This document provides information about platelets, including their structure, formation, and role in hemostasis (blood clotting).
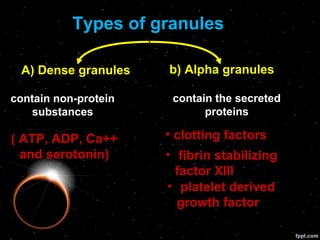
Platelets are cell fragments without a nucleus that play a key role in hemostasis. They have a cell membrane, microtubules, and cytoplasm containing granules and proteins. Platelets are formed from fragmentation of large megakaryocytes in the bone marrow.
During hemostasis, platelets initially adhere to damaged blood vessel walls, become activated, and aggregate to form a platelet plug. This is followed by a blood coagulation cascade that converts prothrombin to thrombin, leading to conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin and formation of a fibrin clot. Overall, the
































































































![RReeffeerreenncceess--2
ARTICLES:
1.Rafique S1, Fiske J, Palmer G, Daly B. Special care dentistry:
part 1. Dental management of patients with inherited bleeding
disorders. Dent Update. 2013 Oct;40(8):613-6, 619-22, 625-6
passim.
2.Dental management of medically compromised patient-Little
J,Falace D,Miller C,Rhodes N.
3. Bergmeier W, Chauhan A, Wagner D (2008) Glycoprotein
Ibalpha and von Willebrand factor in primary platelet adhesion and
thrombus formation: lessons from mutant mice. Thromb Haemost
99: 264–270 [PubMed]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/platelets-141129124849-conversion-gate01/85/Platelets-98-320.jpg)
