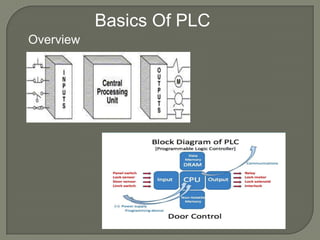
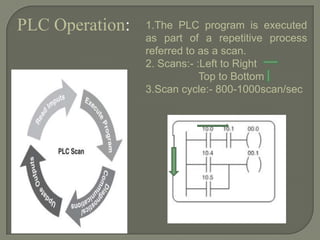
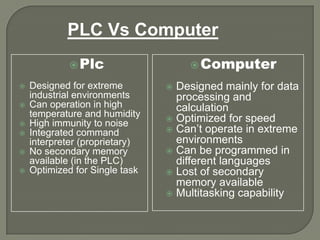
This document provides an overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It discusses what a PLC is, common PLC brands and software, PLC components and operation, programming languages, uses of HMIs and SCADA systems, differences between PLCs and computers, why PLCs are used, their advantages, and common application areas. The document also describes an industrial automation company and its PLC training and services.