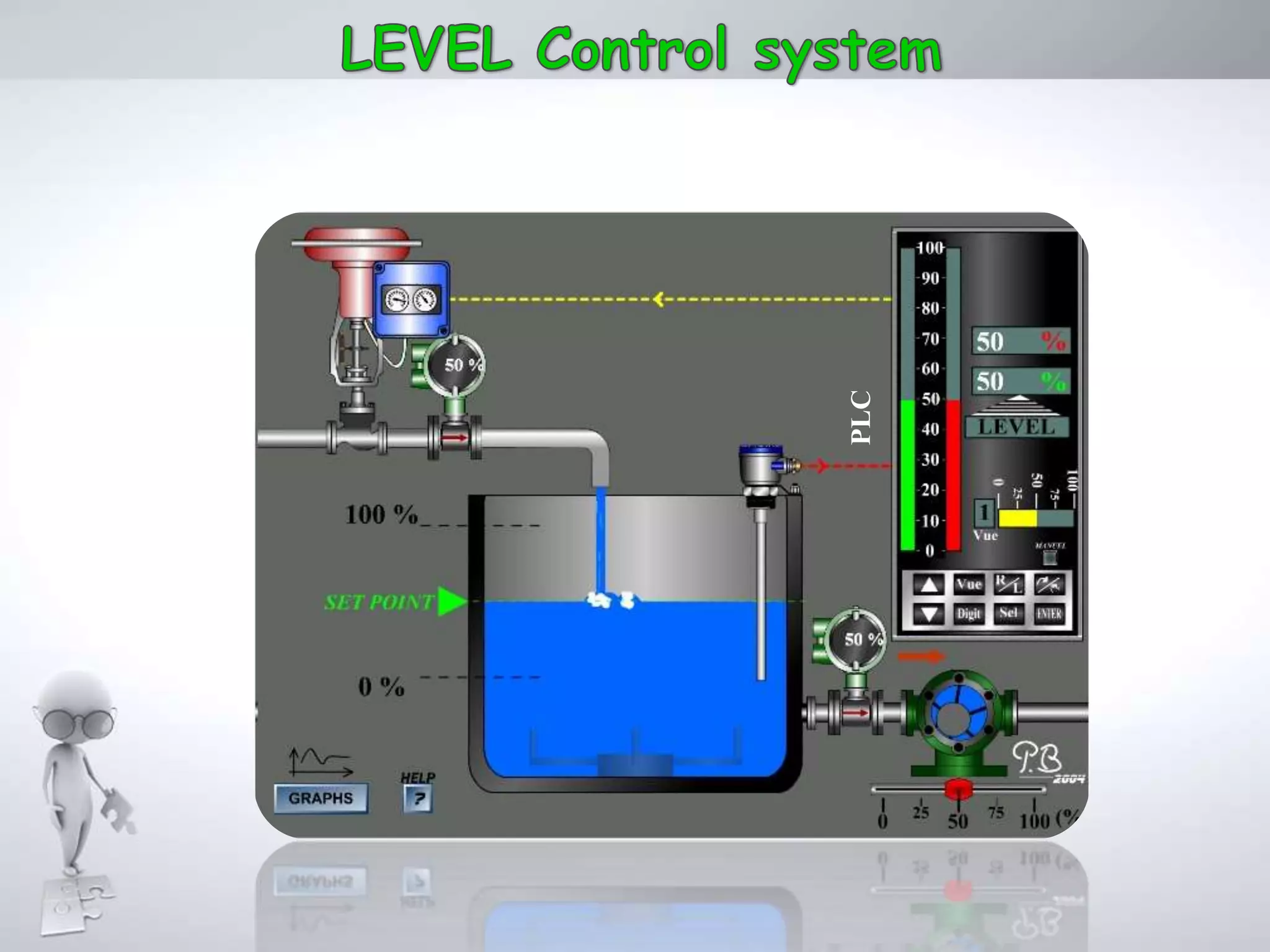
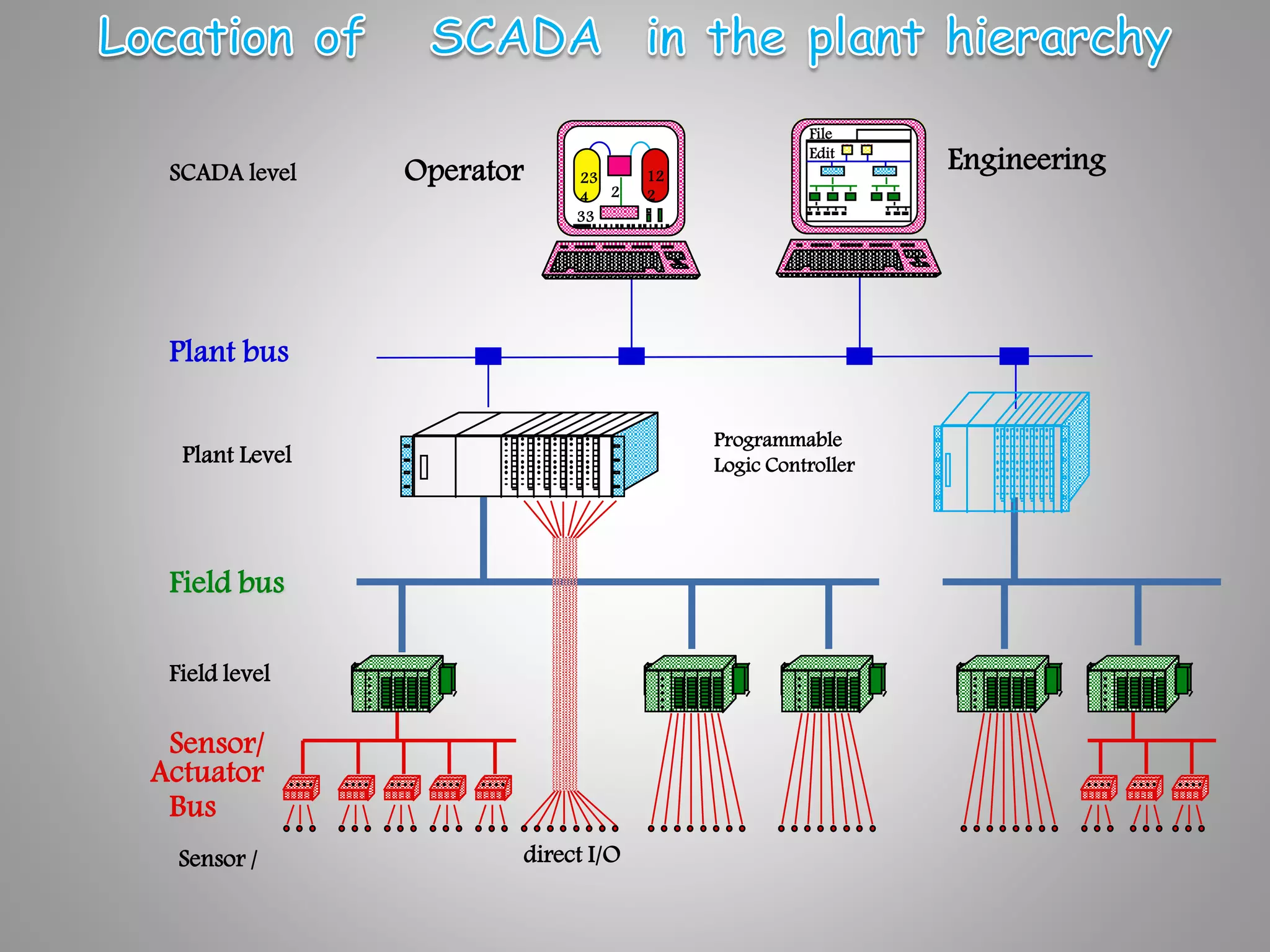
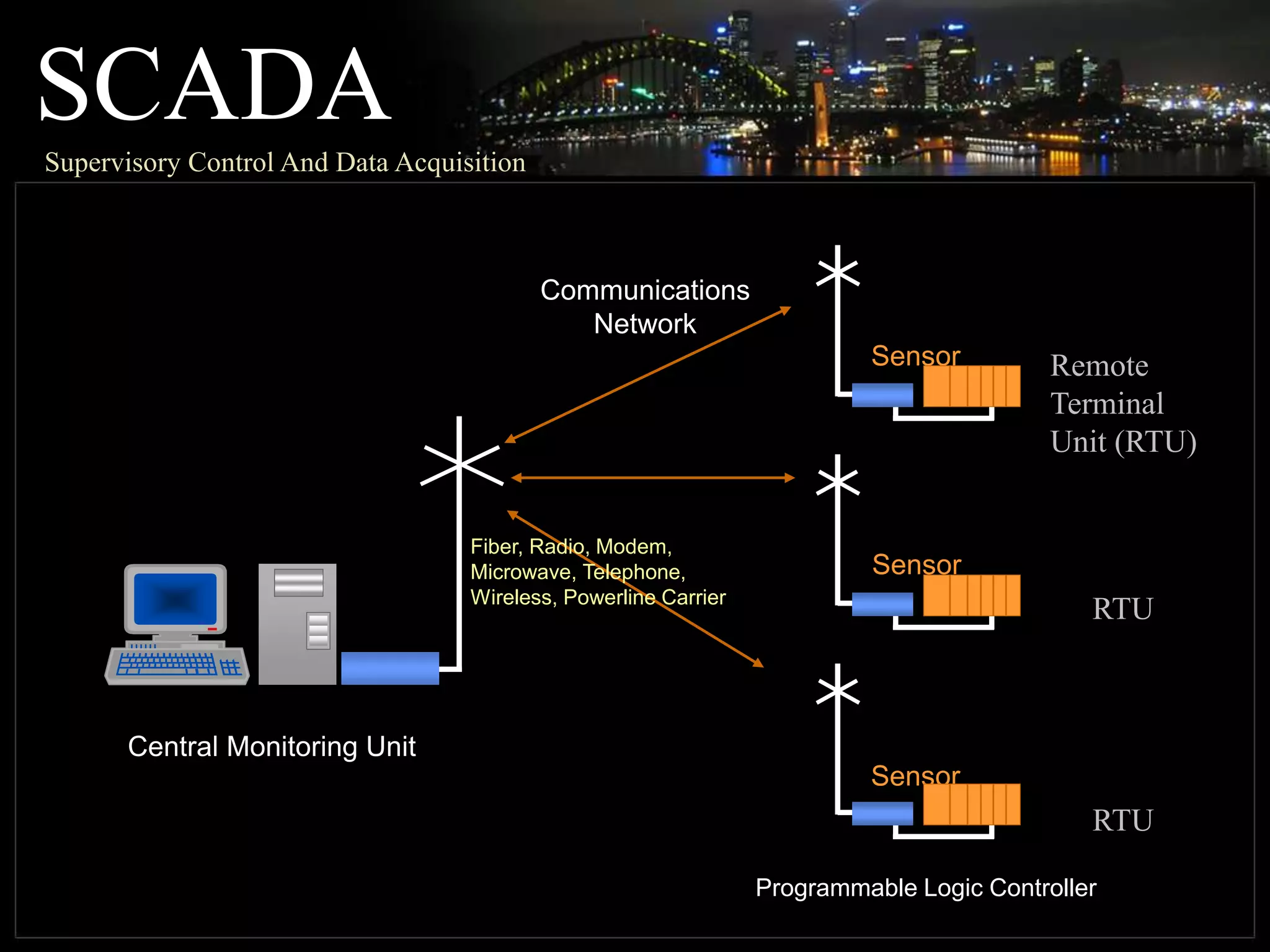
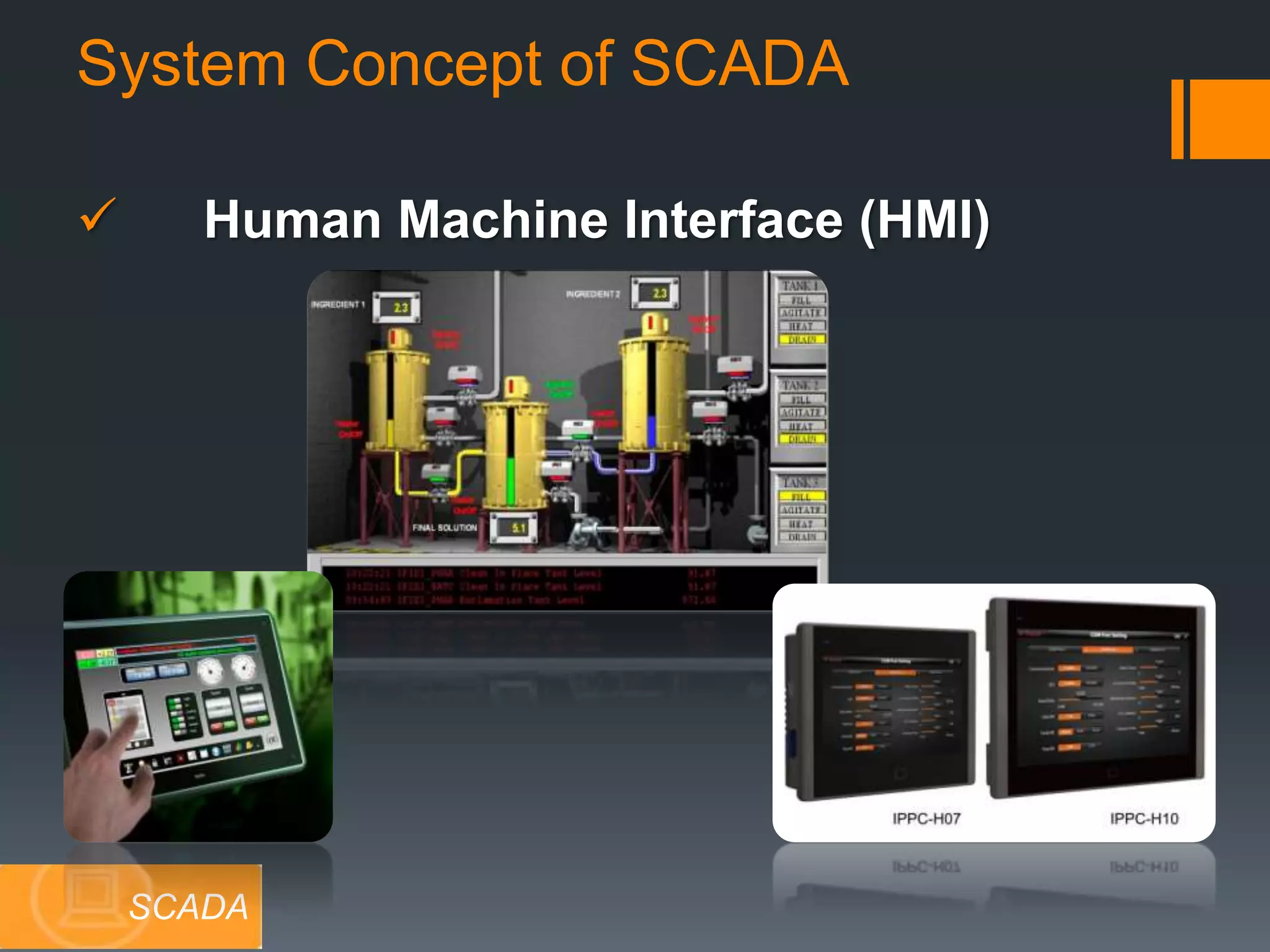
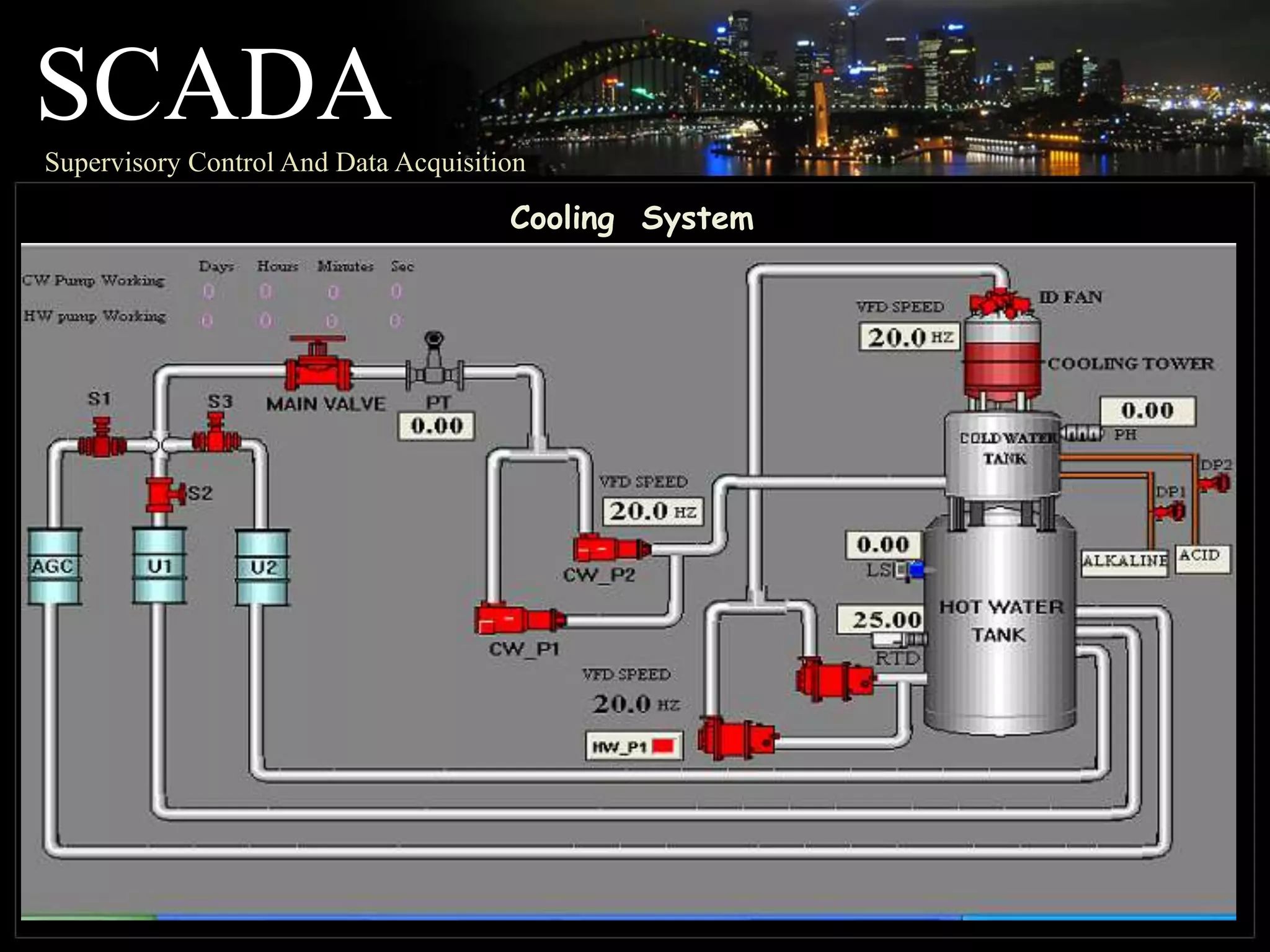
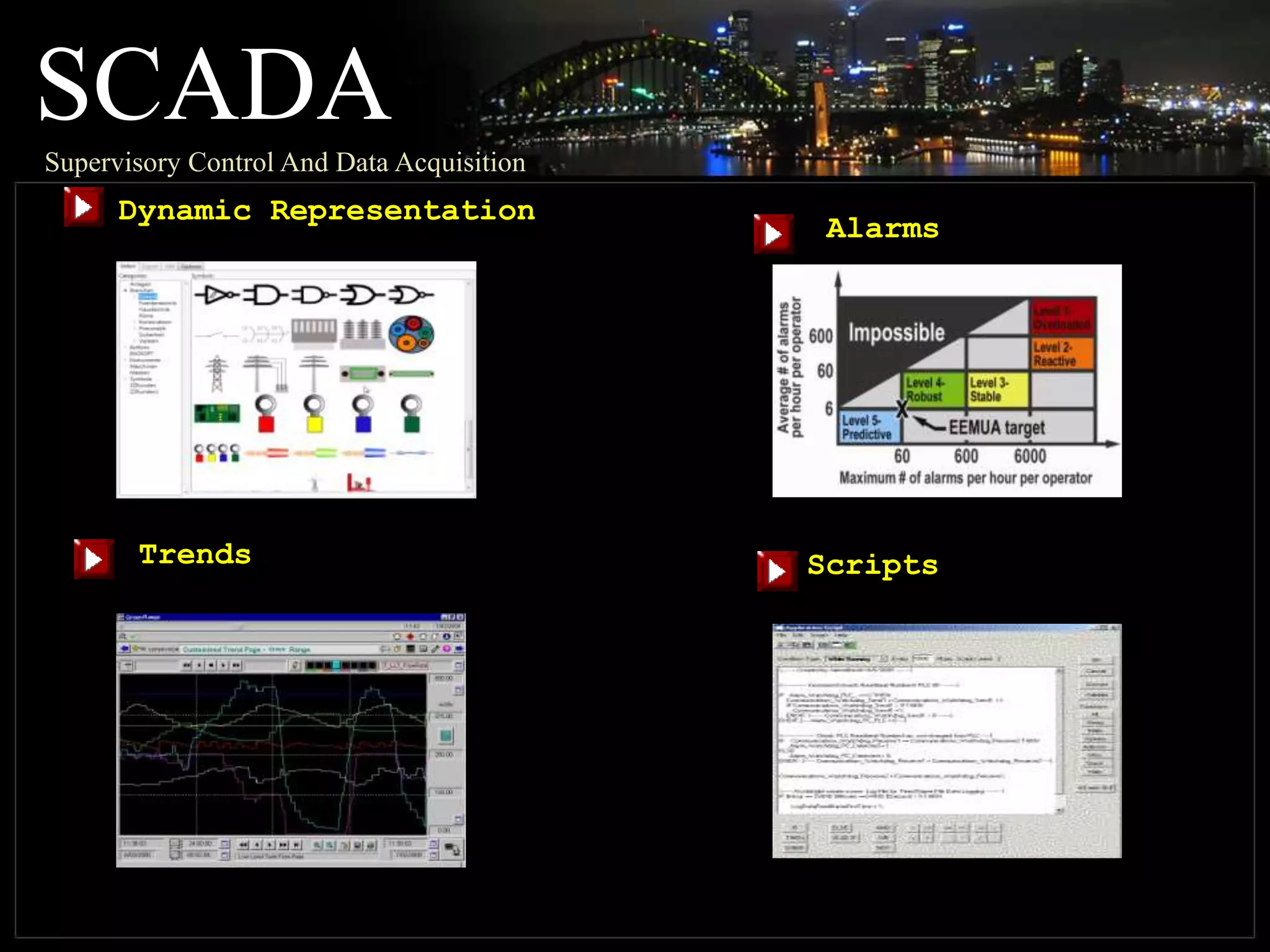
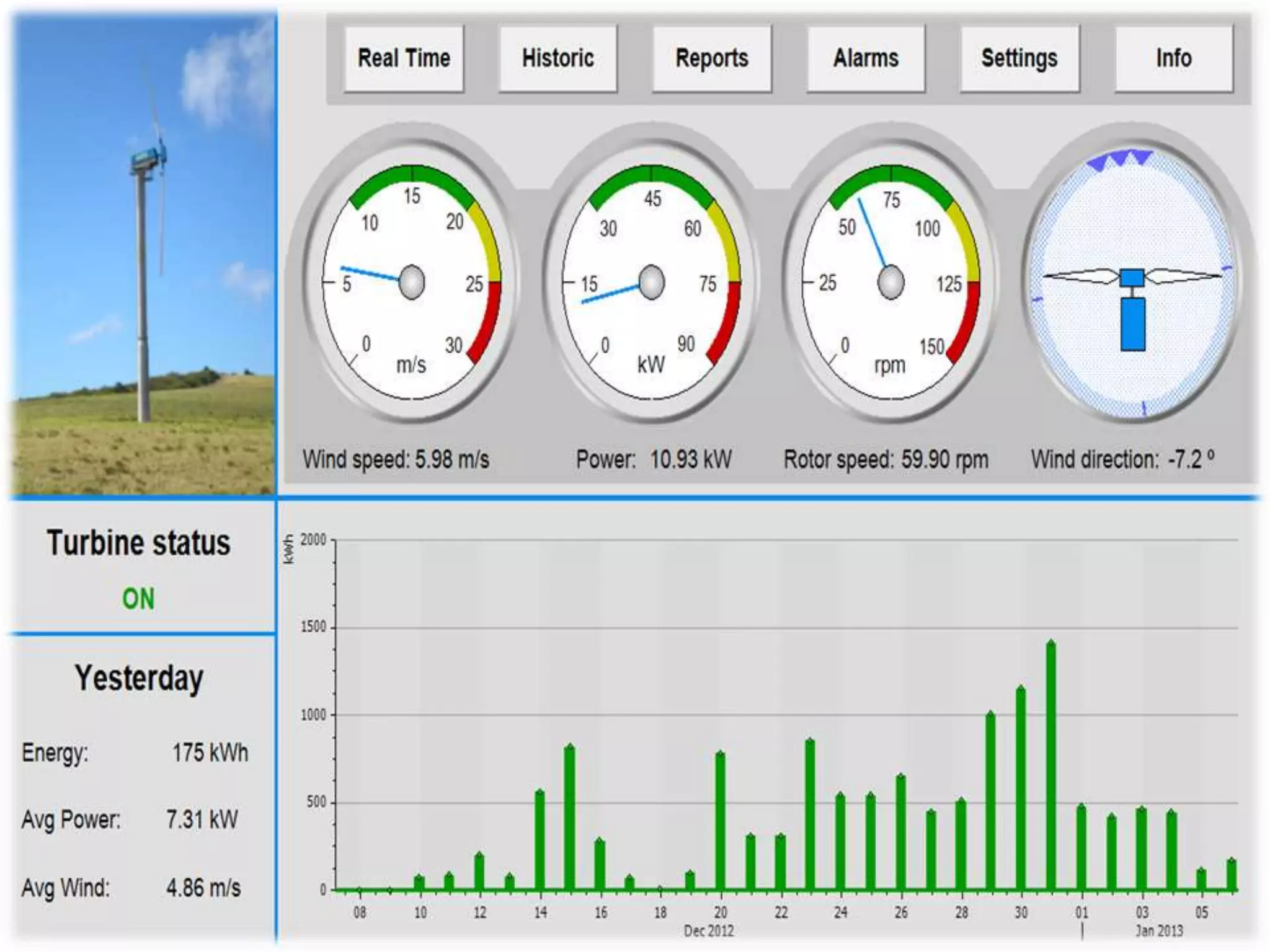
The document discusses automation as the delegation of human control to technical systems to increase productivity, quality, and safety while reducing costs. It details the architecture and operation of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, emphasizing their roles in controlling industrial processes. Key features of PLCs, including their input/output capabilities and self-testing functions, are also covered.