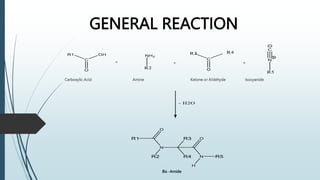
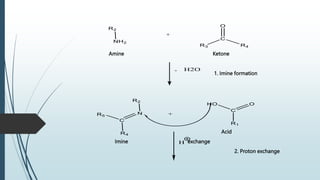
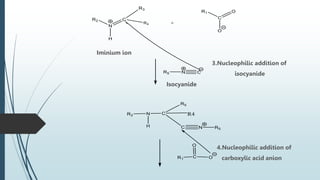
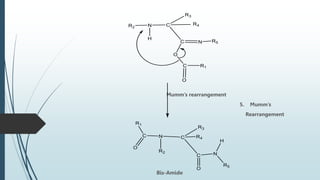
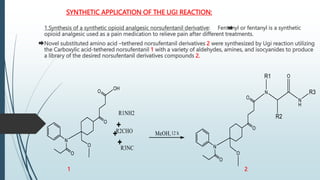
The document describes the Ugi reaction, a multi-component reaction where a ketone or aldehyde, amine, isocyanide, and carboxylic acid come together to form a bis-amide. It was first reported in 1959 by Ivar Karl Ugi. The reaction has high atom economy and yields, occurs rapidly at room temperature, and is uncatalyzed. It has applications in synthesizing chemical libraries and multiple compounds in one step, such as the HIV drug Crixivan. The mechanism involves imine formation, proton exchange, additions of the isocyanide and carboxylic acid, and a Mumm's rearrangement.