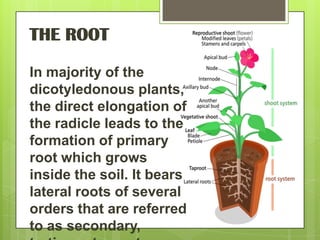
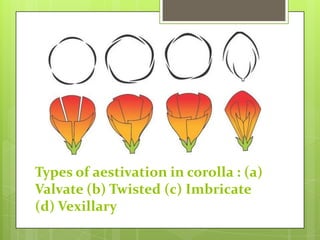
The document discusses the morphology of flowering plants. It describes the root system as either taproot or fibrous, and the regions of the root including the root cap, region of elongation and region of maturation. Stems can be modified as tubers, bulbs, rhizomes or stolons for storage and support. Leaves originate from the stem and their venation and arrangement is described. Flowers make up the inflorescence and have four whorls - calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium. Their symmetry and arrangement on the thalamus is also detailed.