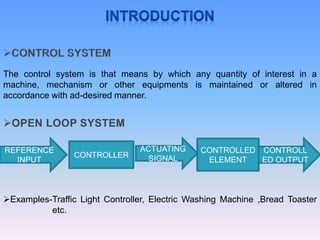
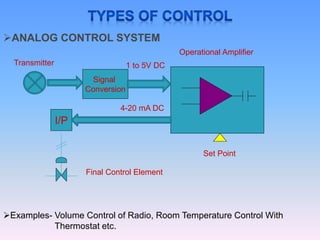
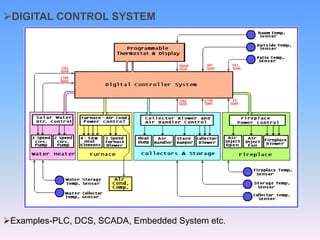
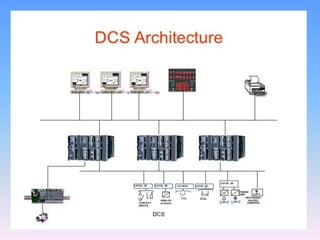
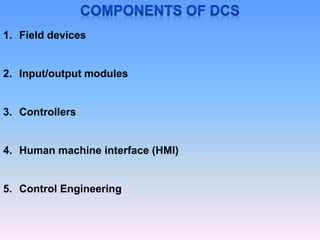
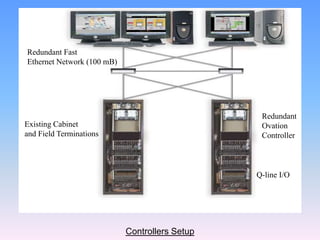
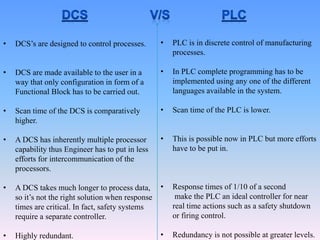
The document discusses control systems and distributed control systems (DCS). It defines a control system as using feedback to maintain or alter quantities according to a desired state. A DCS uses distributed controllers and communication networks to control large, complex industrial processes. Key components of a DCS include field devices, input/output modules, controllers, human-machine interfaces, and control engineering software. DCS are suitable for large chemical plants, refineries, and other industrial applications where centralized control is not feasible.