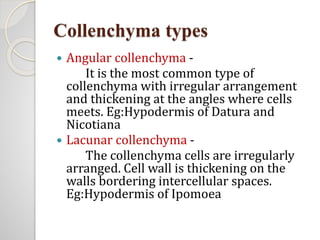
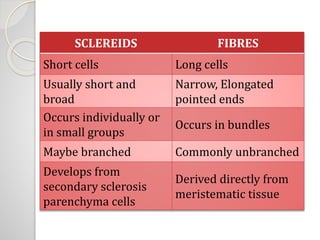
Plant anatomy is the study of internal plant structure and organization. There are two main tissue types: meristematic and permanent tissues. Meristematic tissues are made of actively dividing cells found in growth zones, and can be classified based on position, origin, function, and plane of division. Permanent tissues develop from meristematic tissues and lose the ability to divide. The two types of permanent tissues are simple tissues composed of one cell type (parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma), and complex tissues with multiple cell types. Parenchyma is the most common simple tissue and can be storage, aeration or photosynthetic. Collenchyma and sclerenchyma provide