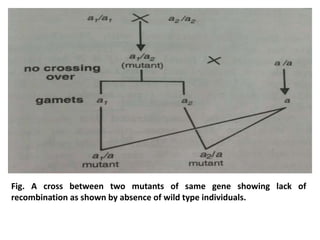
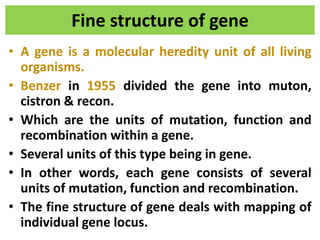
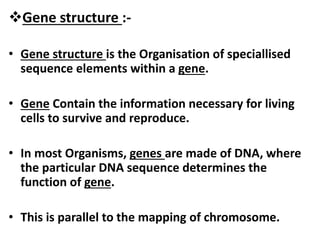
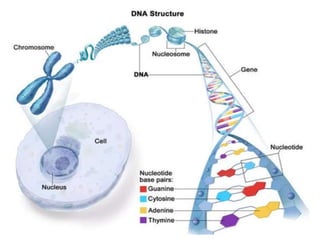
1. The document discusses the classical concepts of genes and alleles, including that genes were viewed as indivisible units of structure, mutation, and function. 2. Experiments in the 1940s-50s showed intragenic recombination was possible, challenging the classical view. 3. Benzer then proposed that genes comprise smaller units of mutation (mutons), function (cistrons), and recombination (recons) based on his work mapping the fine structure of genes.