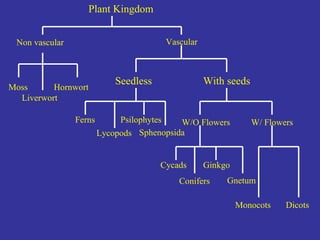
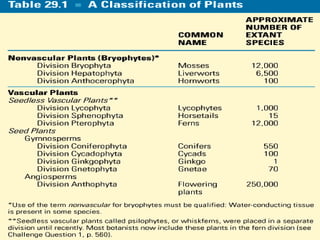
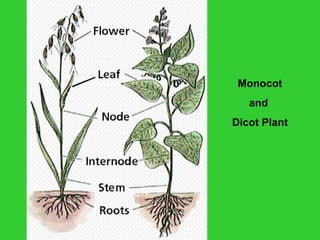
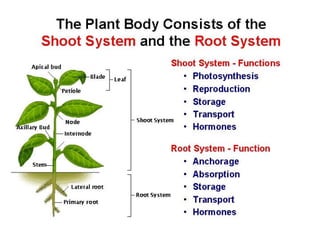
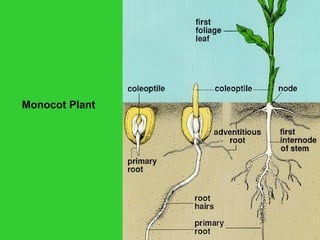
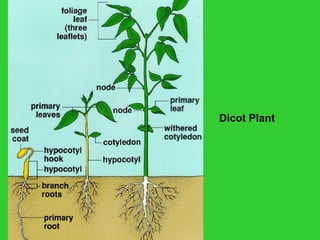
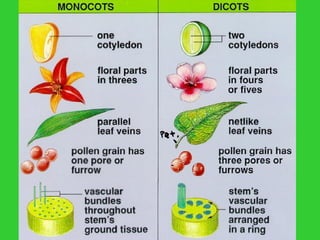
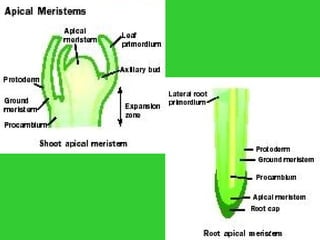
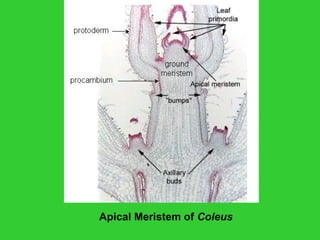
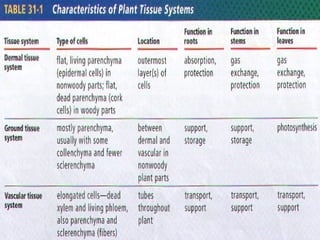
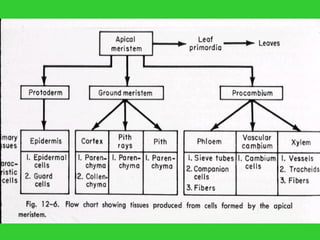
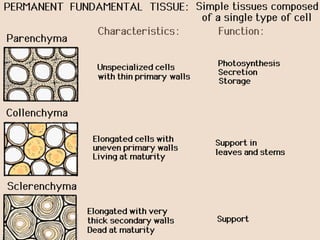
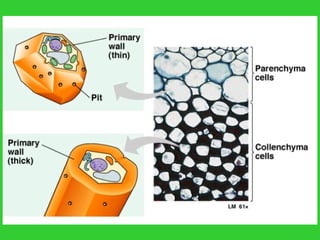
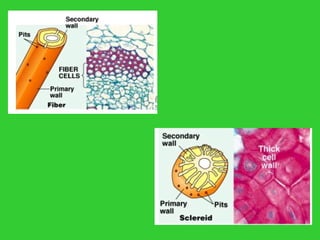
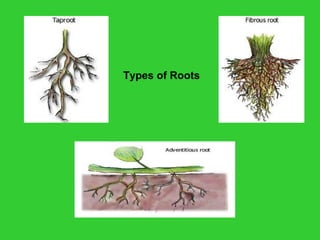
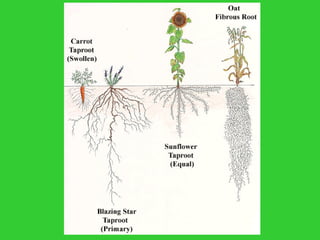
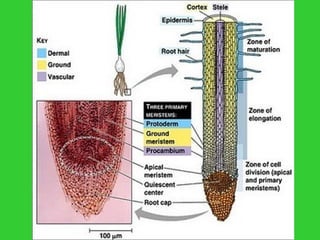
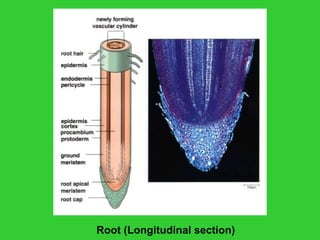
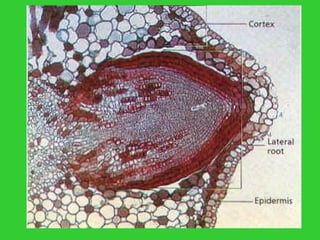
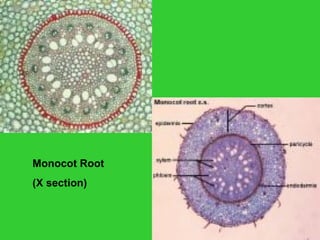
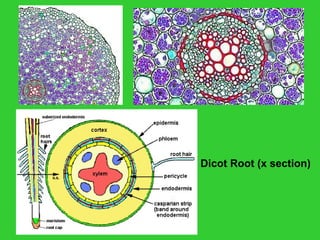
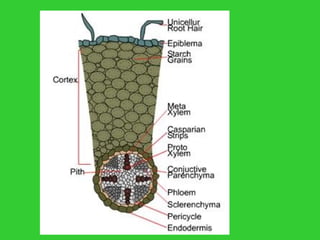
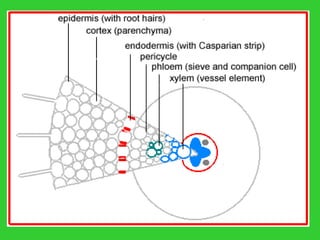
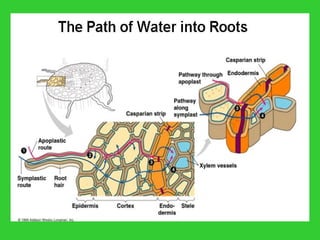
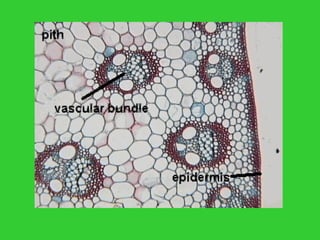
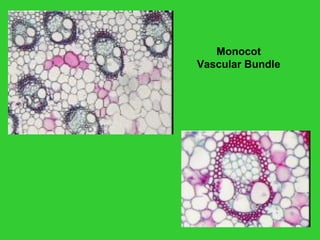
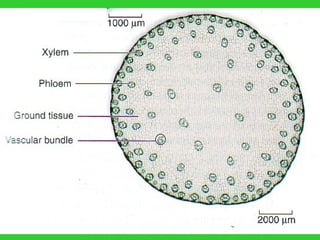
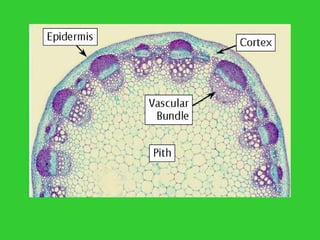
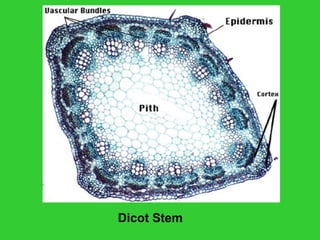
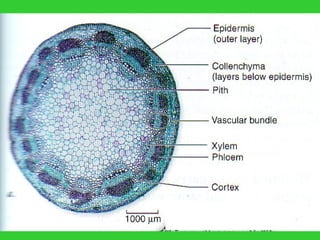
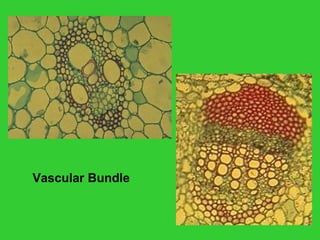
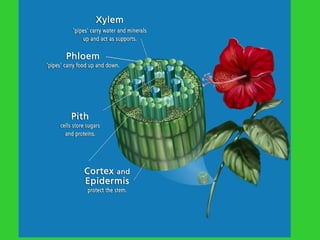
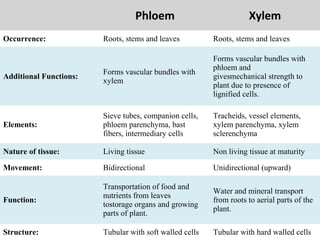
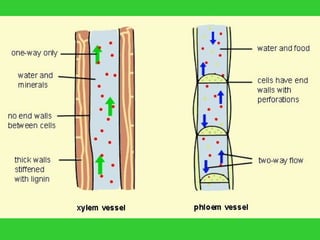
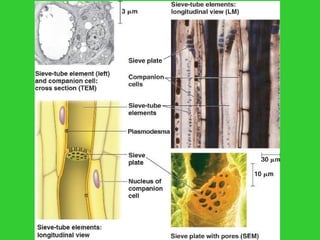
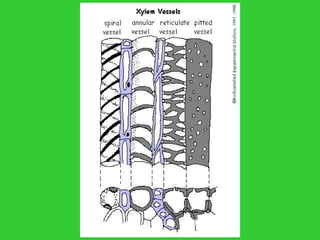
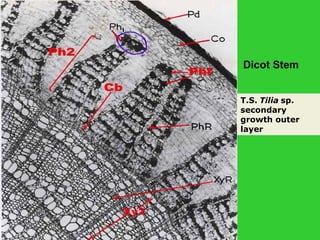
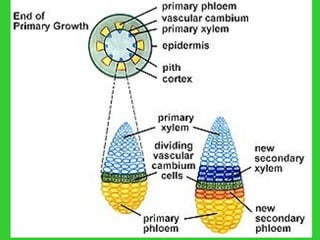
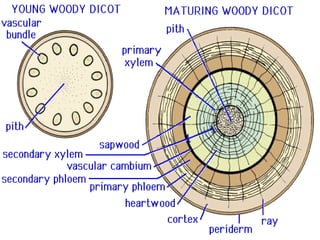
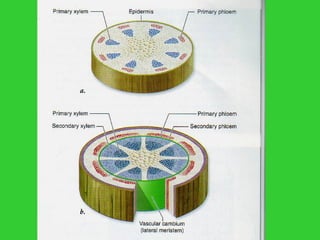
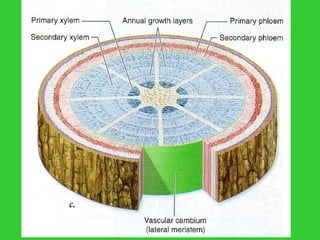
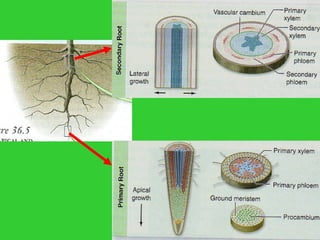
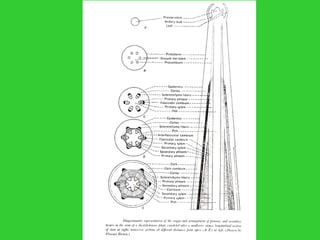
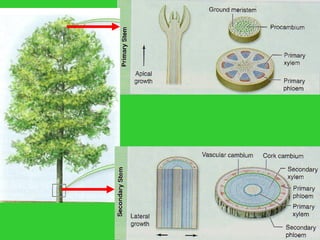
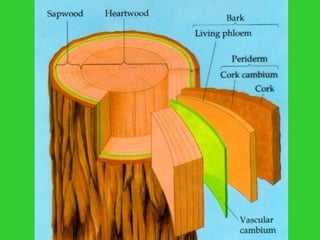
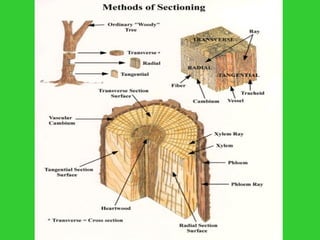
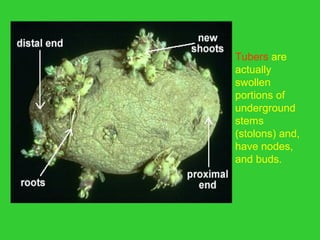
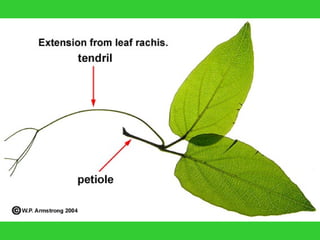
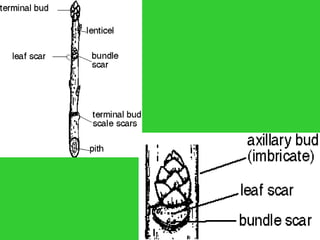
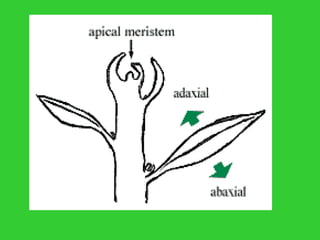
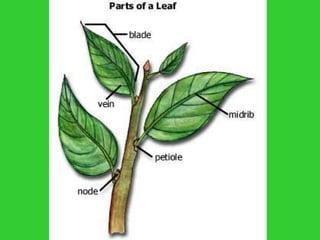
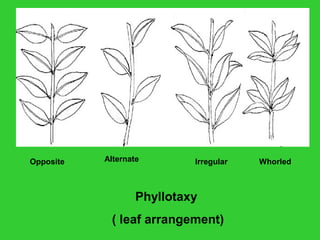
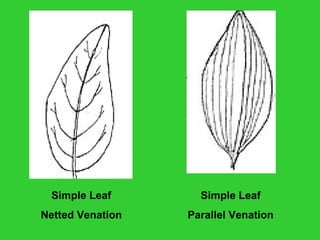
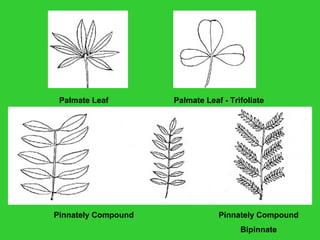
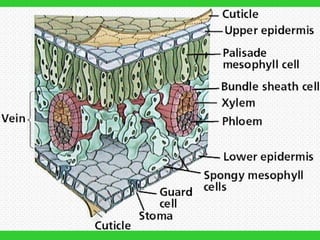
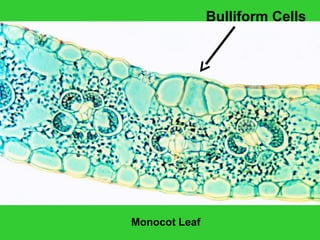
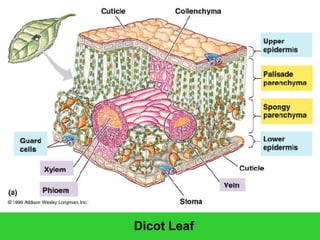
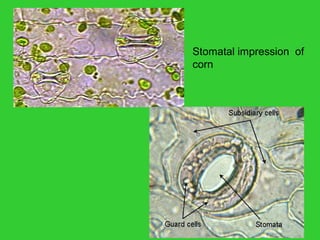
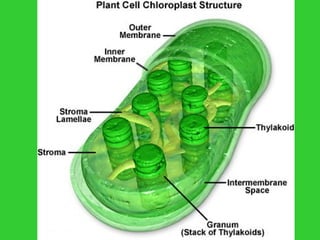
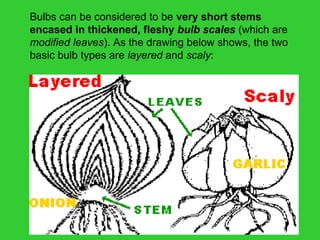
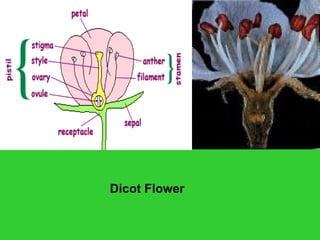
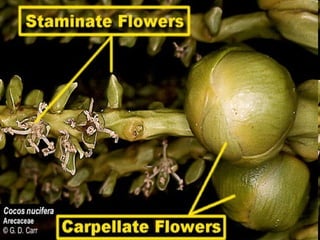
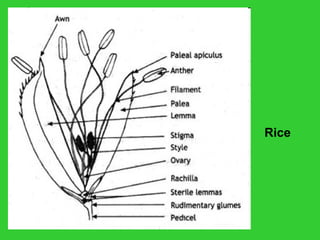
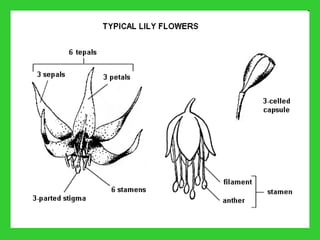
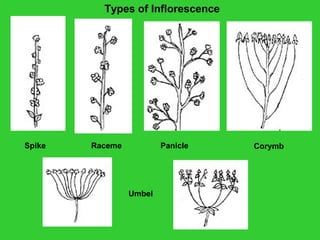
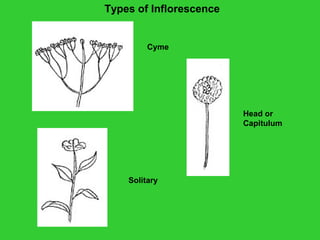
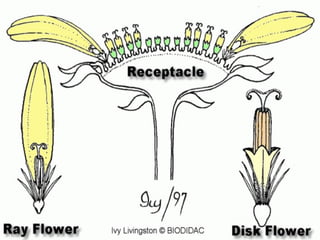
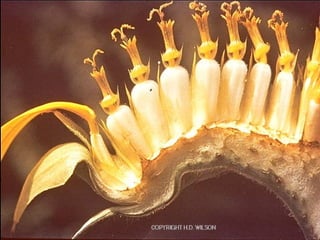
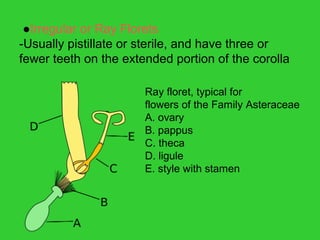
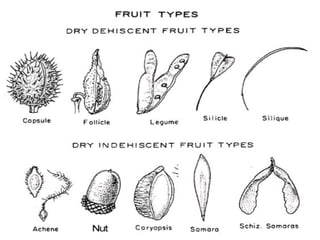
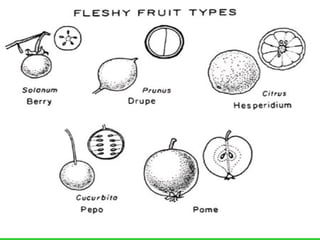
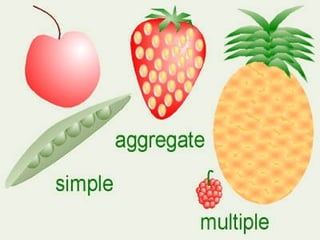
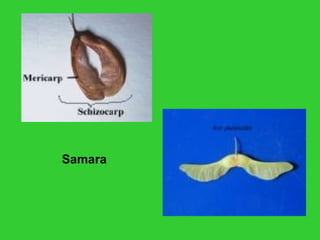
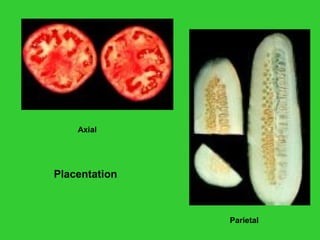
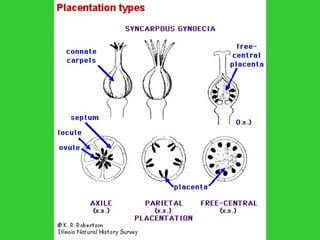
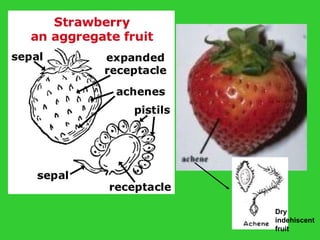
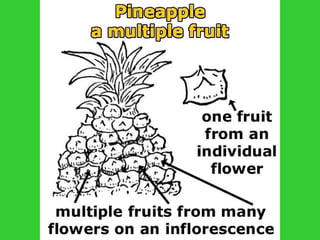
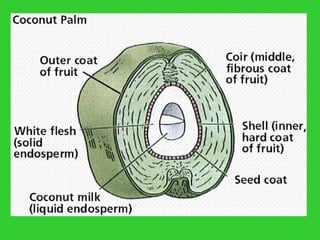
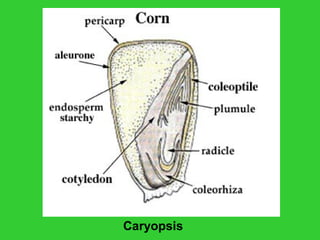
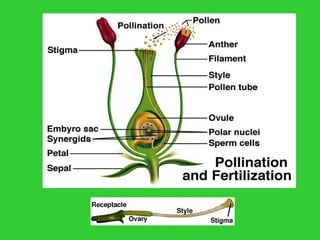
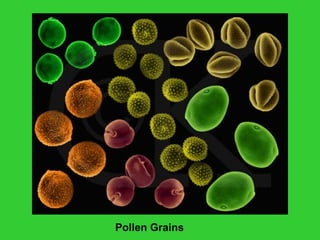
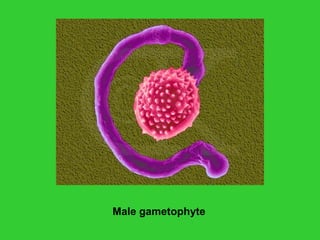
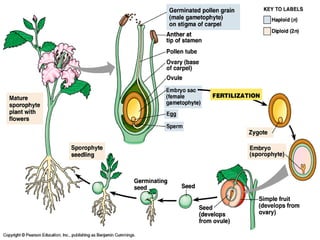
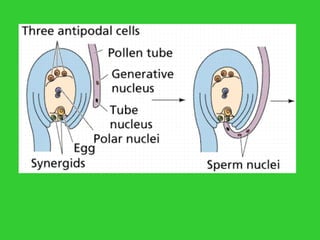
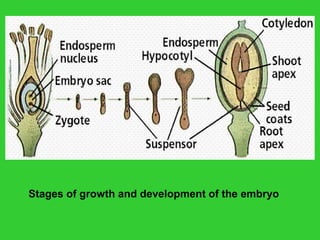
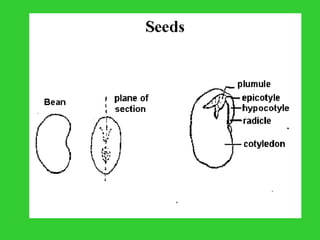
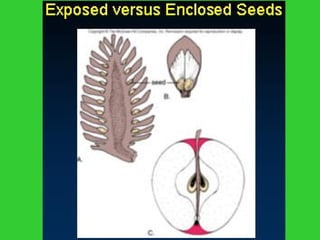
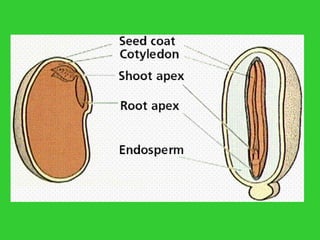
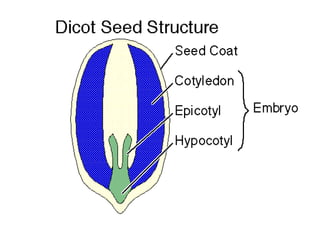
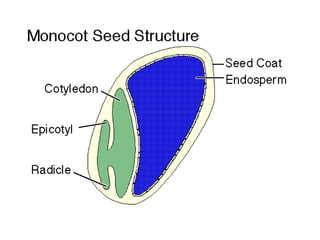
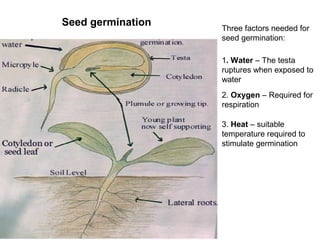
This document provides an overview of plant taxonomy and anatomy. It begins by outlining the major divisions of the plant kingdom from non-vascular plants like mosses to vascular plants with and without seeds. It then describes the distinguishing features of monocots and dicots. The remainder of the document details plant structures like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds through diagrams and descriptions.