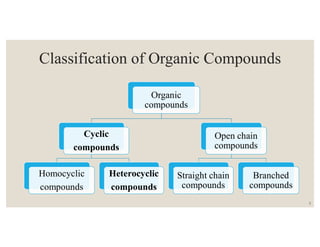
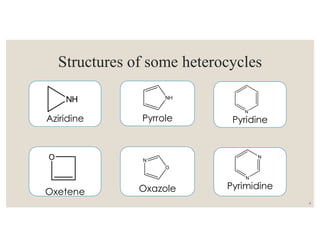
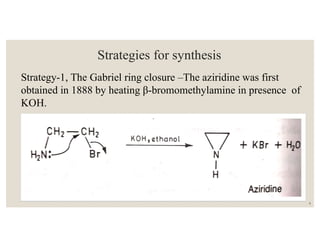
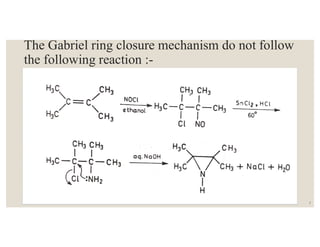
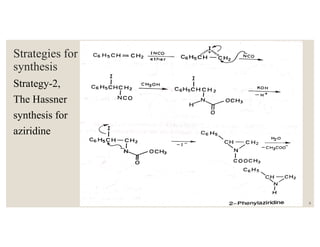
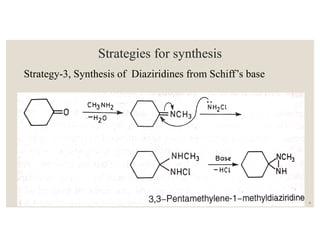
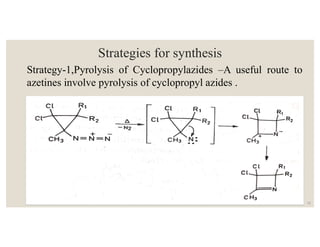
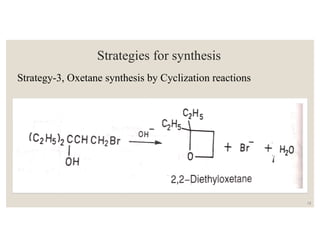
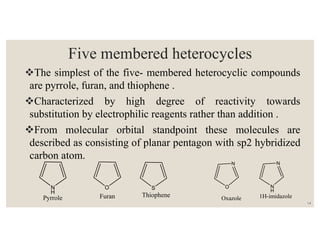
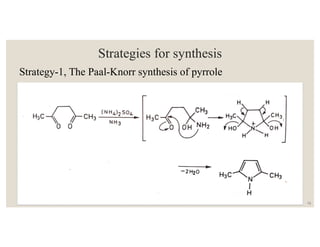
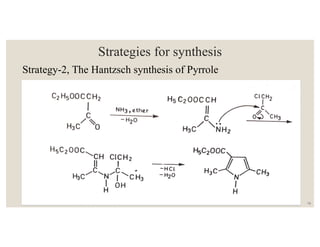
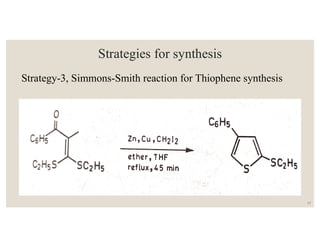
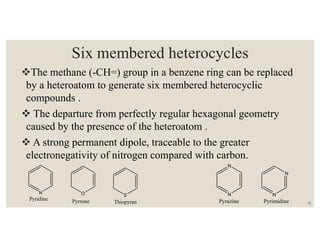
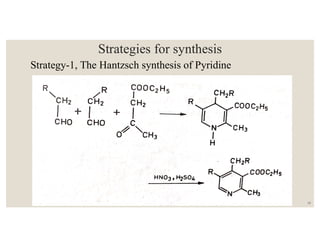
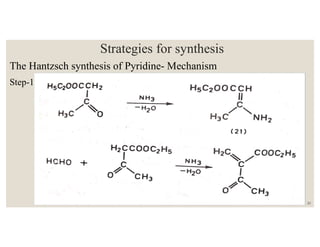
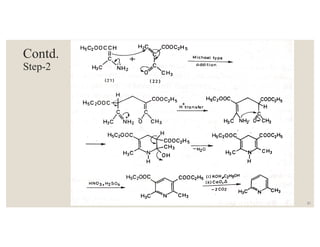
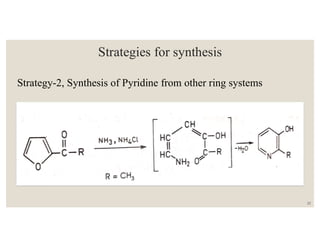
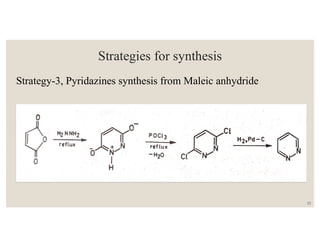
This document discusses strategies for synthesizing three, four, five, and six-membered heterocyclic rings. It outlines three strategies for each ring size, including the Gabriel ring closure and Hassner synthesis for aziridines, pyrolysis of cyclopropyl azides and photocycloaddition for azetines, the Paal-Knorr and Hantzsch syntheses for pyrroles, and the Hantzsch synthesis and reactions with maleic anhydride for pyridines and pyridazines. A variety of heterocyclic compounds are derived from carbocyclic precursors by replacing carbon atoms with heteroatoms like nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur.