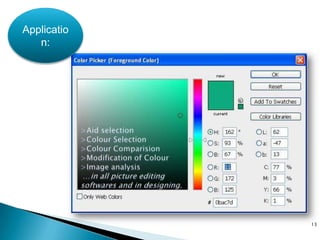
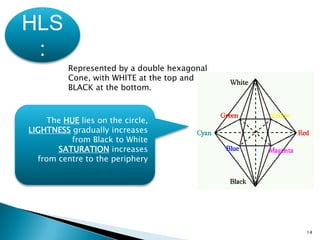
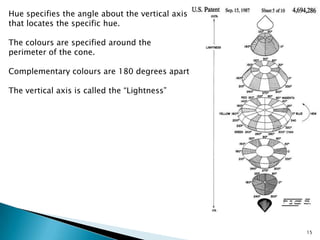
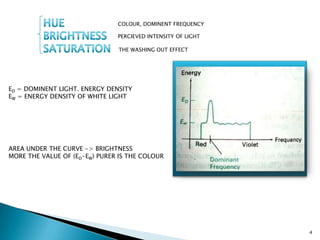
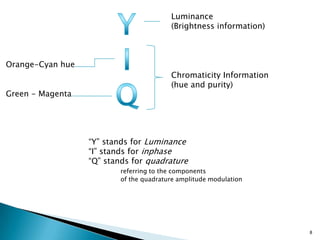
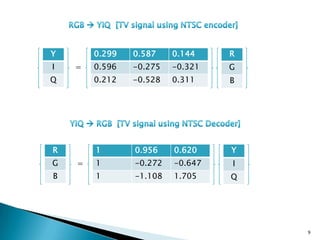
The document discusses color models including HLS and YIQ. It provides background on visible light wavelengths and introduces the YIQ and HLS color models. The YIQ model with Y for luminance, I for in-phase, and Q for quadrature was used in analog television to transmit color information using one signal. The HLS and HSV models represent color as Hue, Lightness/Value, and Saturation in a double hexagonal cone with white at the top and black at the bottom to better match human color perception compared to the RGB model. The models have applications in color selection, comparison, editing and image analysis.





![RGB YIQ [TV signal using NTSC encoder] 9=YIQ RGB [TV signal using NTSC Decoder] =9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colourmodels-100902110857-phpapp01/85/Colour-models-10-320.jpg)