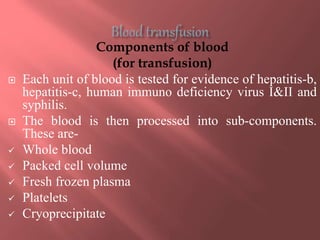
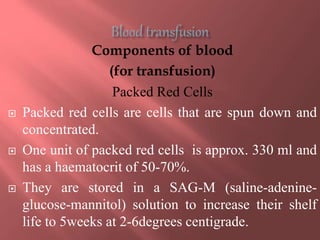
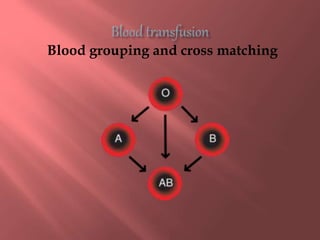
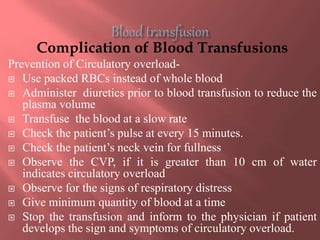
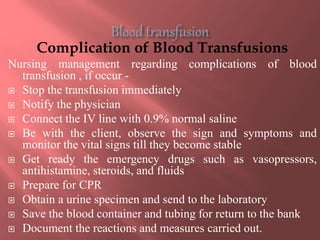
This document provides information about blood transfusion, including its definition, purposes, components, blood grouping and cross matching, types of transfusions, general instructions, and complications. Blood transfusion involves collecting blood from a donor and administering it to a recipient. It can be used to treat anemia, restore blood volume after hemorrhaging, and provide antibodies or clotting factors. Blood components include whole blood, packed red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and cryoprecipitate. Cross matching must ensure compatibility of blood types and Rh factor. Potential complications include acute and delayed hemolytic reactions, circulatory overload, and infections.