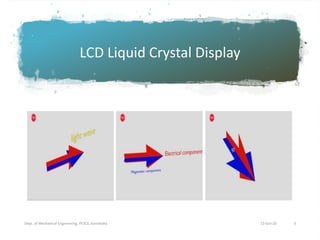
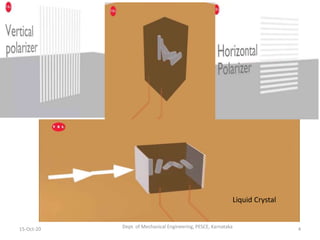
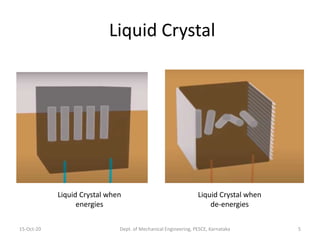
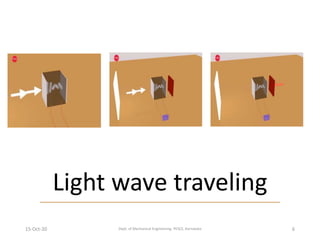
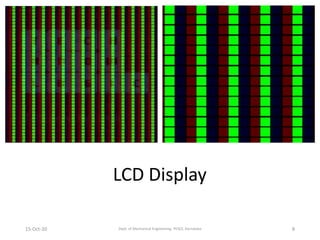
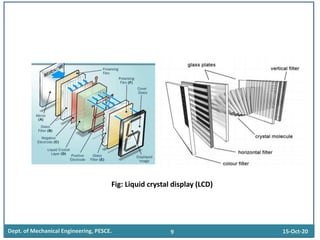
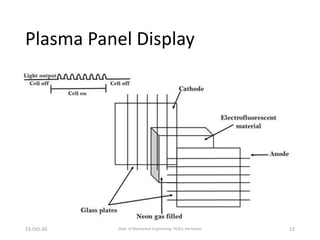
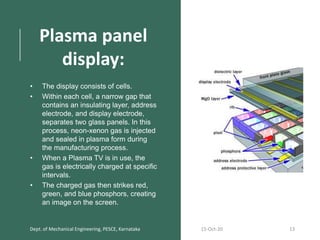
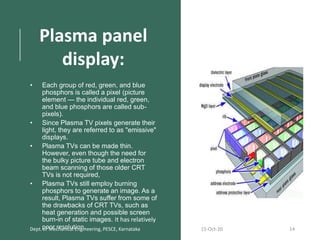
This document discusses different display technologies, including LCD, plasma, and LED displays. It provides details on how LCD displays work, such as using liquid crystals between polarized glass substrates that twist to allow light to pass or not. Plasma displays are described as having cells filled with gas that illuminates phosphors when charged to create pixels. LED displays are similar to LCDs but use LEDs for backlighting instead of fluorescence. Storage devices for CAD/CAM systems are also listed, ranging from floppy disks to solid-state devices.