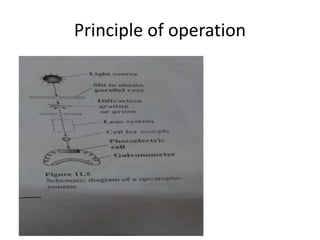
This document discusses photometry, colorimetry, and spectrophotometry, including their principles, instrumentation, and applications. Photometry measures light absorption to determine concentrations of elements. Colorimetry uses the human eye to determine concentrations of colored compounds, following Beer's and Lambert's laws relating absorbance to concentration and path length. Spectrophotometry identifies compounds by their absorption spectra and is used for enzyme assays, molecular weight determination, and studying protein interactions. These techniques are important in biochemical research for concentration determination, reaction monitoring, and compound identification.