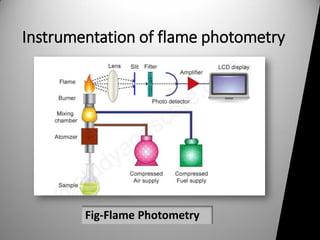
Flame photometry, also known as flame emission spectroscopy, is an analytical technique first introduced in the 19th century, primarily for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of alkali and alkaline earth metals like sodium and potassium. This method works by measuring the intensity of light emitted when metallic ions are introduced into a flame, with specific wavelengths corresponding to different elements. While flame photometry is a simple and cost-effective process, it has limitations in accurately measuring higher concentrations of certain metals and cannot detect non-radiating elements like carbon and hydrogen.