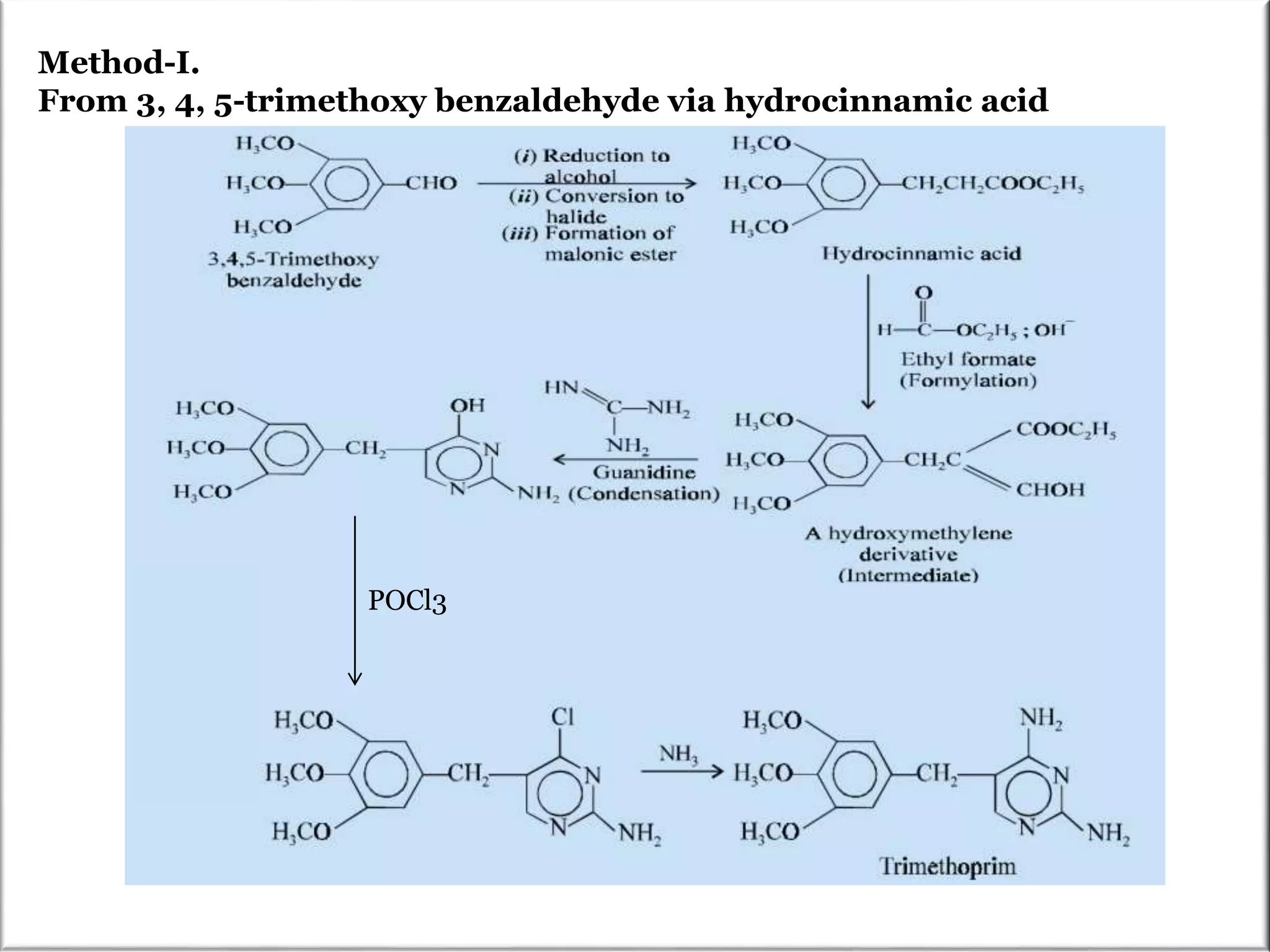
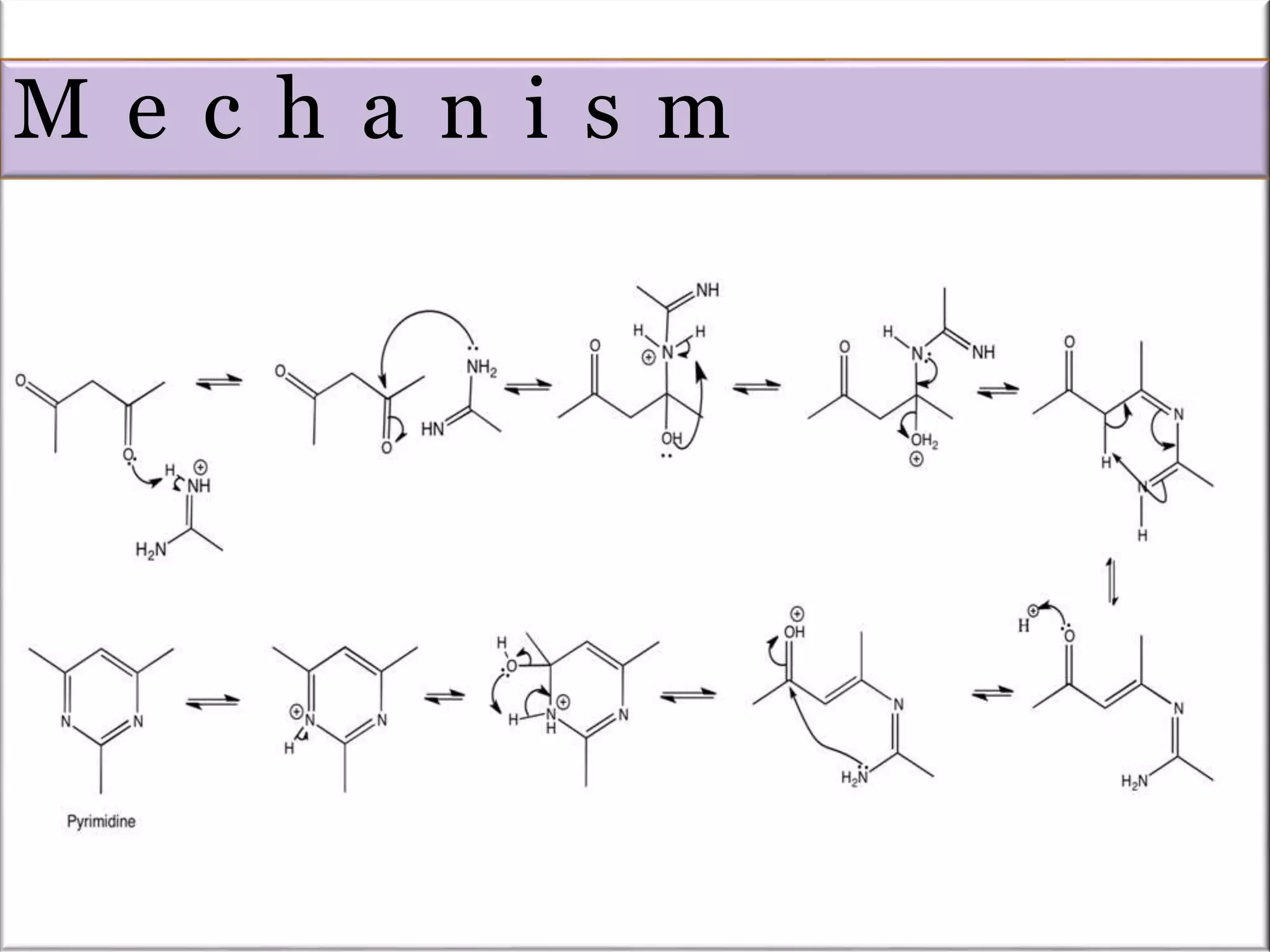
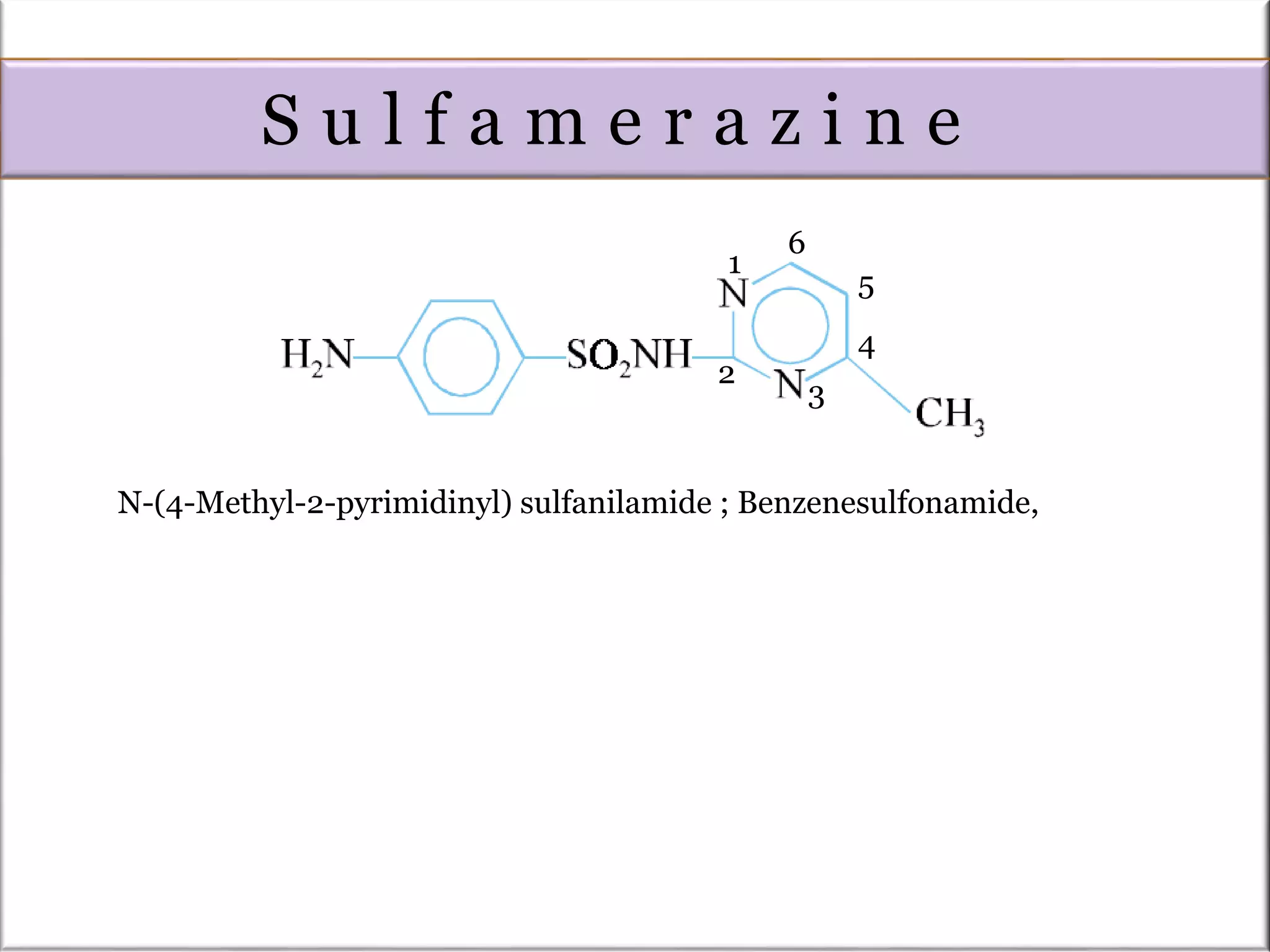
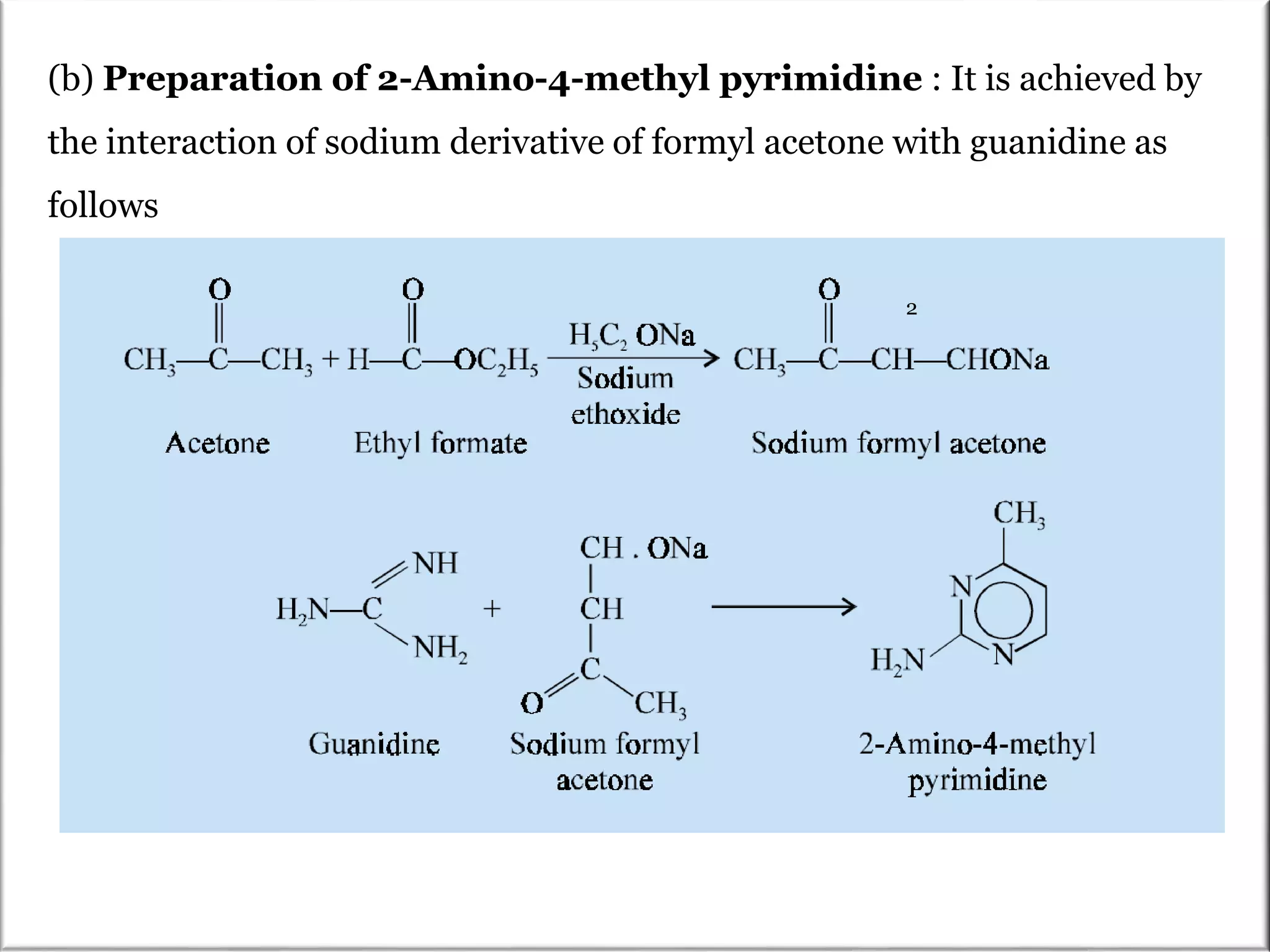
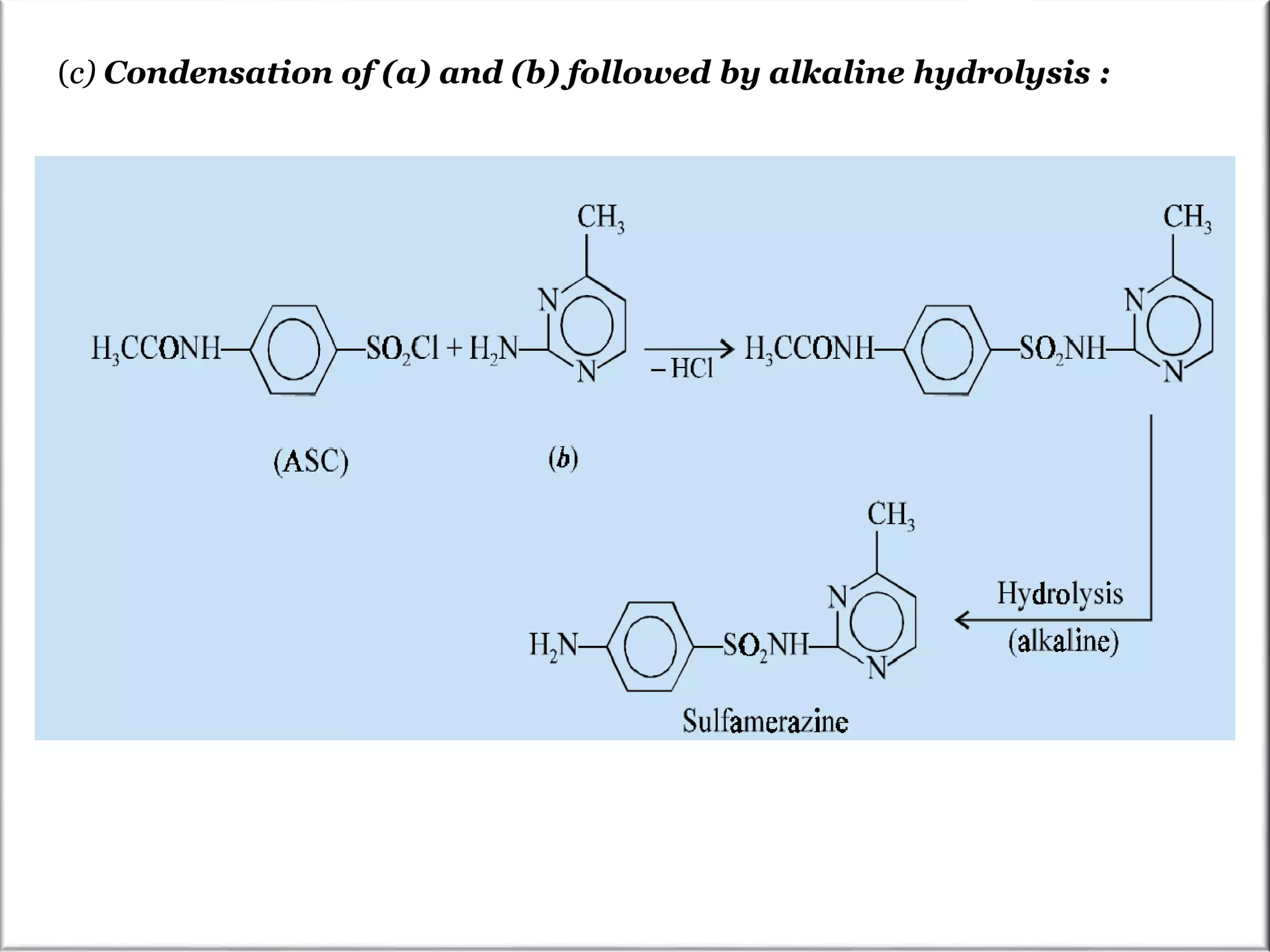
The Pinner pyrimidine synthesis involves the condensation of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds with amidines catalyzed by acids or bases to form pyrimidine derivatives. Specifically, it describes the reaction of amidine derivatives with β-keto esters, malonic esters, or β-diketones to produce various substituted pyrimidines. Examples are provided of important pyrimidine drugs synthesized using this method, such as sulfamerazine and trimethoprim.







![The 1,3-dicarbonyl components can be replaced by an en0l ether, which can be
prepared by Claisen condensation from an ortho ester RC(OR′)3 and a
reactive methylene compound [CH2].
En0l ether
RCN + 3 R′OH → RC(OR′)3 + NH3
Orthoesters can be prepared by the Pinner reaction, in which nitriles react
with alcohols under acid catalysis:
Nitriles alcohols Orthoesters
Orthoesters
Claisen condensation
+ CH2
methylene
compound En0l ether
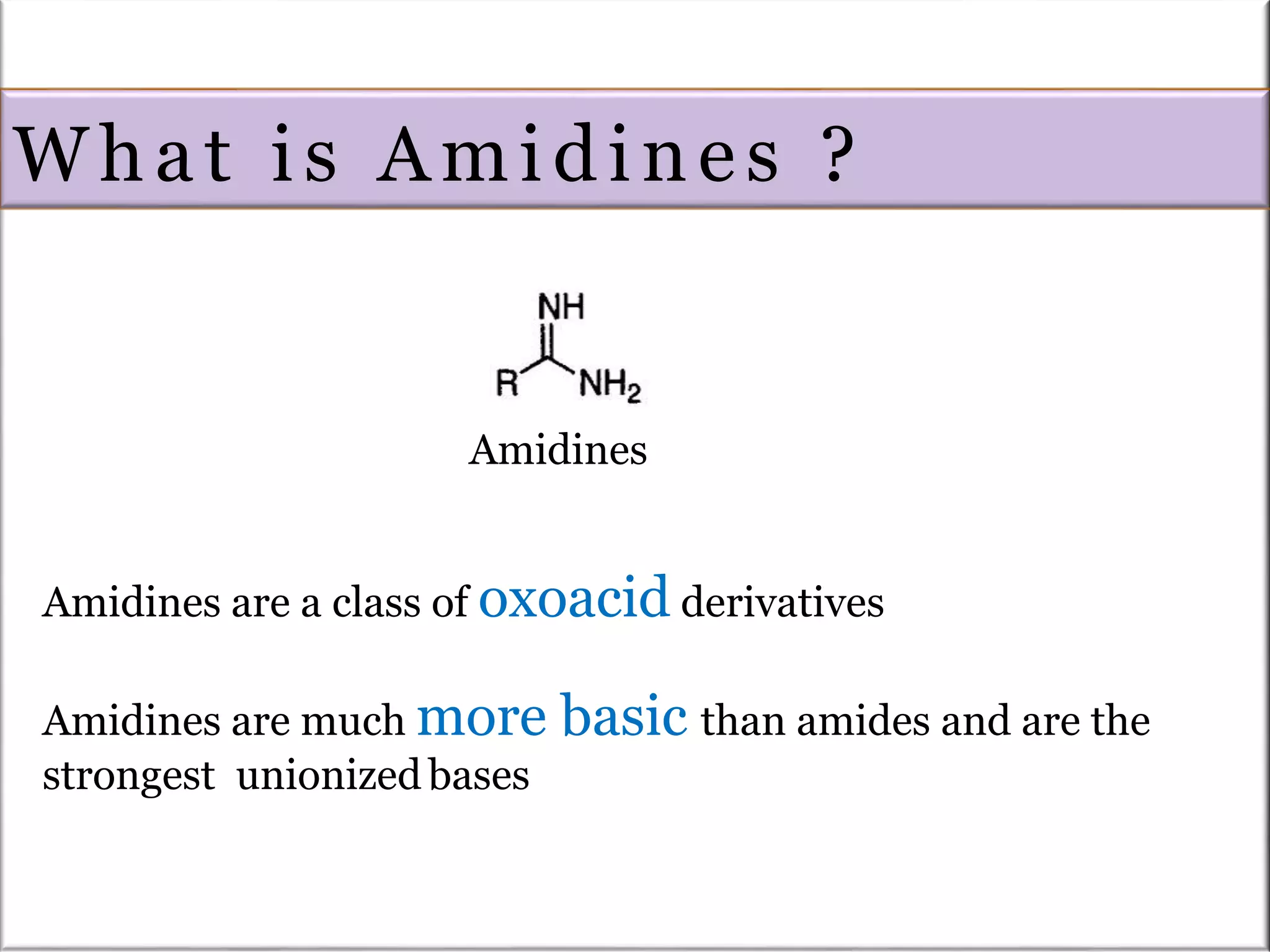
Amidines
2-methyl-6-hydroxy-
5-nitrile pyrimidine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-171011125521/75/Pinner-pyrimidine-synthesis-12-2048.jpg)

![Trimethoprim
2, 4-Diamino-5-(3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzyl) pyrimidine ;
2,4-Pyrimidinediamine, 5-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl) methyl]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-171011125521/75/Pinner-pyrimidine-synthesis-17-2048.jpg)