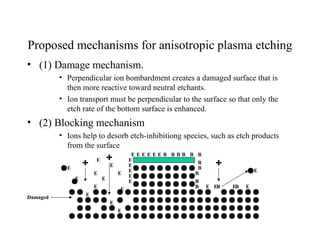
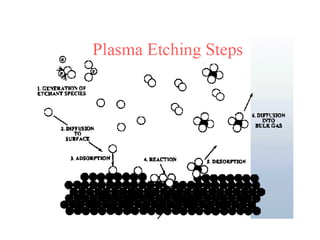
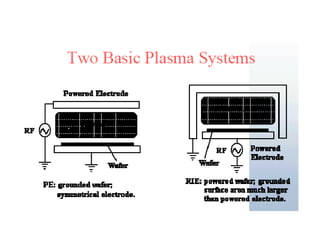
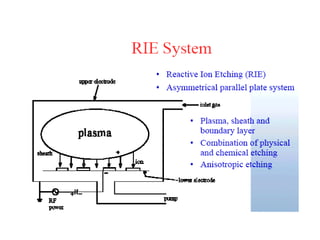
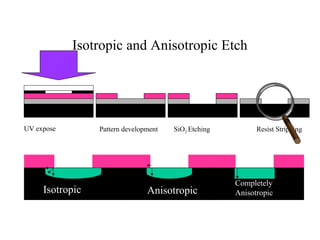
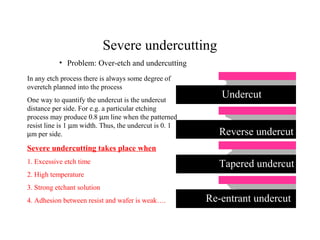
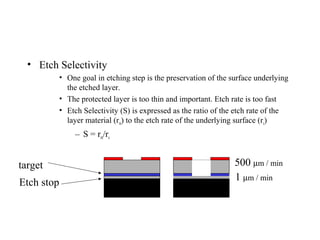
This document discusses wet and dry etching techniques. Wet etching involves immersing wafers in chemical solutions and results in isotropic etching. Common wet etchants include HNO3/HF for silicon, HF for silicon dioxide, and hot phosphoric acid for silicon nitride. Dry etching uses plasma to etch materials and can produce anisotropic profiles. Factors that influence dry etching include etch rate, damage, anisotropy, uniformity, selectivity, and cleanliness. Reactive ion etching combines chemical etching with ion bombardment to increase etch rates while maintaining anisotropic profiles.














![(111)
[001]
[010]
[100]
(100)
[100]
[001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide2-140625025537-phpapp01/85/Wet-and-Dry-Etching-19-320.jpg)