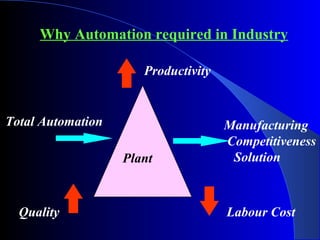
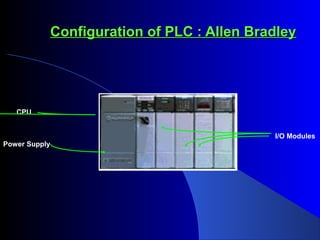
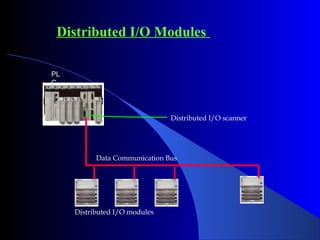
This document provides an overview of industrial automation and its components. It discusses the history of automation from manual control to modern programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) software. PLCs are now widely used as the control hardware in automation systems. They read input signals from sensors and execute user-programmed instructions to control downstream machines. SCADA software collects data from PLCs and allows remote monitoring and operation of automated processes. Engineers play an important role in designing, implementing, maintaining and troubleshooting industrial automation systems.