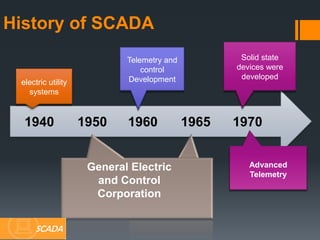
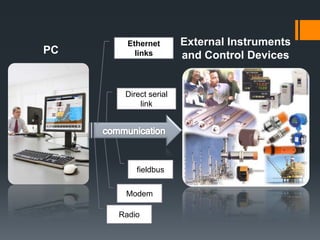
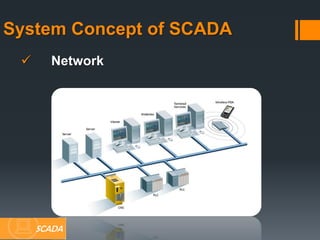
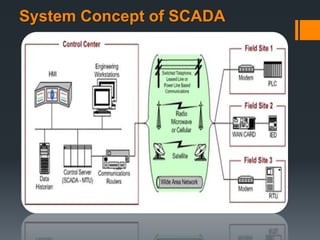
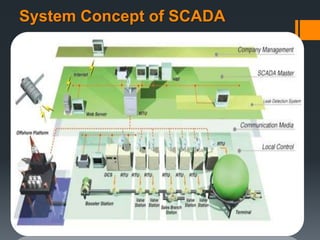
This document provides information about SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. It discusses what SCADA is, the advantages of SCADA over HMI, the system concept of SCADA including RTUs, and future trends in SCADA. Specific topics covered include the history and purpose of SCADA, where SCADA is used, alarm features in SCADA, and applications of RTUs in remote monitoring and control.