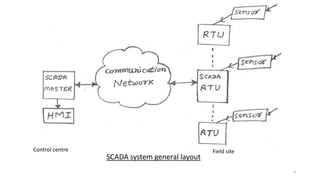
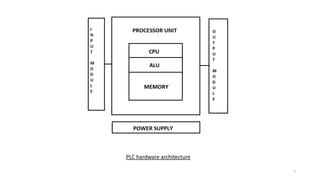
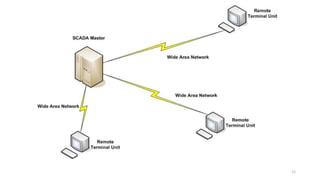
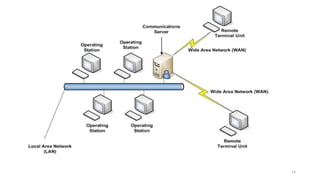
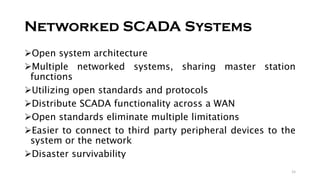
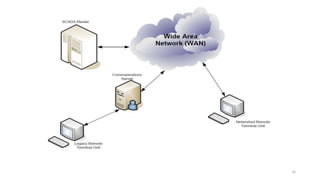
SCADA systems are used to monitor and control geographically dispersed industrial processes. A SCADA system consists of field devices like PLCs and RTUs that connect to sensors and convert signals to digital data. This data is communicated to a control center via telemetry where it is processed by a data acquisition server and presented to human operators through an HMI. The system allows operators to monitor and control the industrial process. SCADA has evolved from early monolithic centralized systems to modern distributed and networked systems that utilize open standards and protocols to distribute functionality across a wide area network. SCADA is commonly used in applications like power generation, water treatment, oil and gas pipelines, and more.