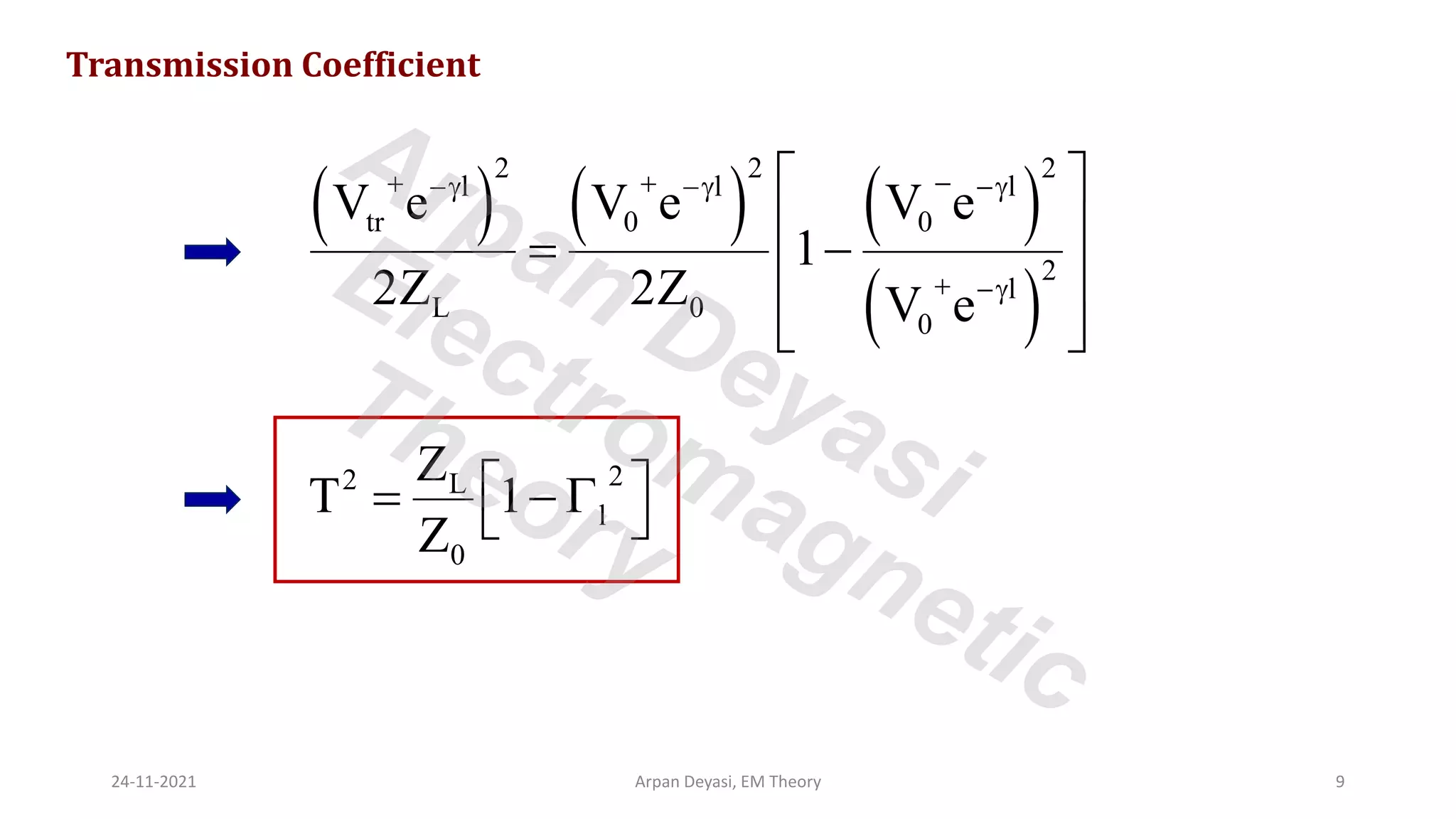
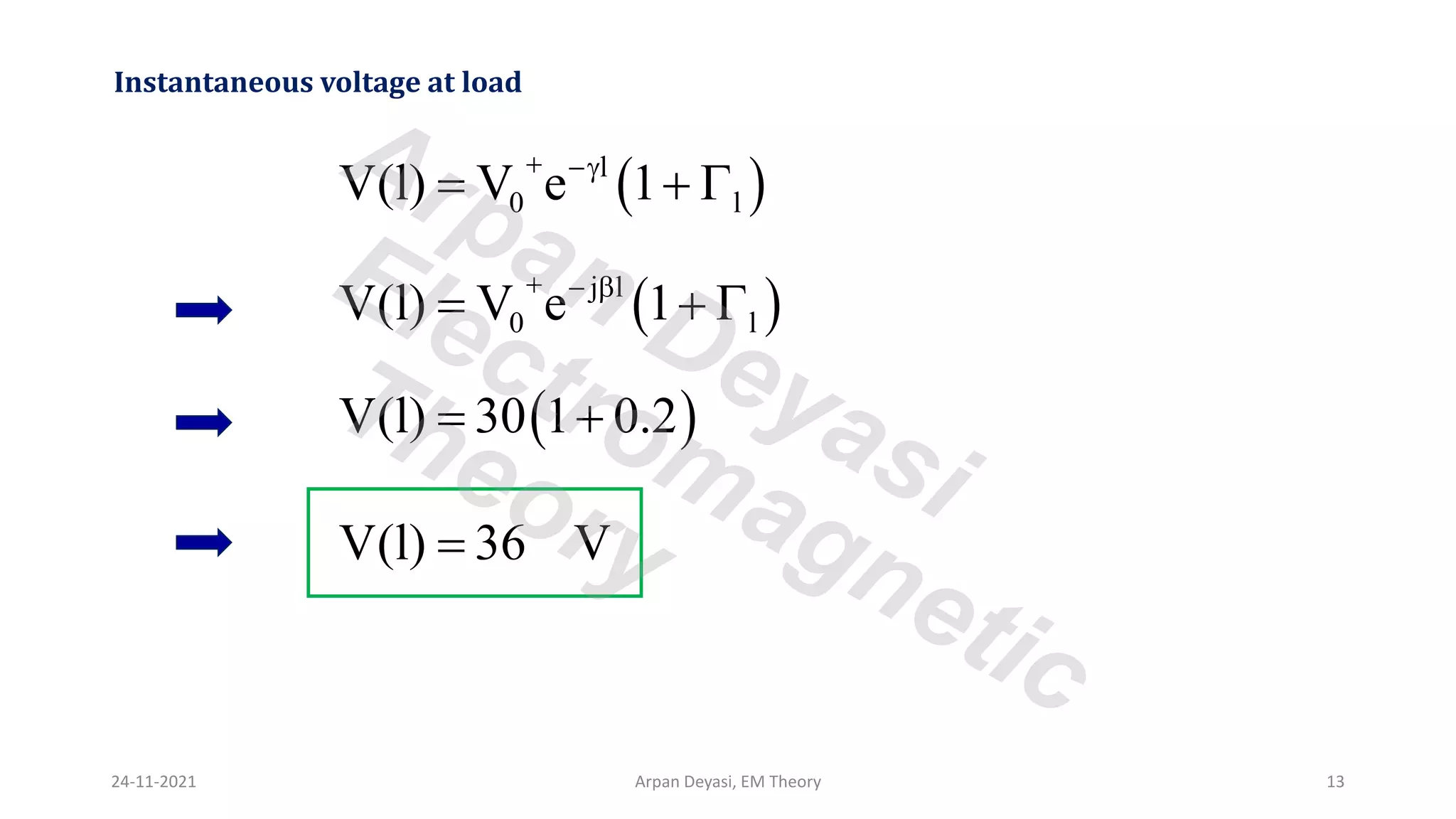
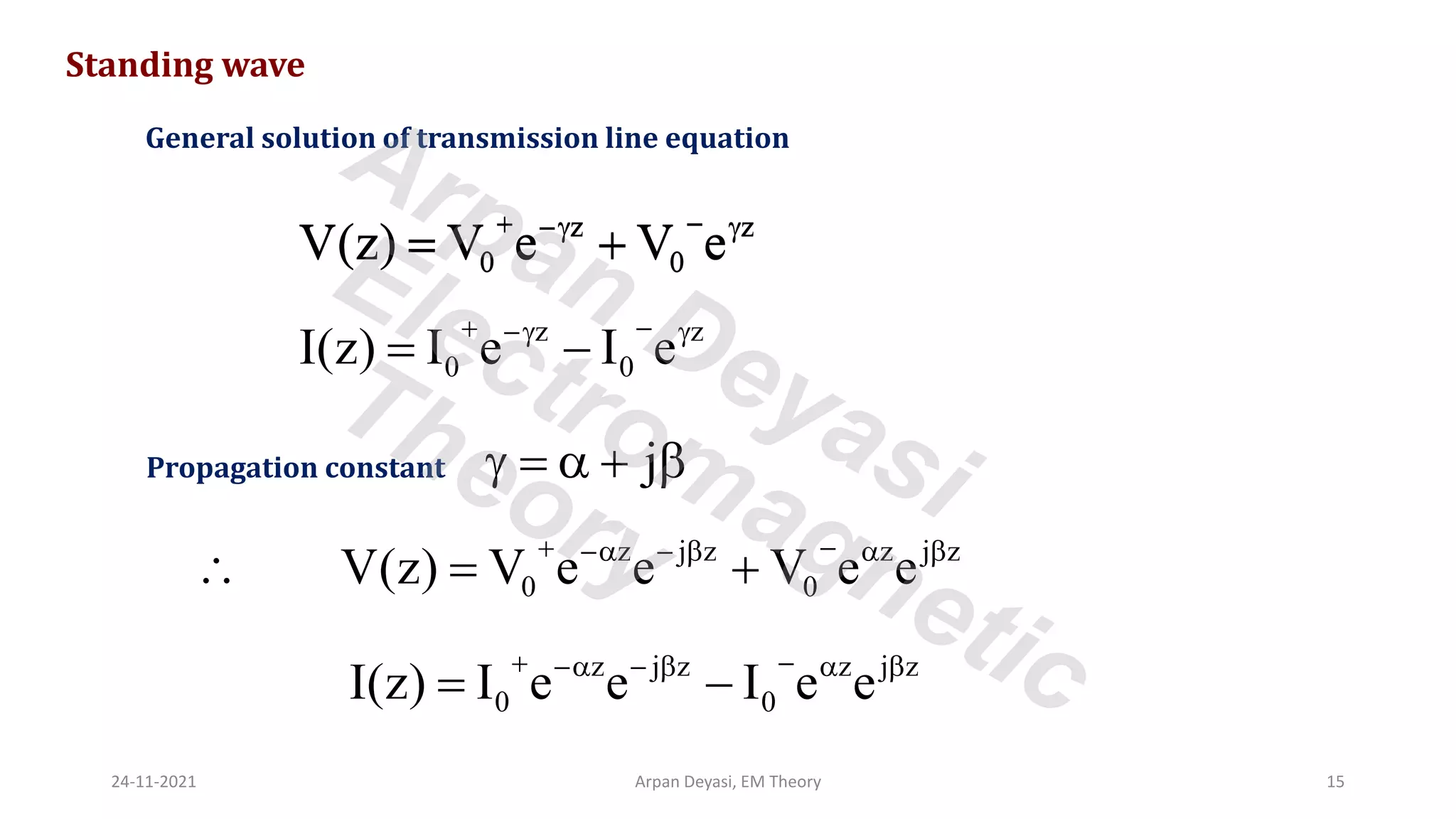
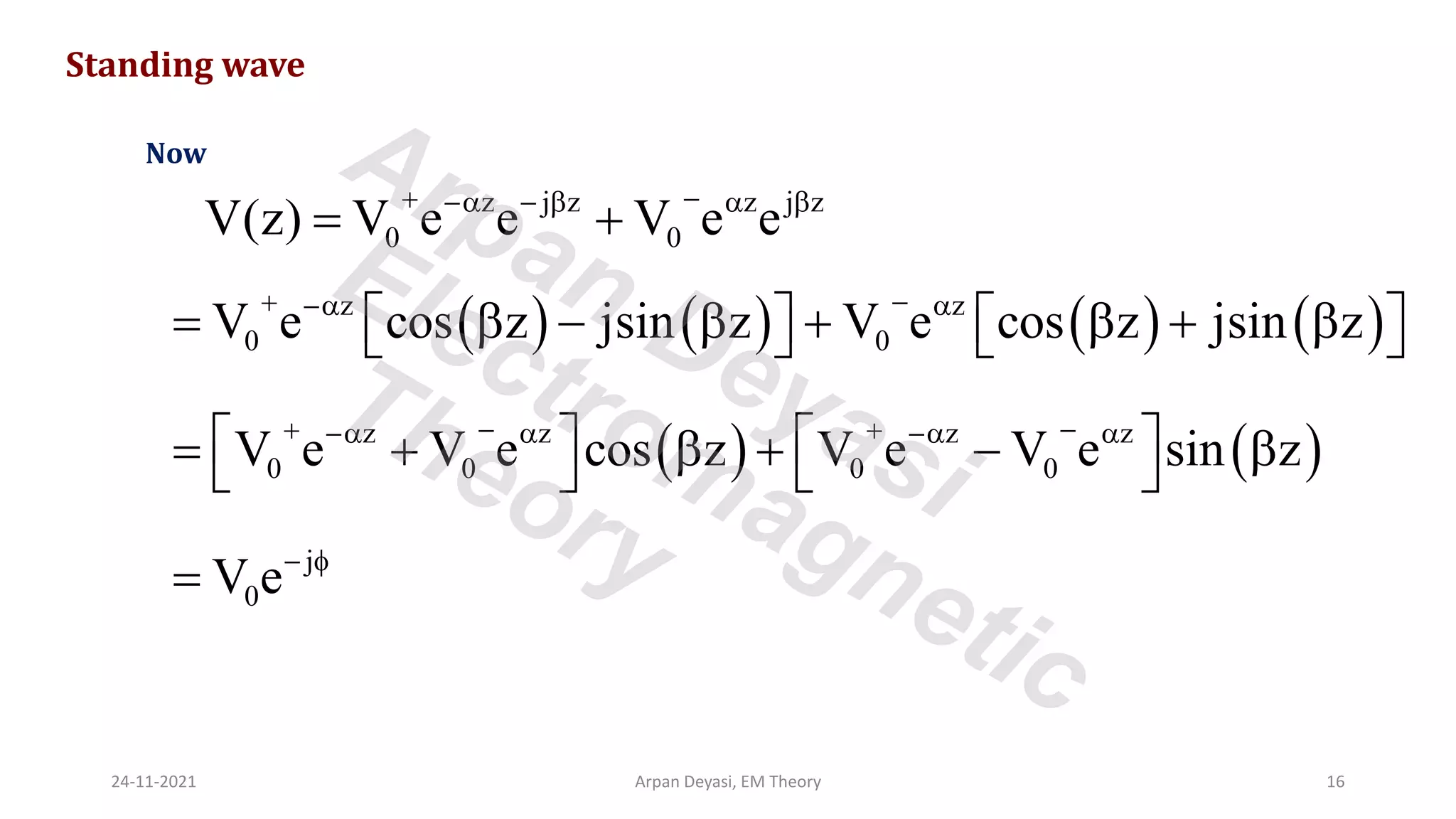
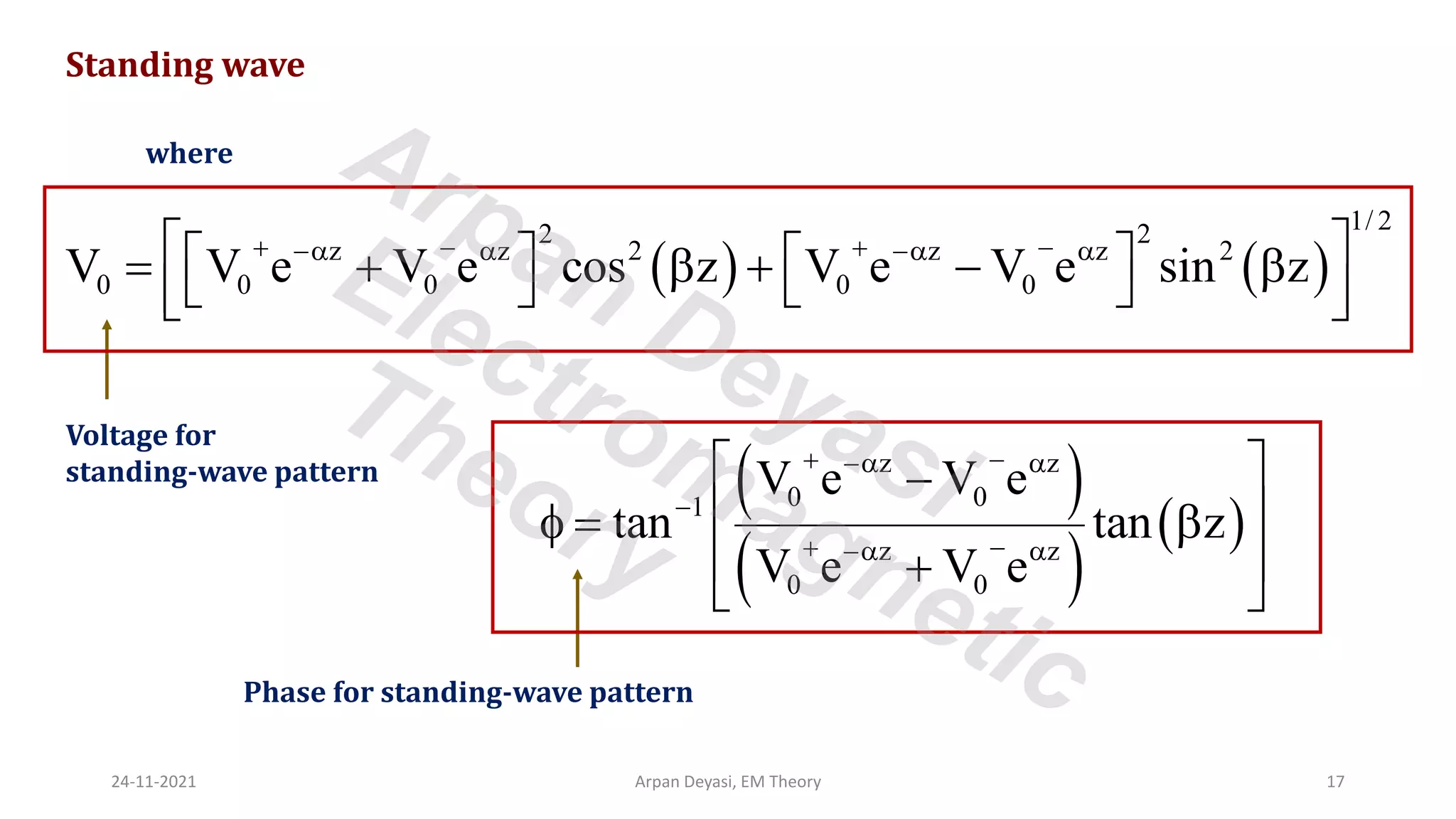
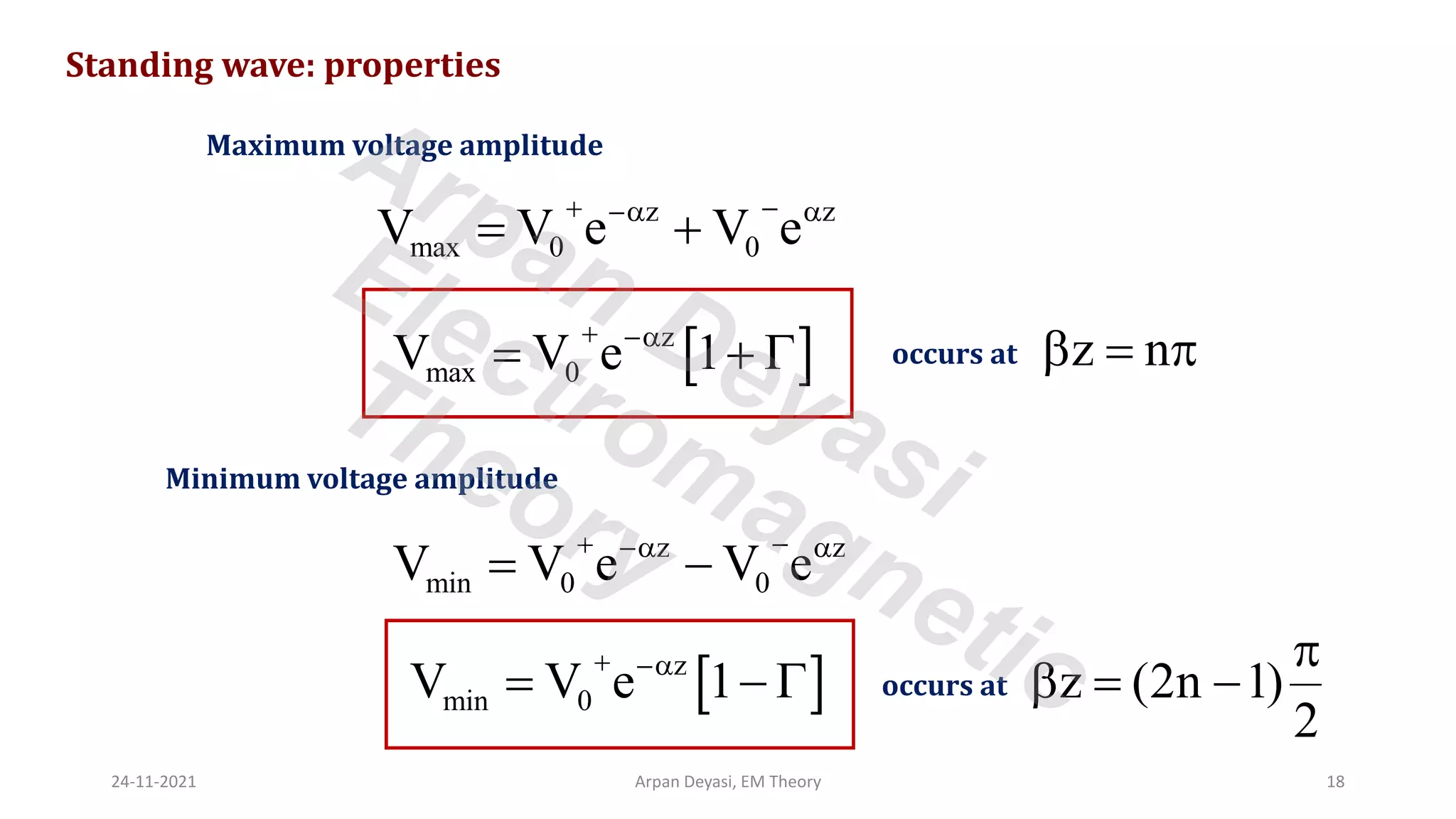
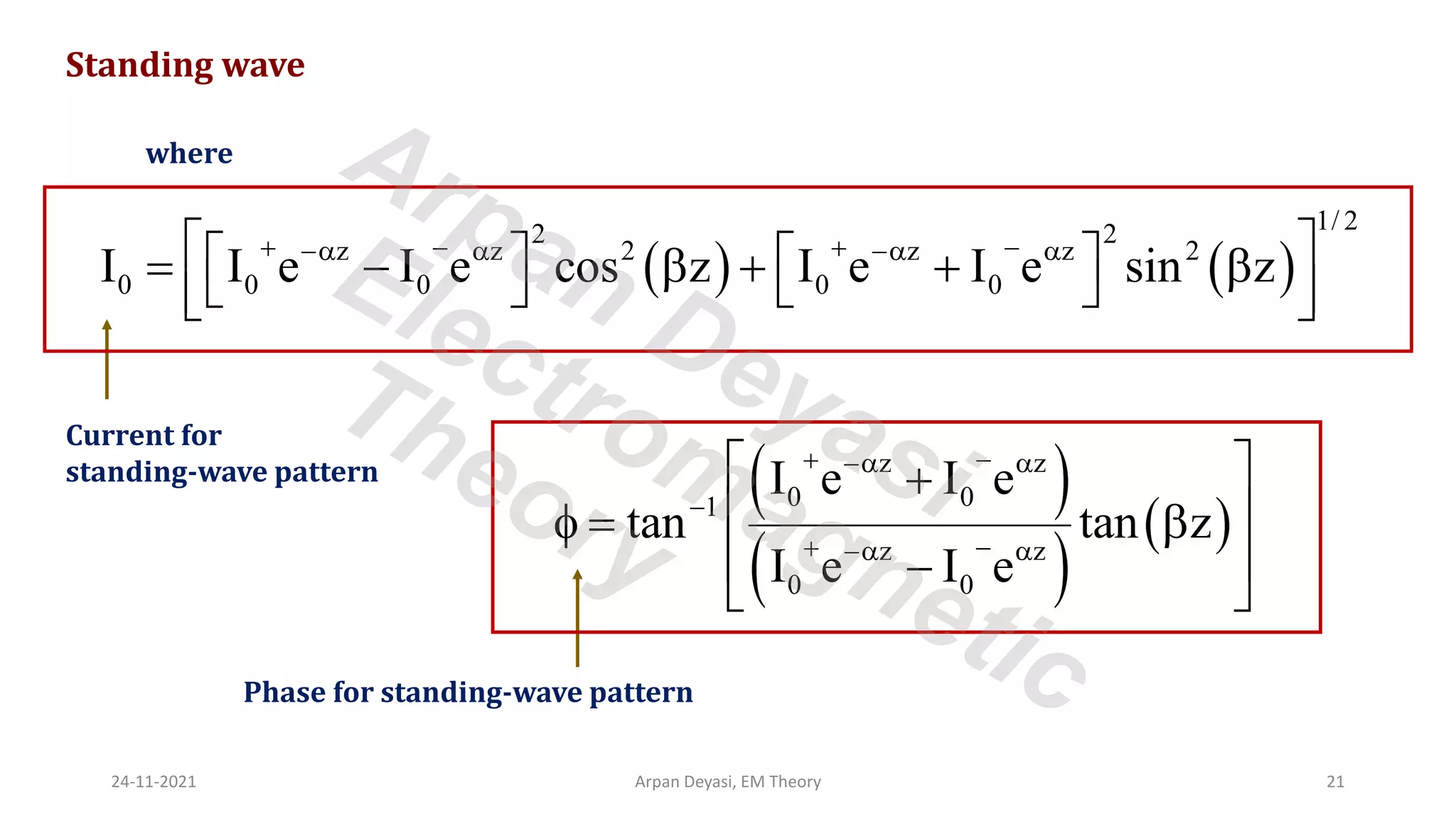
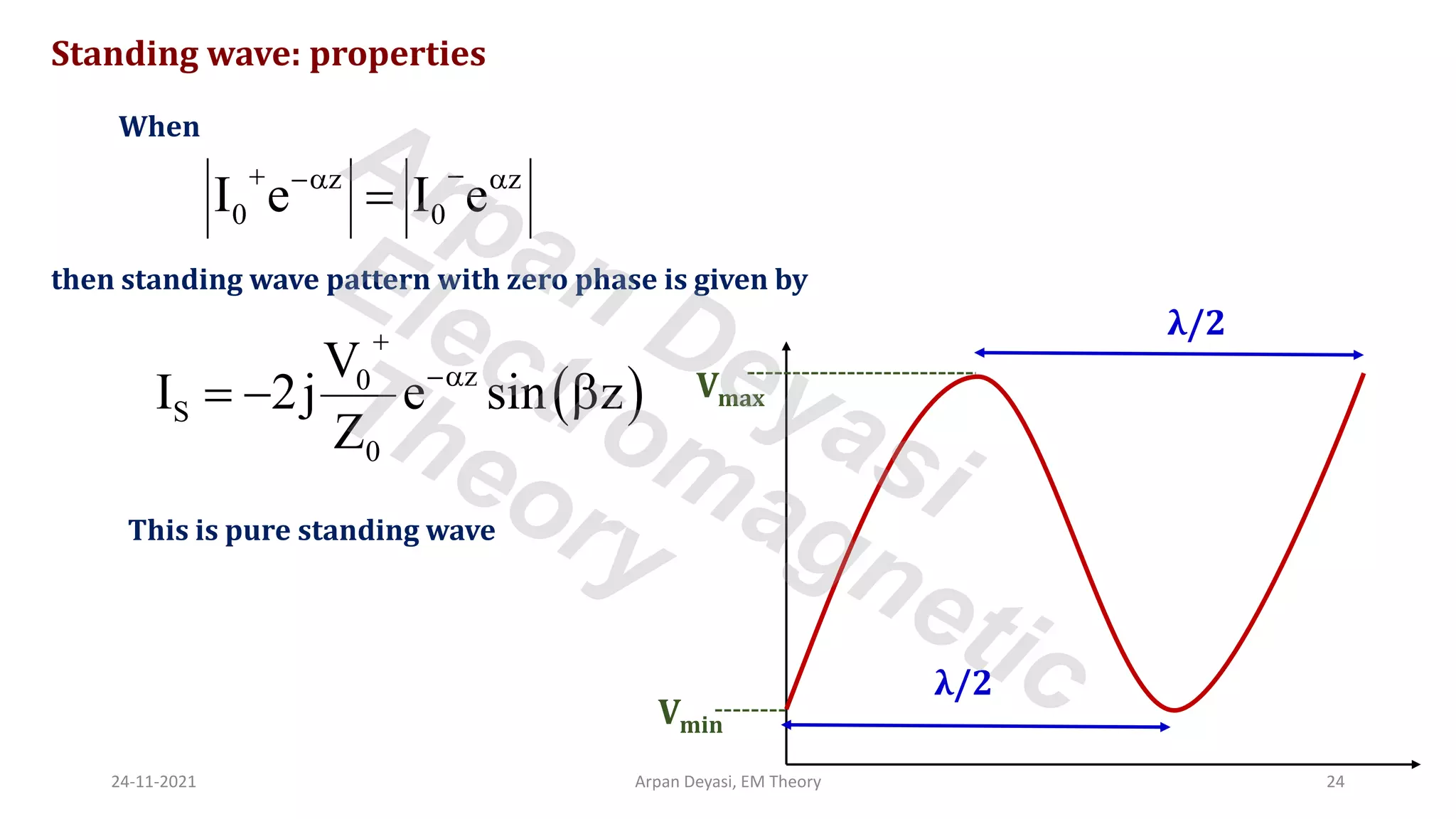
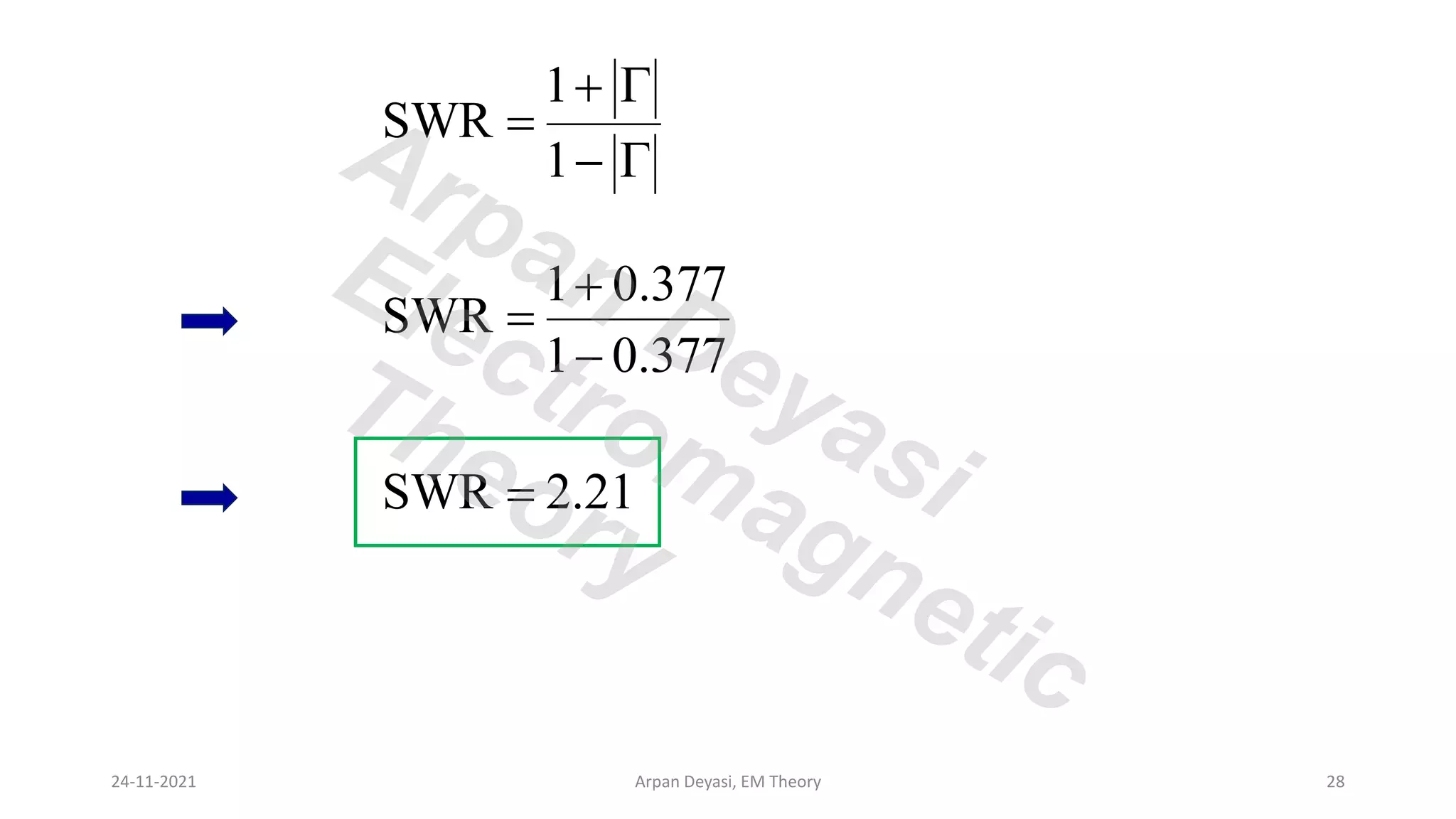
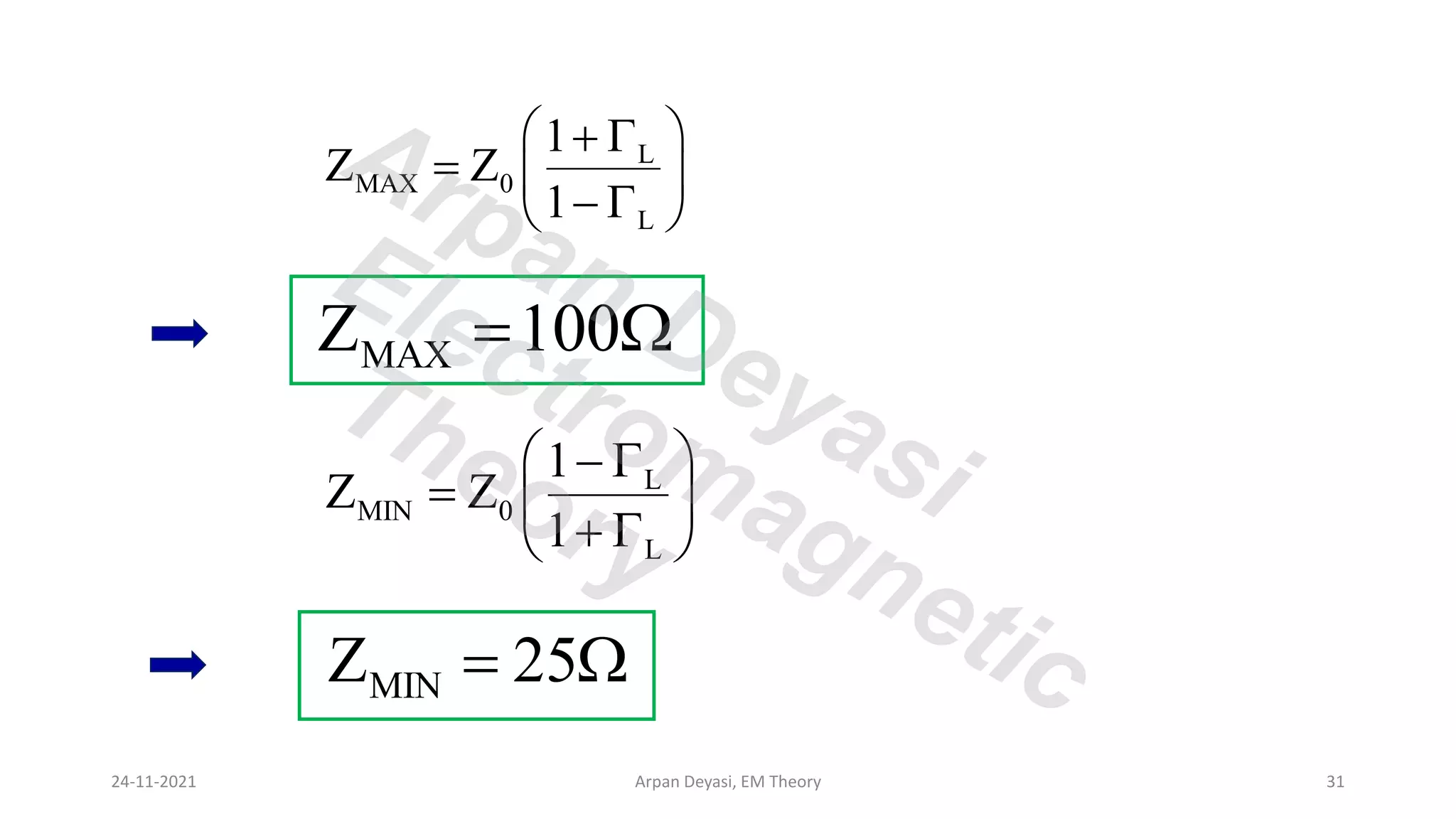
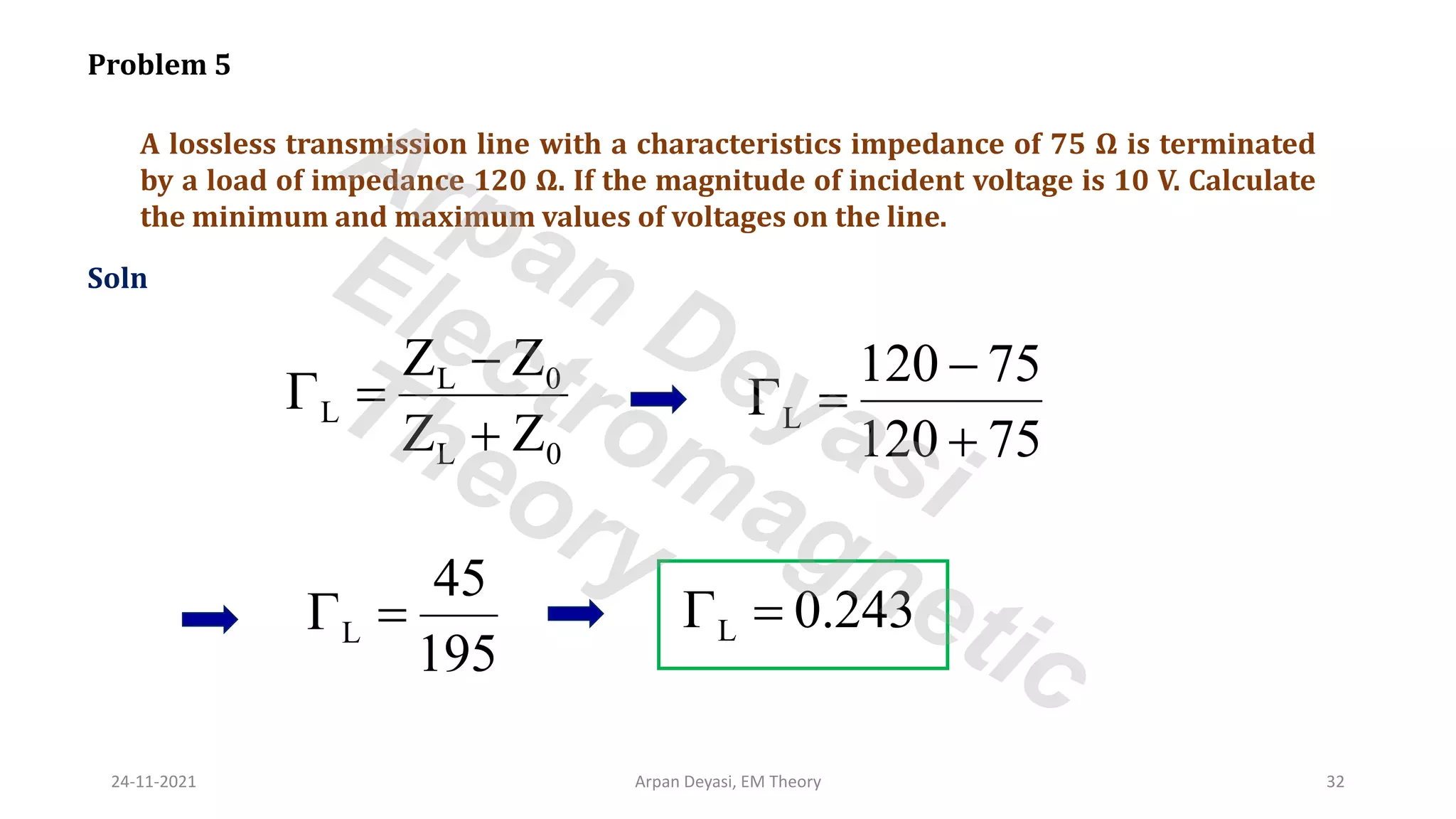
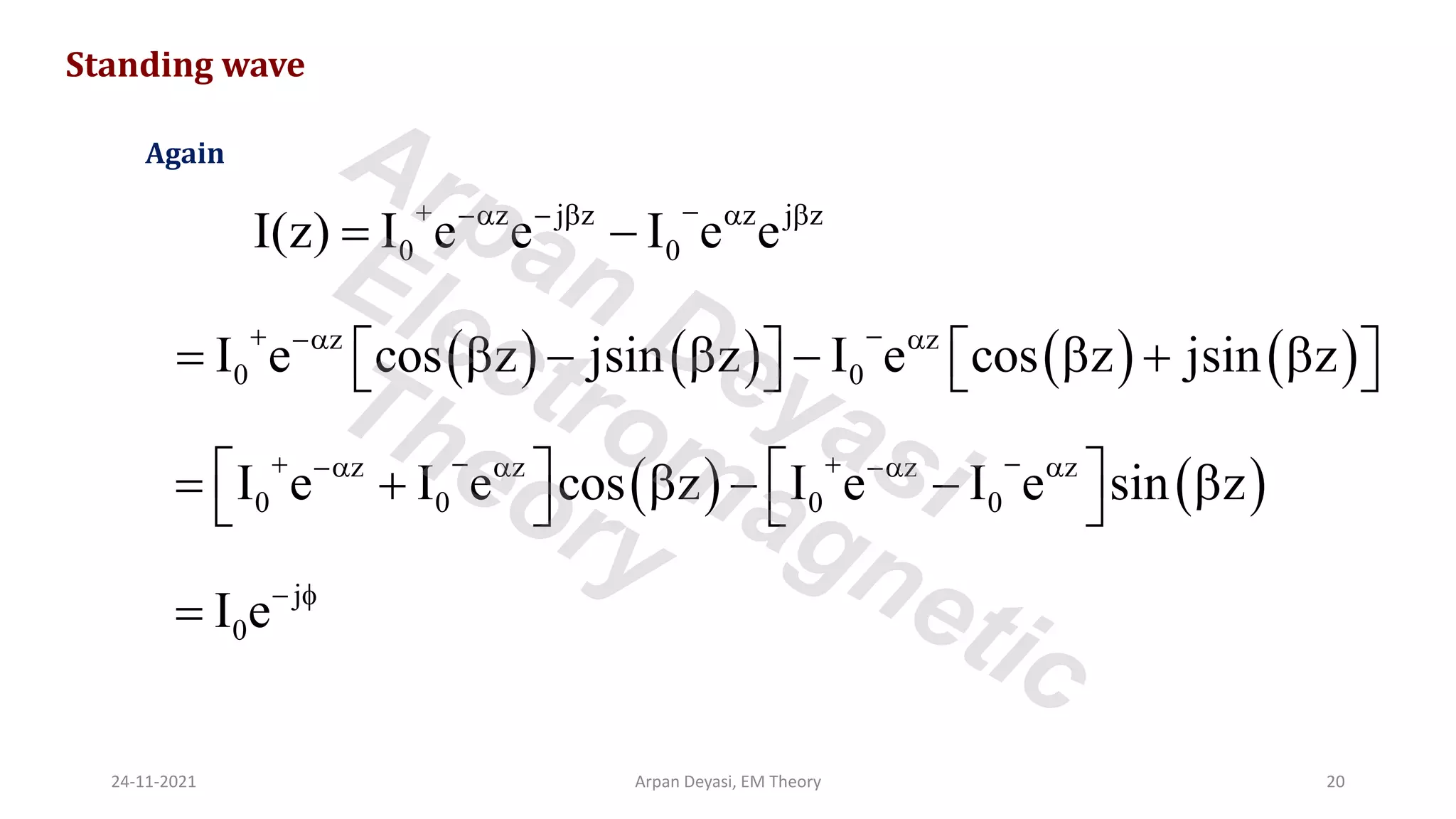This document discusses transmission line propagation coefficients including reflection coefficient and transmission coefficient. It defines the reflection coefficient as the ratio of reflected to incident voltage or current. Reflection and transmission coefficients are derived for a transmission line terminated by a load impedance. Standing wave patterns on transmission lines are also analyzed. Key properties of standing waves include maximum and minimum voltages occurring at intervals of half wavelength and voltages/currents being 90 degrees out of phase.