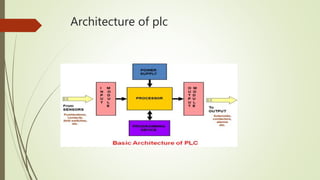
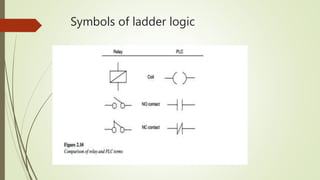
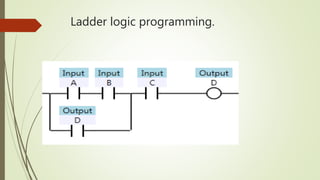
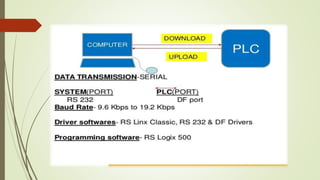
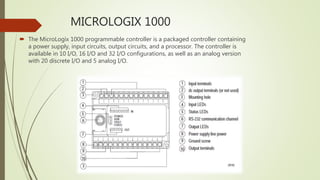
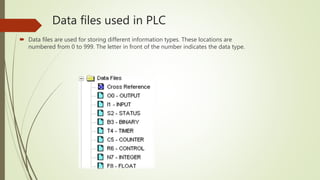
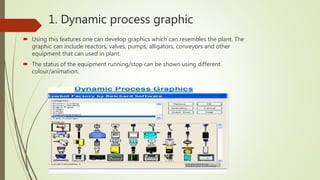
This document provides an overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. It discusses the history and evolution of automation and PLCs, describes common PLC components and programming, and reviews the MicroLogix 1000 PLC and RSLogix5000 programming software. Key features of SCADA systems are also summarized, including dynamic graphics, alarms, recipe management, security, connectivity, databases, and scripting. The document is submitted by Nitish Kumar Singh for review by KL Pursnani and covers automation, PLCs, ladder logic, MicroLogix1000, and SCADA systems at a high level.