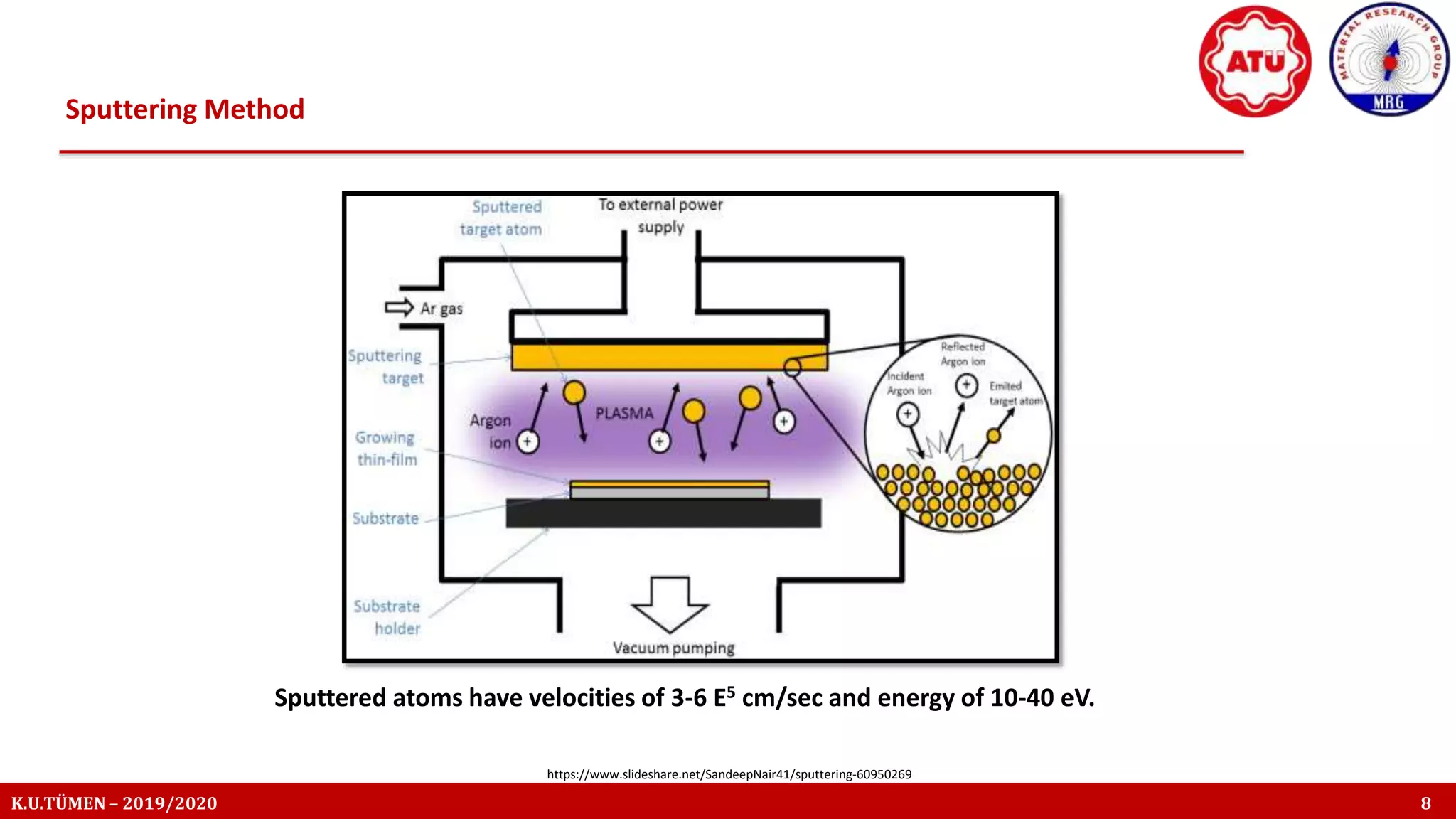
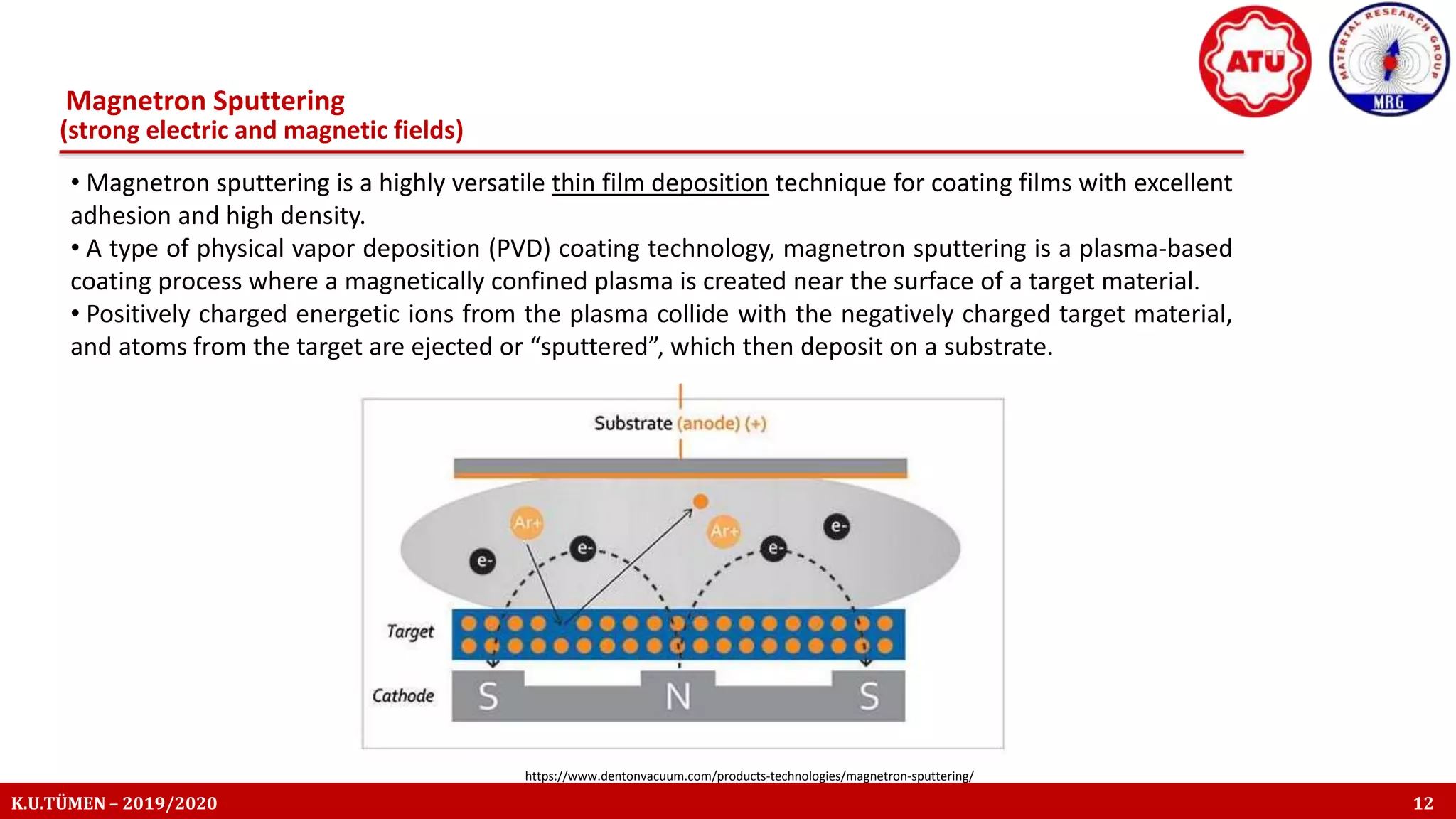
The document discusses the thin film deposition techniques, focusing on magnetron sputtering, which is a type of physical vapor deposition (PVD). It highlights the importance of thin films in various applications such as microelectronics and protective coatings, and explains the mechanisms and advantages of using magnetrons to enhance ionization efficiency. The document also covers the principles of sputtering, including the processes involved in creating and depositing thin films.