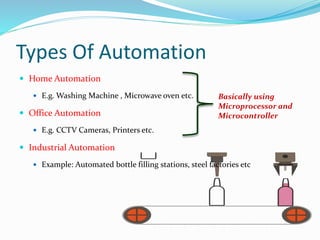
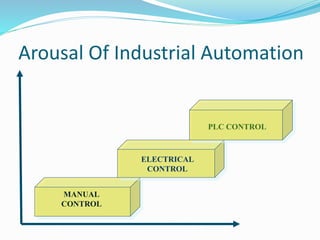
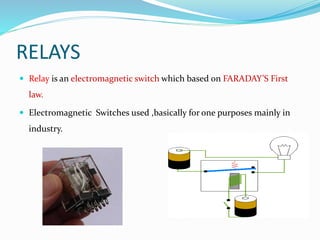
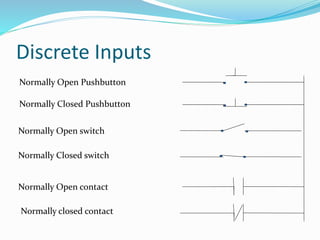
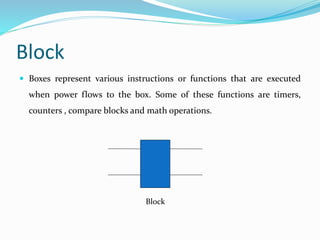
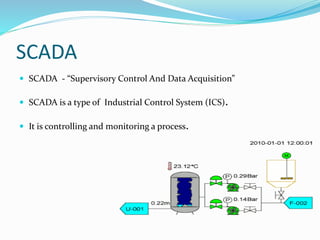
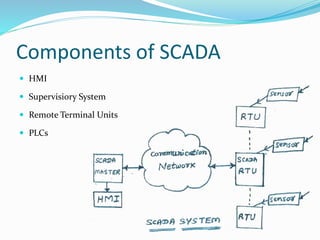
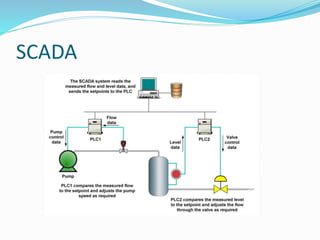
The document provides an overview of automation, detailing its definition, types, and applications in different sectors like home, office, and industrial automation. It explains the role of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in automating electromechanical processes, emphasizing their components, advantages, and programming techniques. Additionally, it discusses SCADA systems and their importance in monitoring and controlling industrial processes, along with associated concepts like HMI and variable frequency drives (VFD).