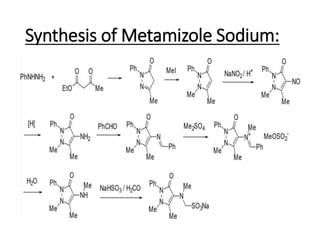
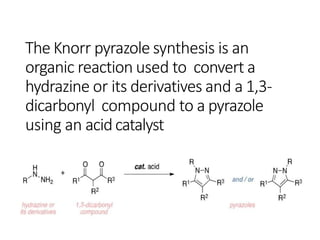
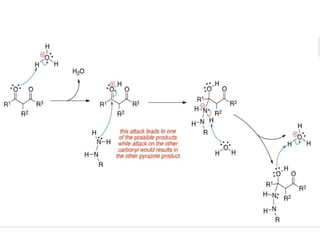
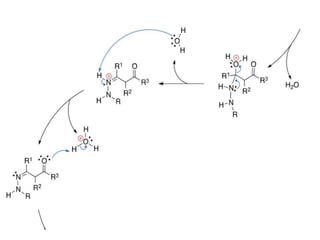
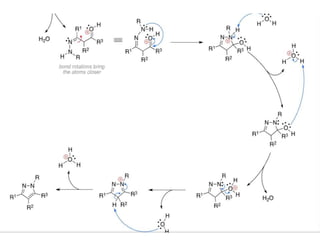
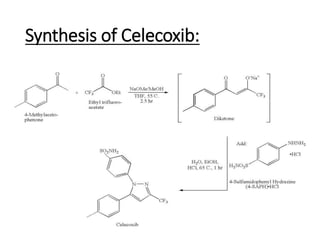
The document discusses the Knorr pyrazole synthesis reaction which converts hydrazines or derivatives and 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds to pyrazoles using an acid catalyst. The mechanism involves acid-catalyzed imine formation on either carbonyl carbon, followed by attack of the other nitrogen on the other carbonyl group. This forms a diimine compound which deprotonates to generate the final pyrazole product. Several examples of pyrazoles synthesized using this reaction are mentioned, including antipyrine, celecoxib, and metamizole sodium which have various medical applications.




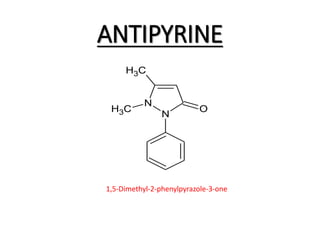

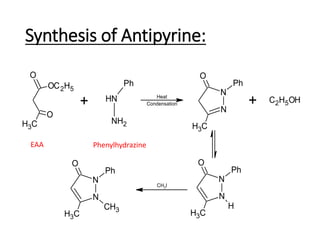
![CELECOXIB
4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazol-1-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knorrpyrazolesynthesis1-210317172526/85/Knorr-Pyrazole-Synthesis-M-Pharm-12-320.jpg)

![METAMIZOLE SODIUM
[(1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenylpyrazol-4-yl)-methylamino]methanesulfonic acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knorrpyrazolesynthesis1-210317172526/85/Knorr-Pyrazole-Synthesis-M-Pharm-15-320.jpg)