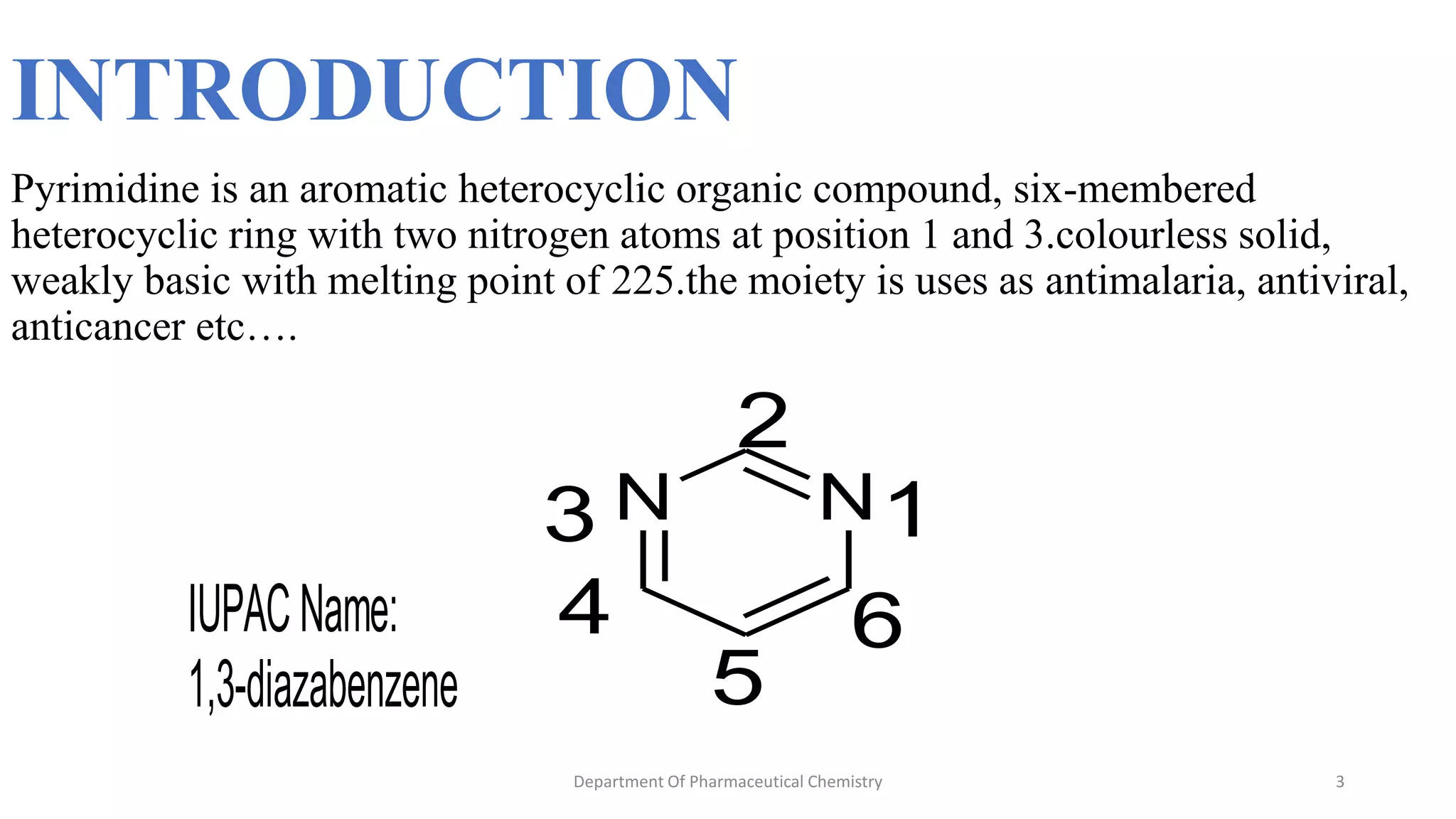
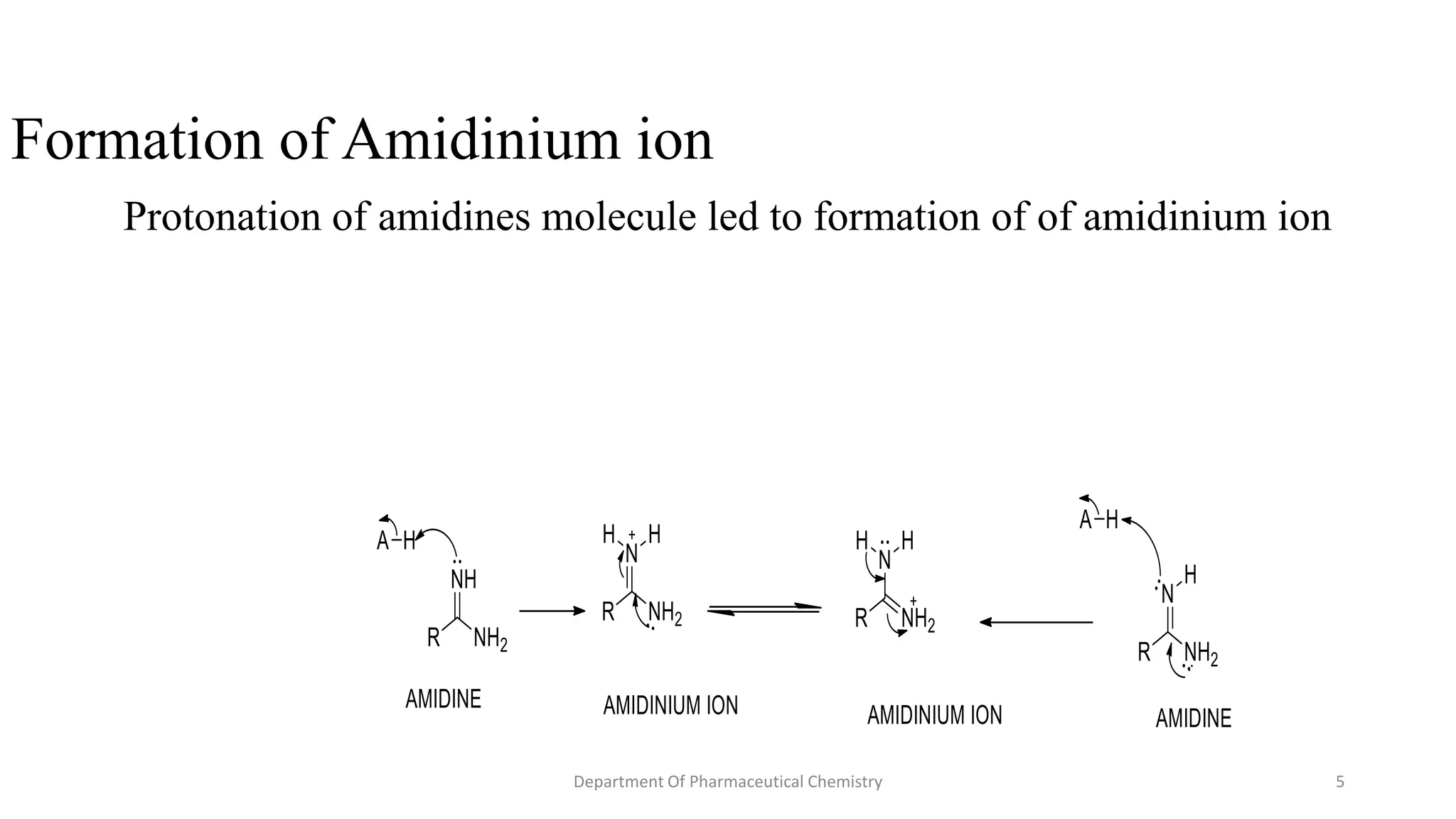
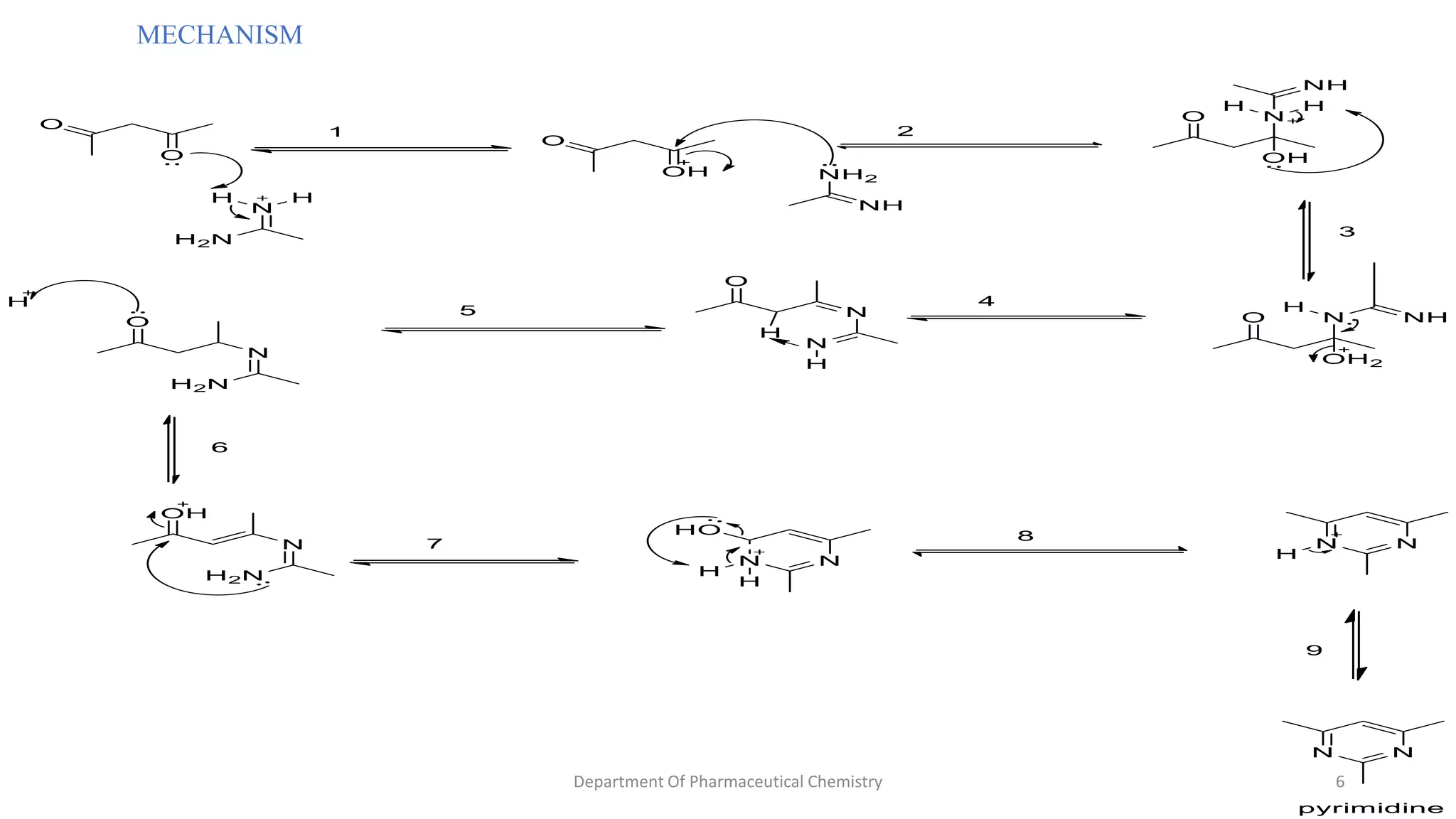
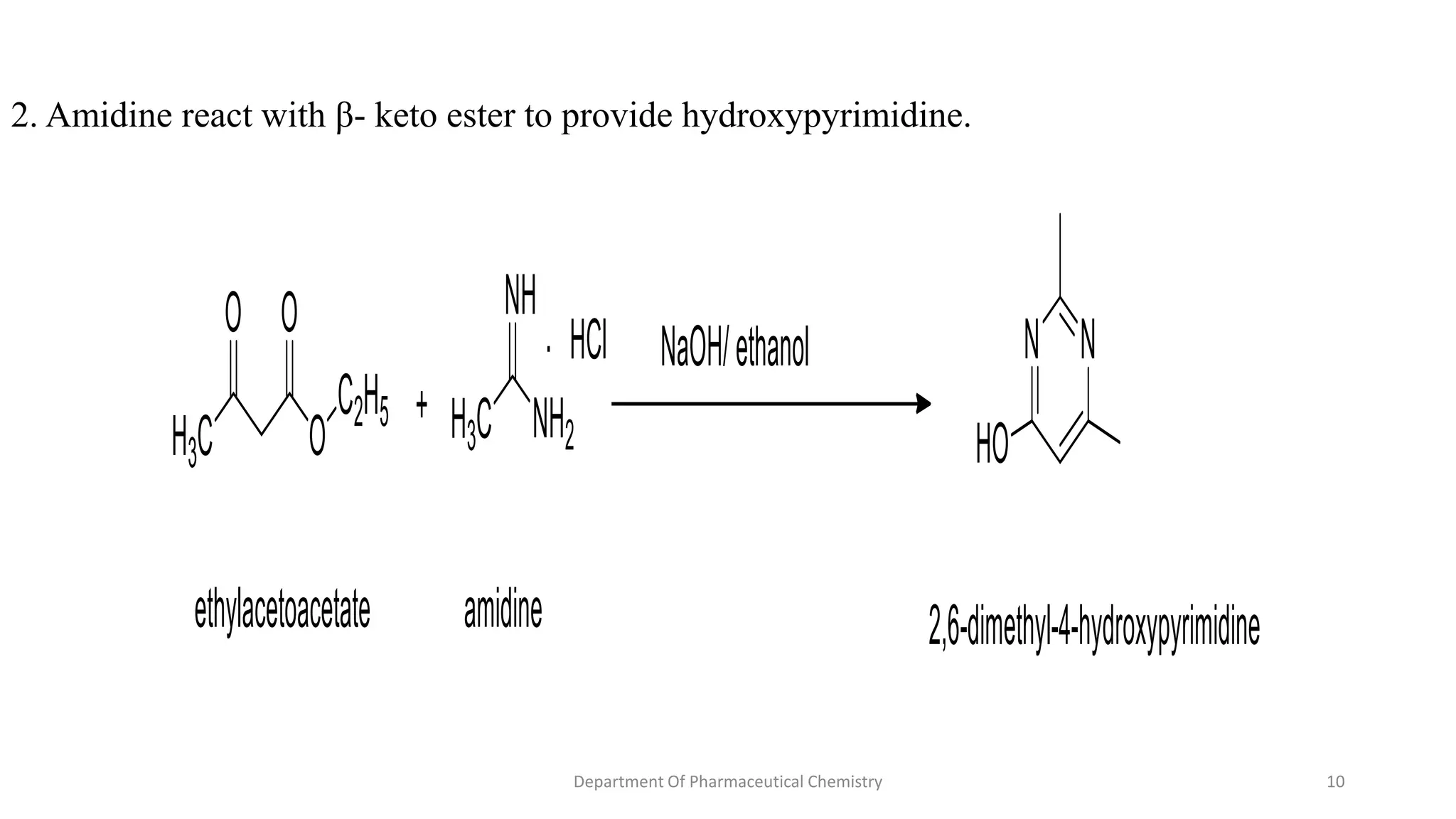
This document summarizes the Pinner pyrimidine synthesis reaction. The reaction involves the condensation of a non-N-substituted amidine and β-keto ester (β-diketone) in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a pyrimidine heterocyclic ring. The mechanism proceeds through protonation, nucleophilic attack, dehydration, and deprotonation steps. Pyrimidine derivatives synthesized via this reaction are used in drugs to treat conditions like malaria, viruses, and cancer.