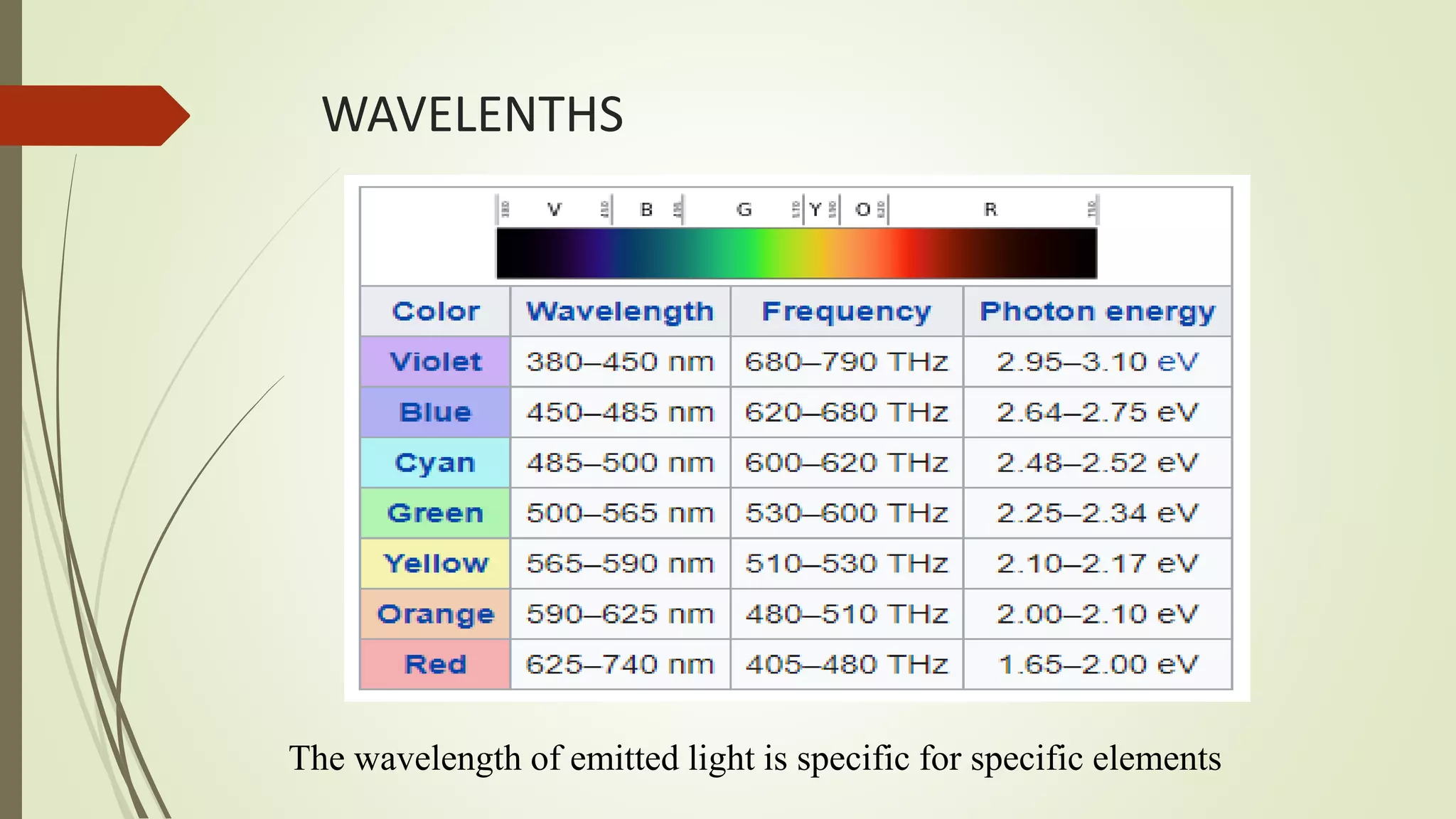
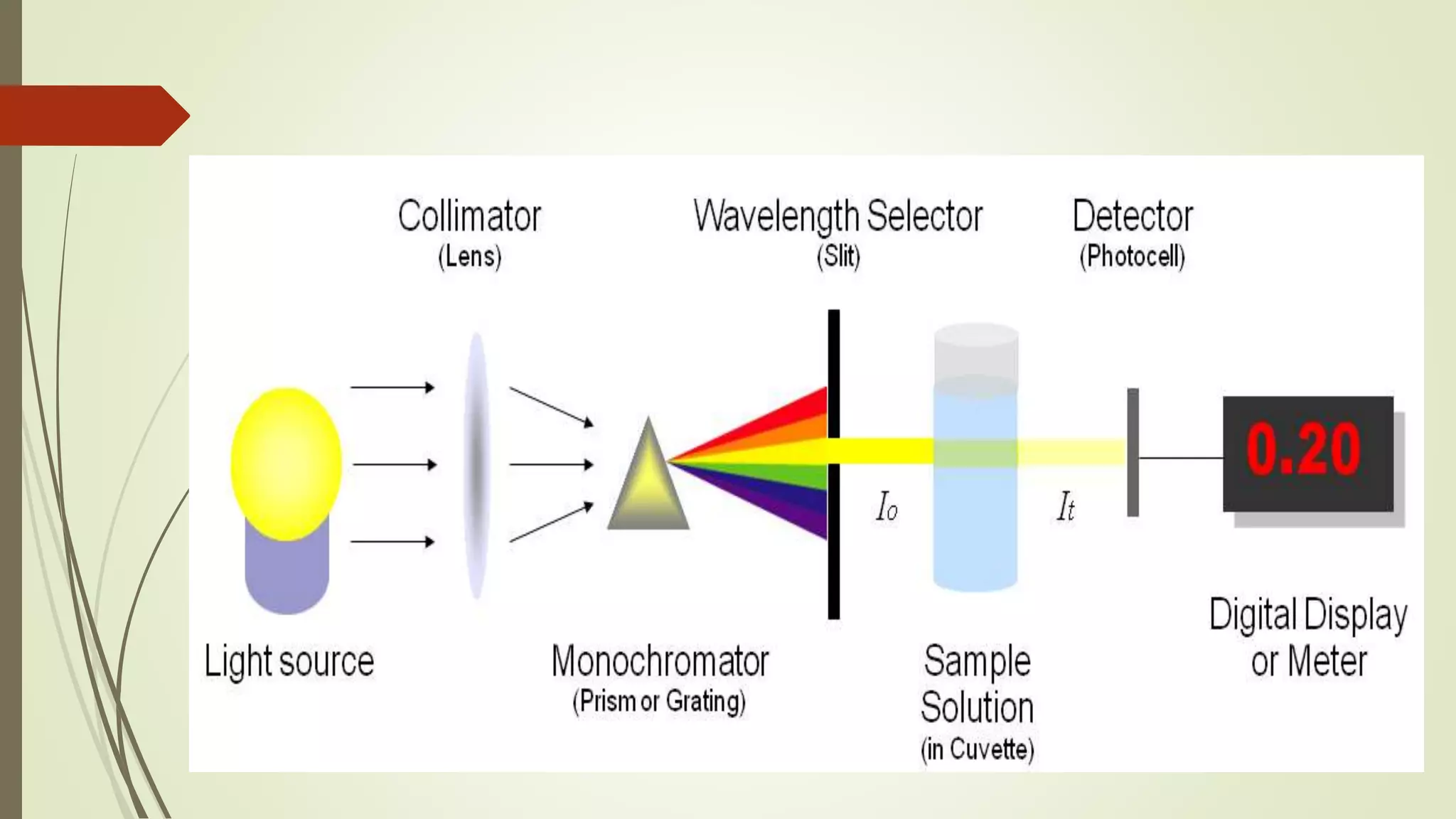
The document discusses photometry and spectrophotometry, focusing on their principles, applications, and differences. Photometry measures the concentration of compounds in solutions by assessing light absorbance, while spectrophotometry measures how much light a substance absorbs at specific wavelengths. Both techniques have important roles in various industries and fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental analysis.