Embed presentation
Downloaded 49 times

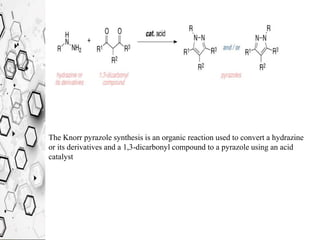
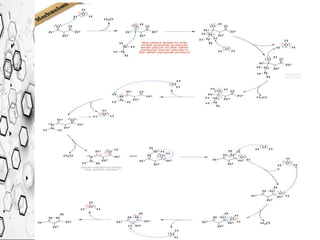

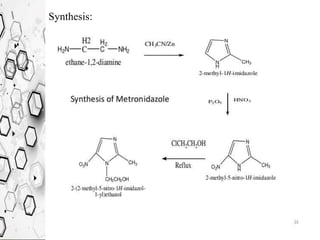
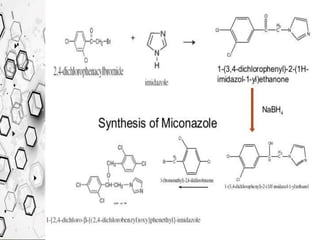
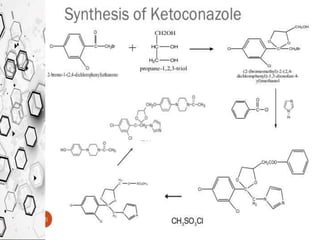
The Knorr pyrazole synthesis converts a hydrazine or its derivatives and a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound to a pyrazole using an acid catalyst. The mechanism involves an acid-catalyzed imine formation where the hydrazine attacks either carbonyl carbon, followed by attack of the other nitrogen on the other carbonyl group. This diimine compound then deprotonates to form the pyrazole product. The reaction is used to synthesize compounds such as metal chelates, photographic dyes, herbicides, and biologically active molecules.






