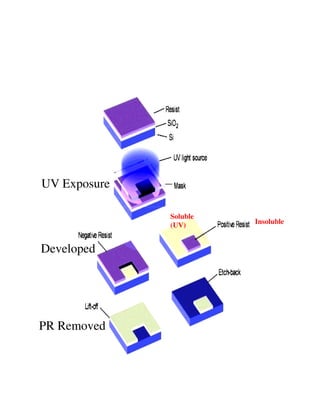
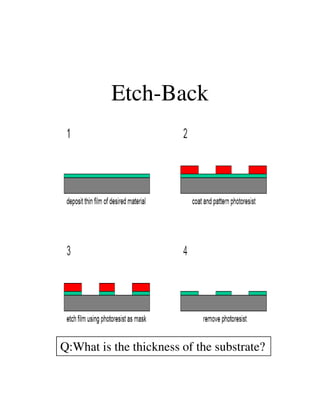
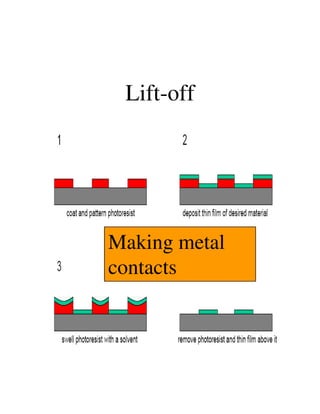
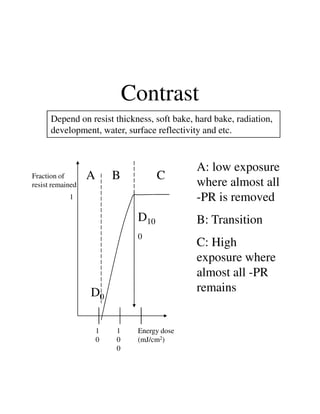
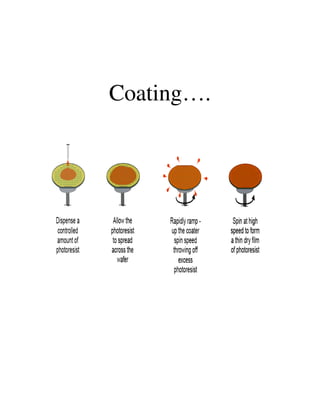
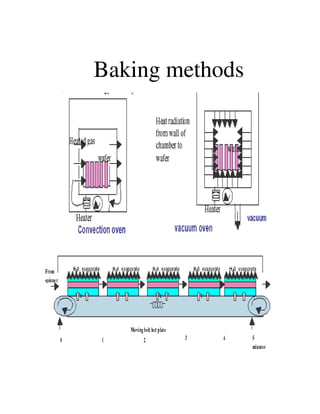
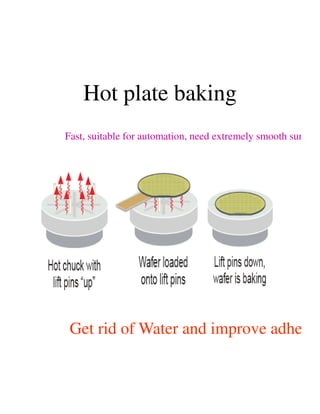
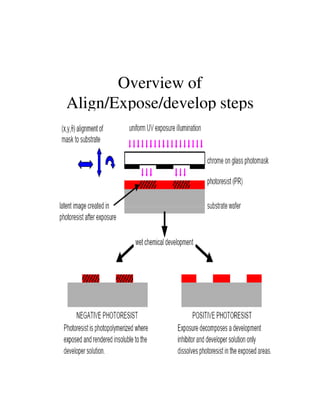
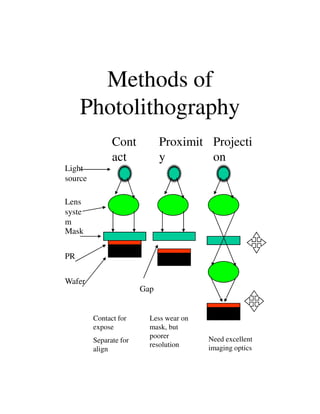
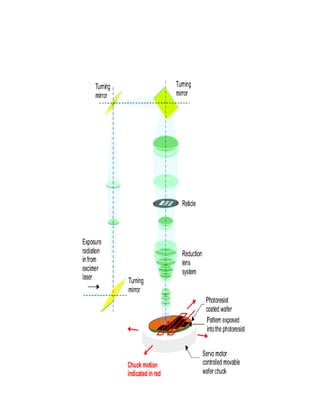
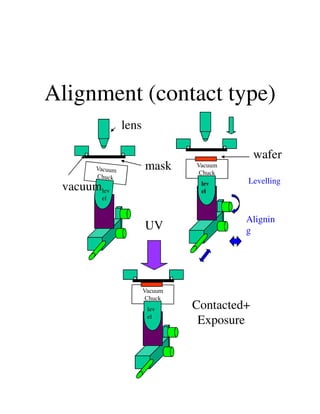
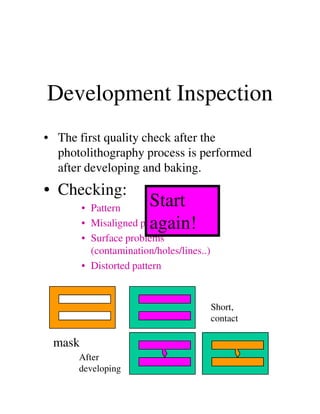
Photolithography is a process for transferring geometric patterns onto a substrate using light. It involves coating a photoresist layer on the substrate, exposing it to light through a photomask, and developing it to selectively remove either the exposed or unexposed areas. The key steps are photoresist coating, soft baking, alignment and exposure, development, hard baking, etching, and photoresist removal. Positive photoresist becomes soluble after exposure while negative photoresist becomes insoluble, allowing selective removal of one area versus the other during development.