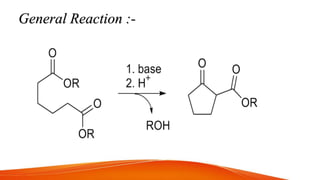
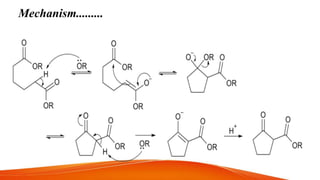
The document summarizes two organic reactions: the Dieckmann reaction and ozonolysis reaction. The Dieckmann reaction involves the intramolecular condensation of diesters in the presence of a strong base to form β-keto esters via a 5-exo-trig cyclization. It is used to synthesize cyclopentane and cyclohexane derivatives. Ozonolysis involves the cleavage of unsaturated bonds like alkenes and alkynes with ozone to form carbonyl groups. It can be used to oxidize alkenes into alcohols, aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids and is useful for structure elucidation of unknown compounds containing carbon-carbon double bonds.
![ADVANCED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Presented by : Niket D.Bajare [M.pharm First year]
Guided by :Dr S. Pekamwar
School of Pharmcy ,Nanded.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/niketreaction-190310185849/85/organic-reaction-1-320.jpg)