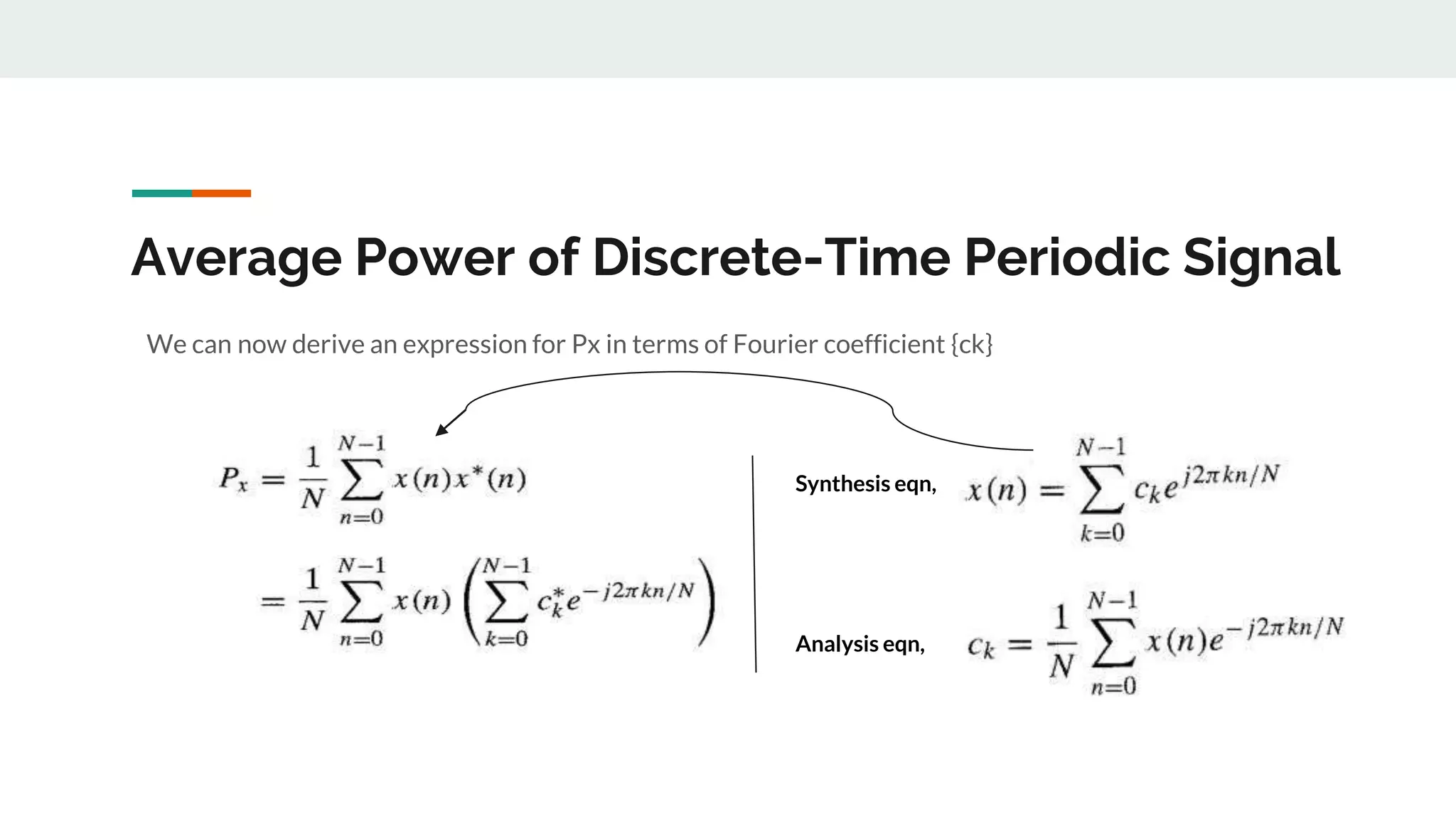
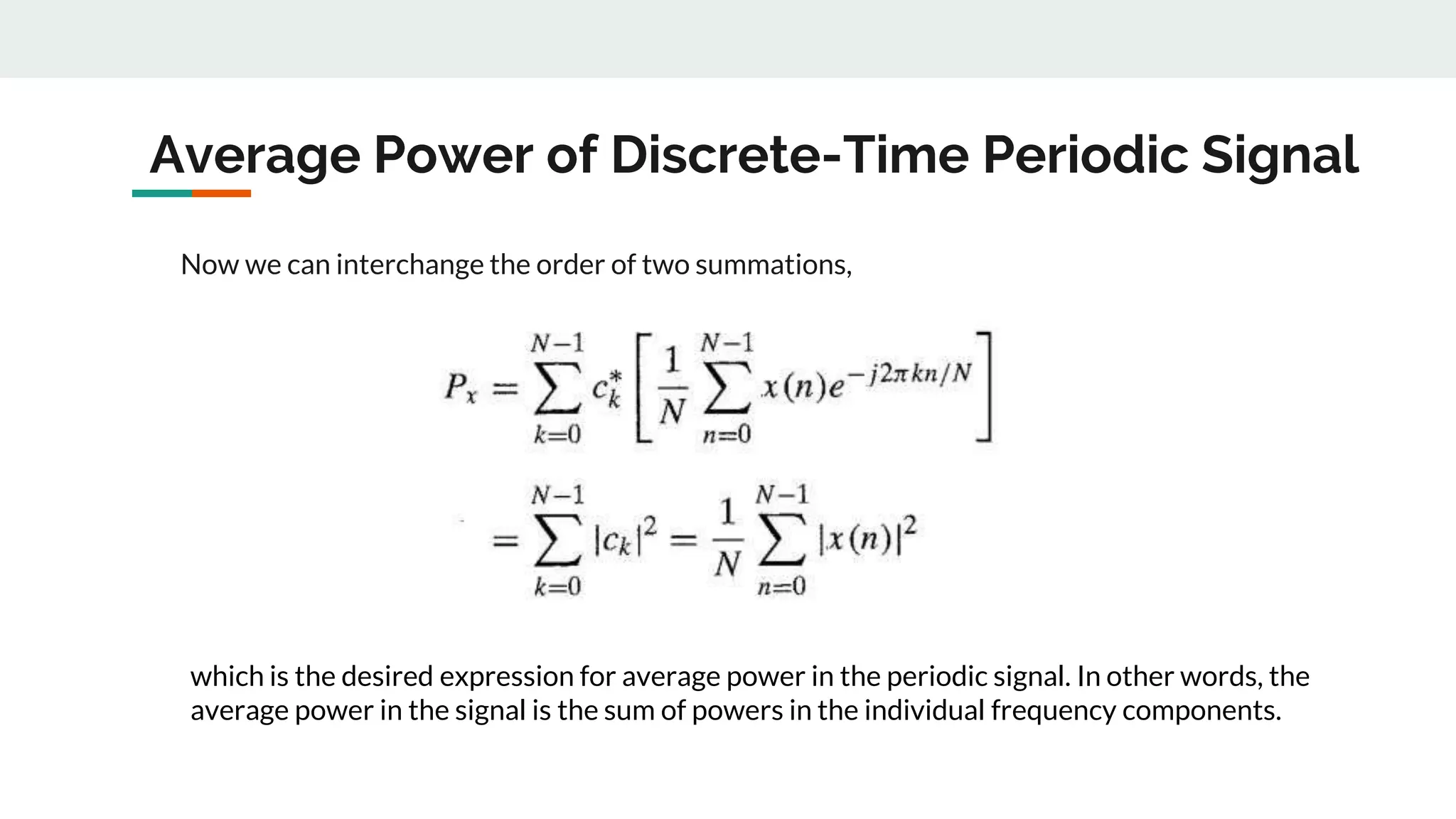
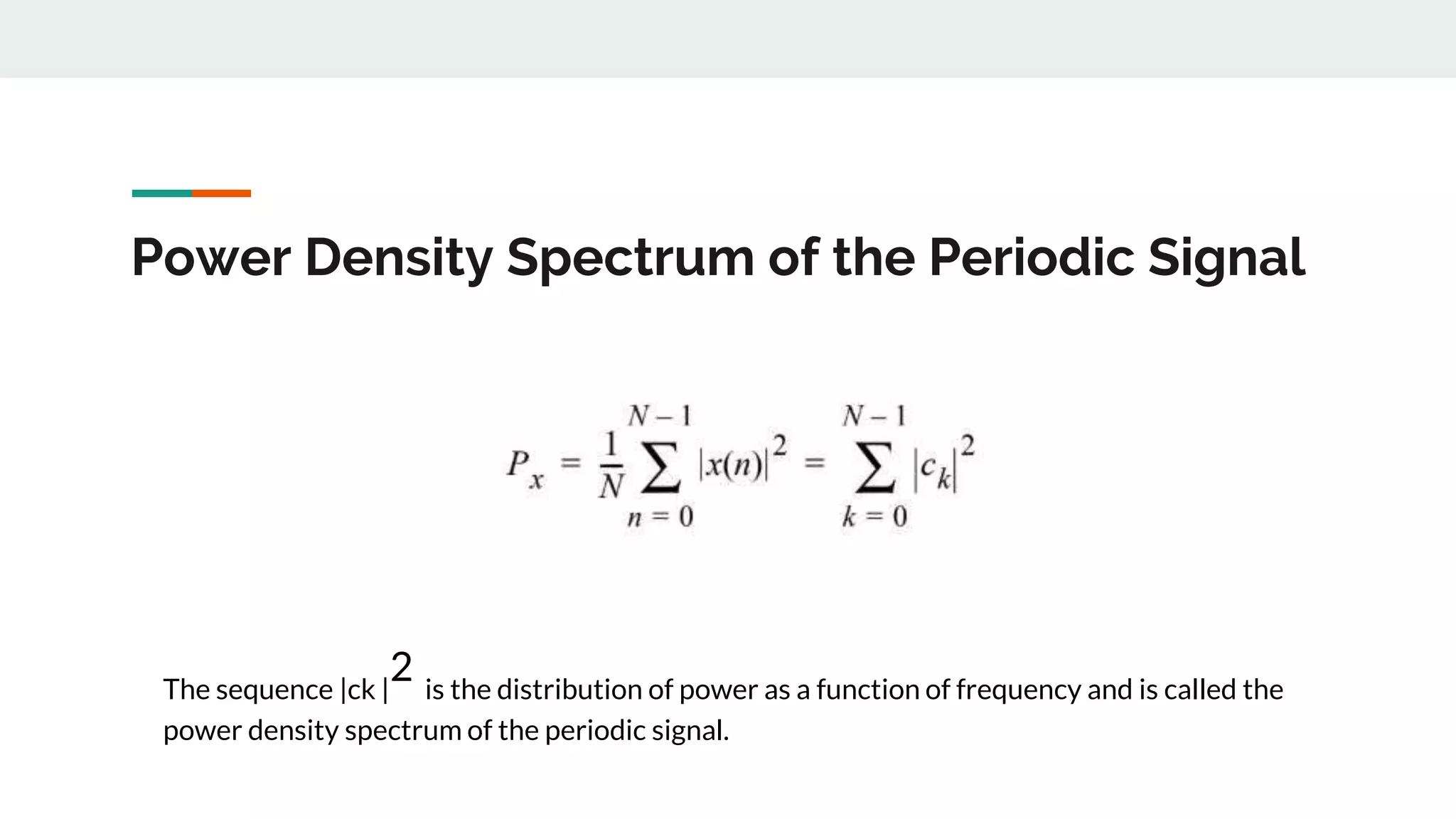
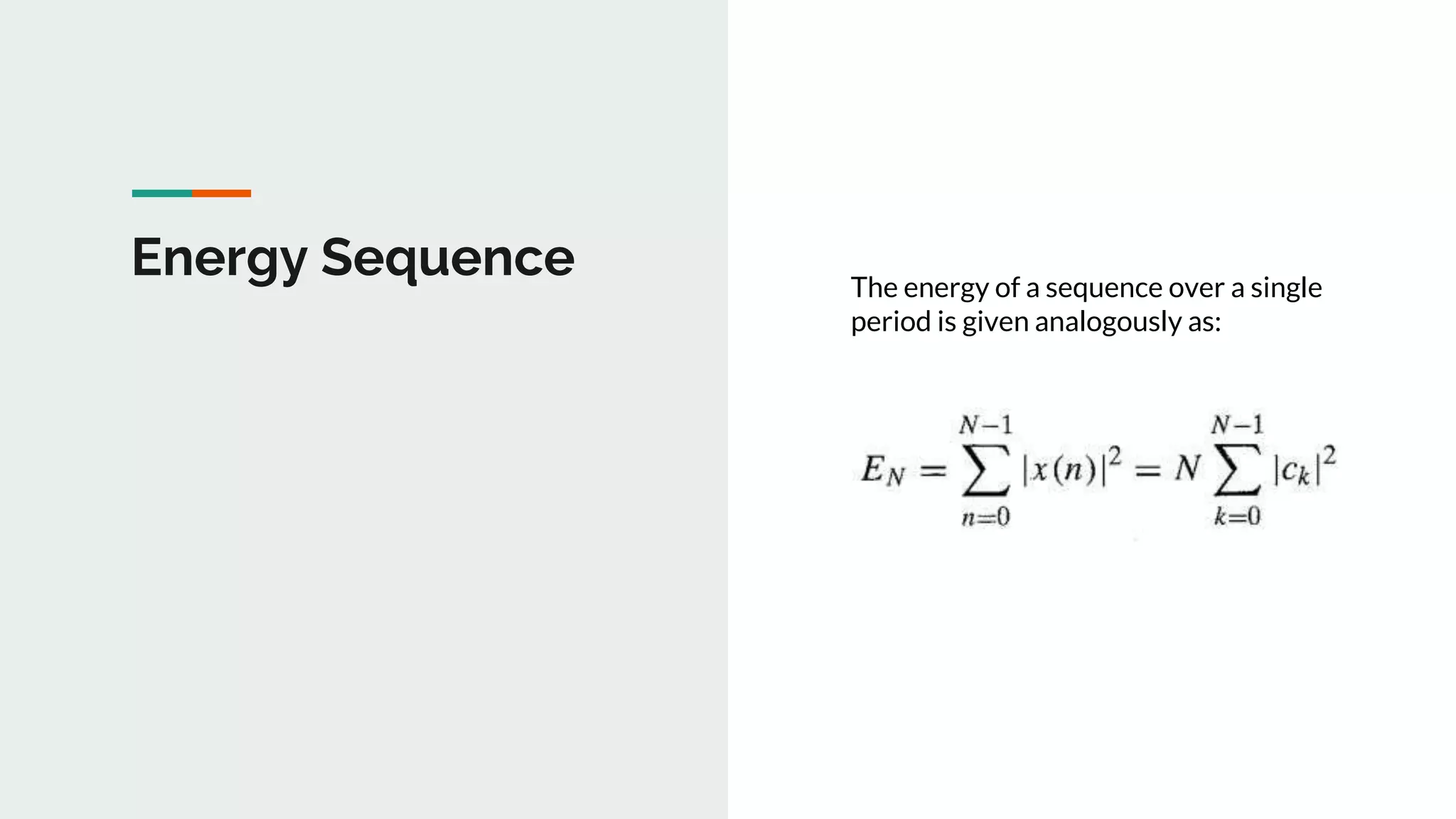
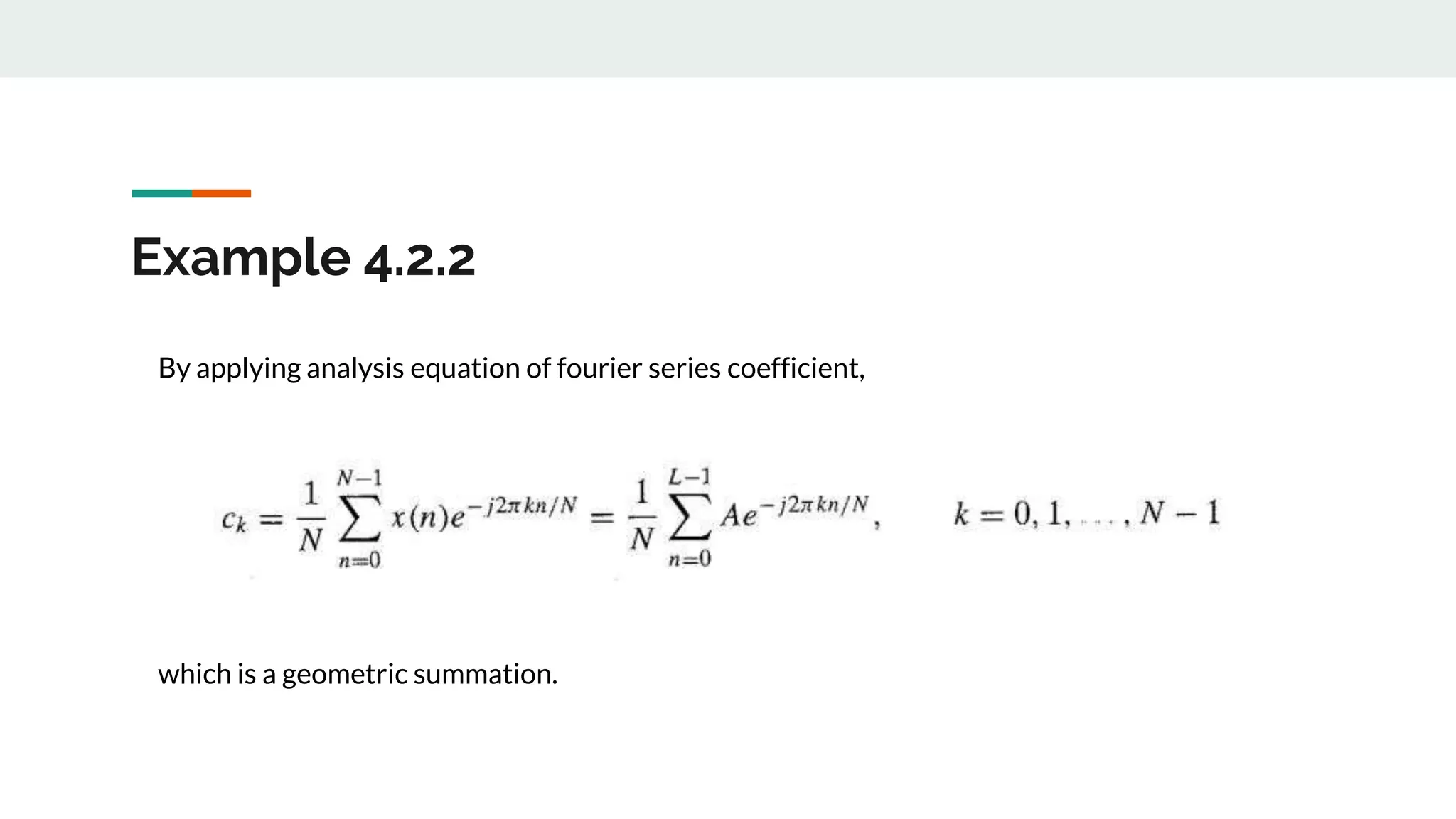
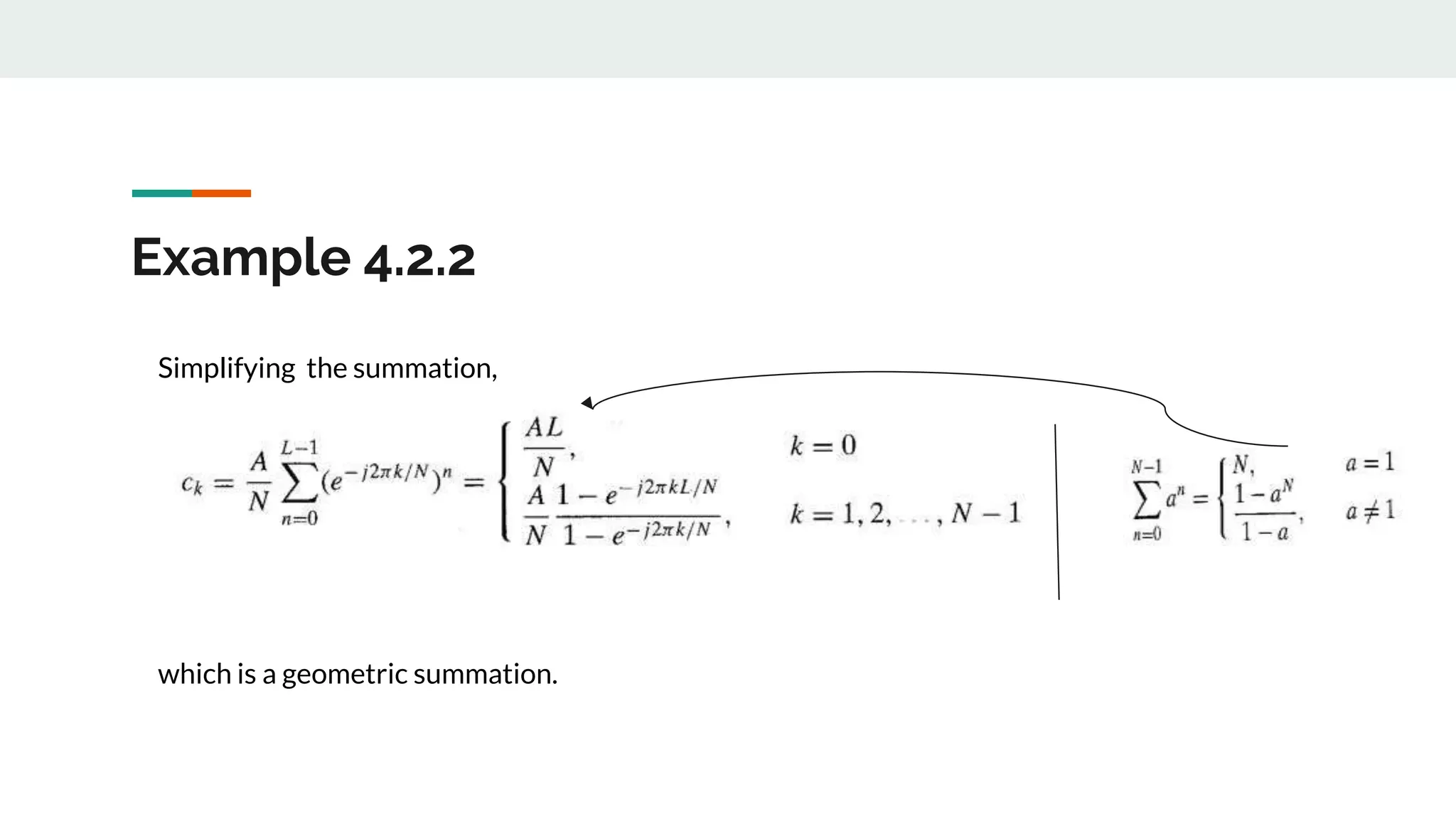
This document discusses power density spectrum, which shows how the energy of a signal is distributed over different frequencies. Any signal can be represented as a summation of sinusoids using Fourier analysis. The Fourier transform breaks down a signal into sine and cosine components. A Fourier series represents periodic signals as an infinite sum of sines and cosines. The frequency spectrum shows the frequencies contained in a signal. Each frequency component is obtained from the Fourier transform. The average power of a discrete-time periodic signal can be expressed as the sum of powers of the individual frequency components. The power density spectrum is the distribution of this power as a function of frequency.