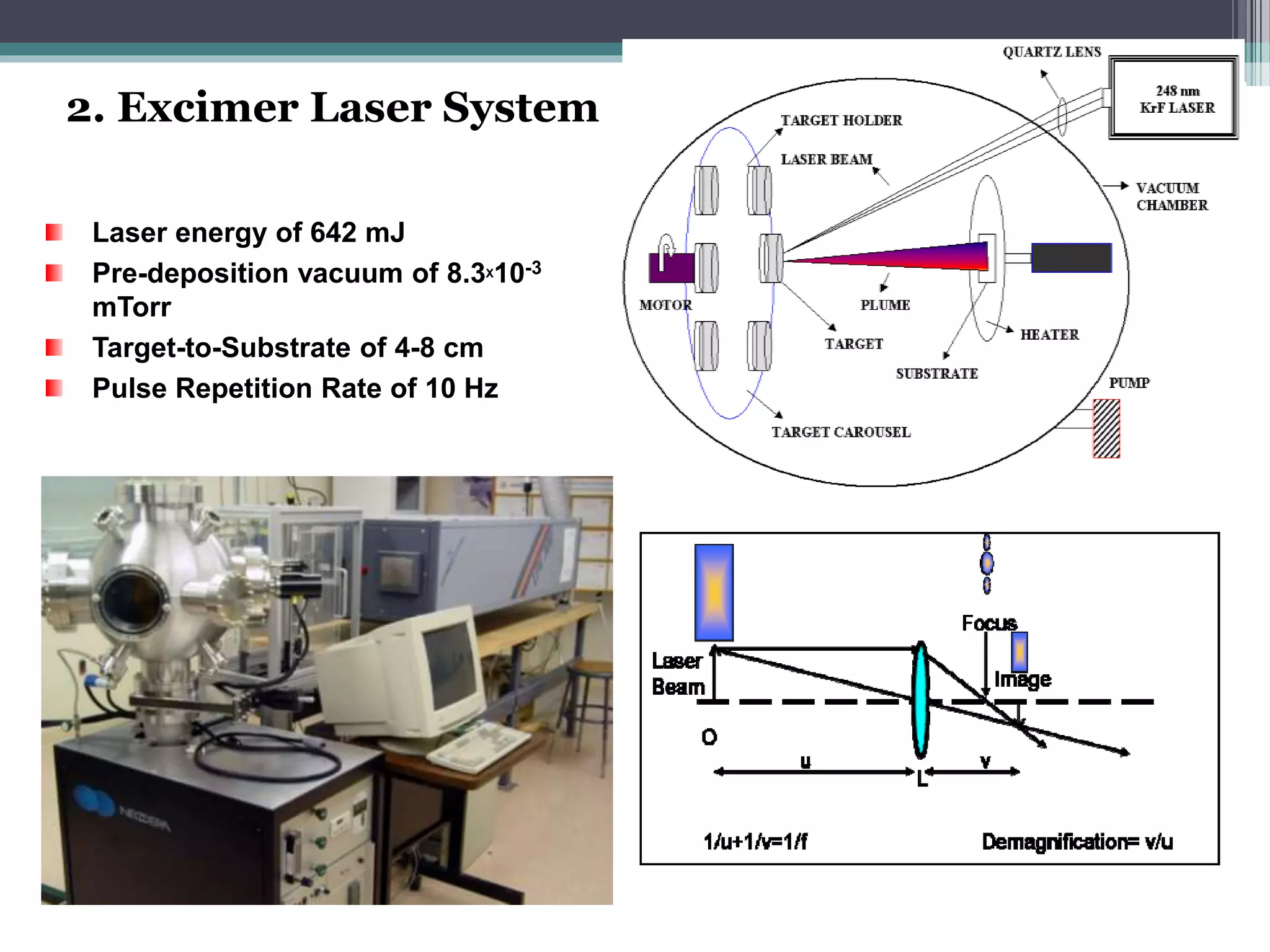
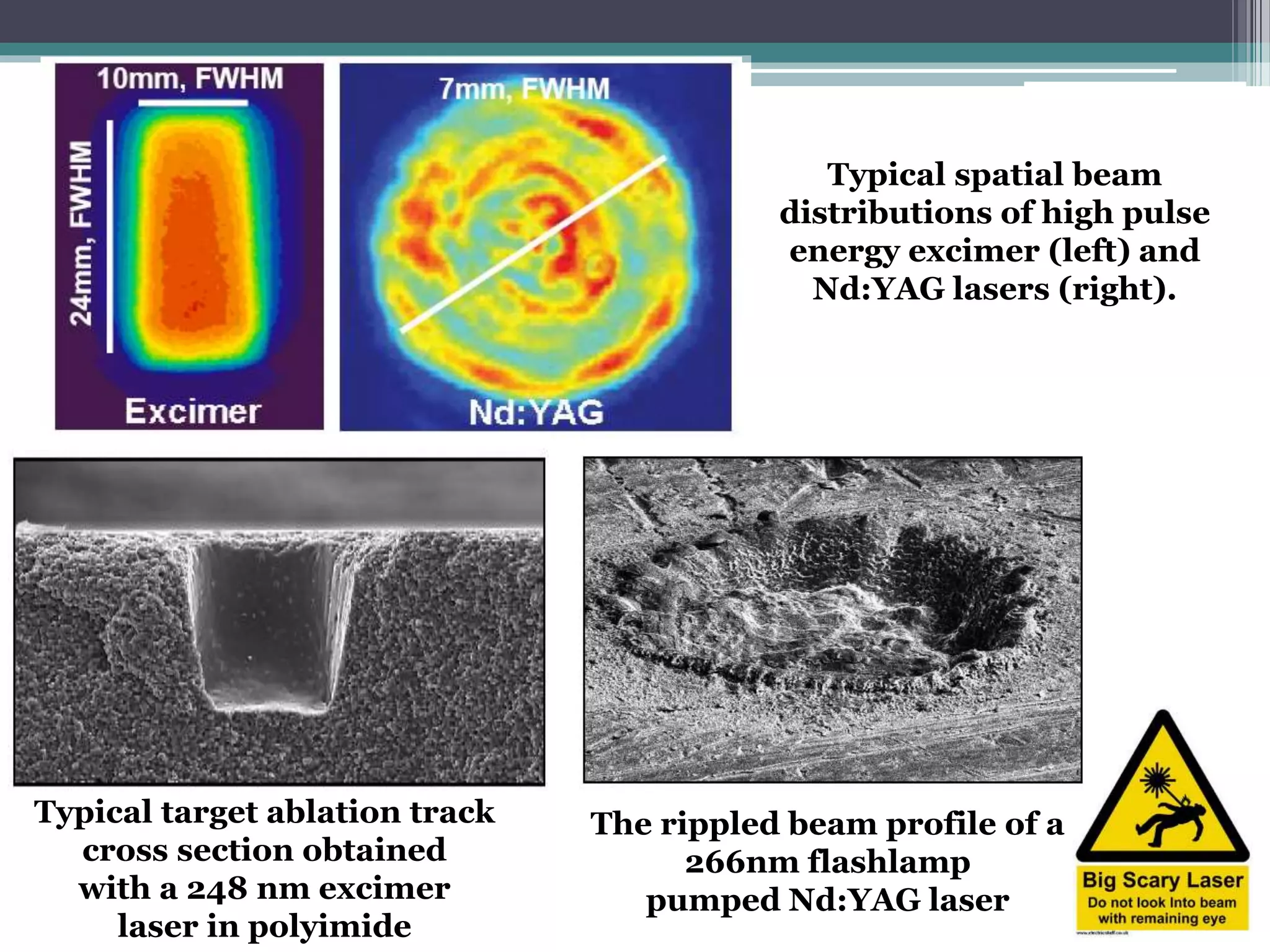
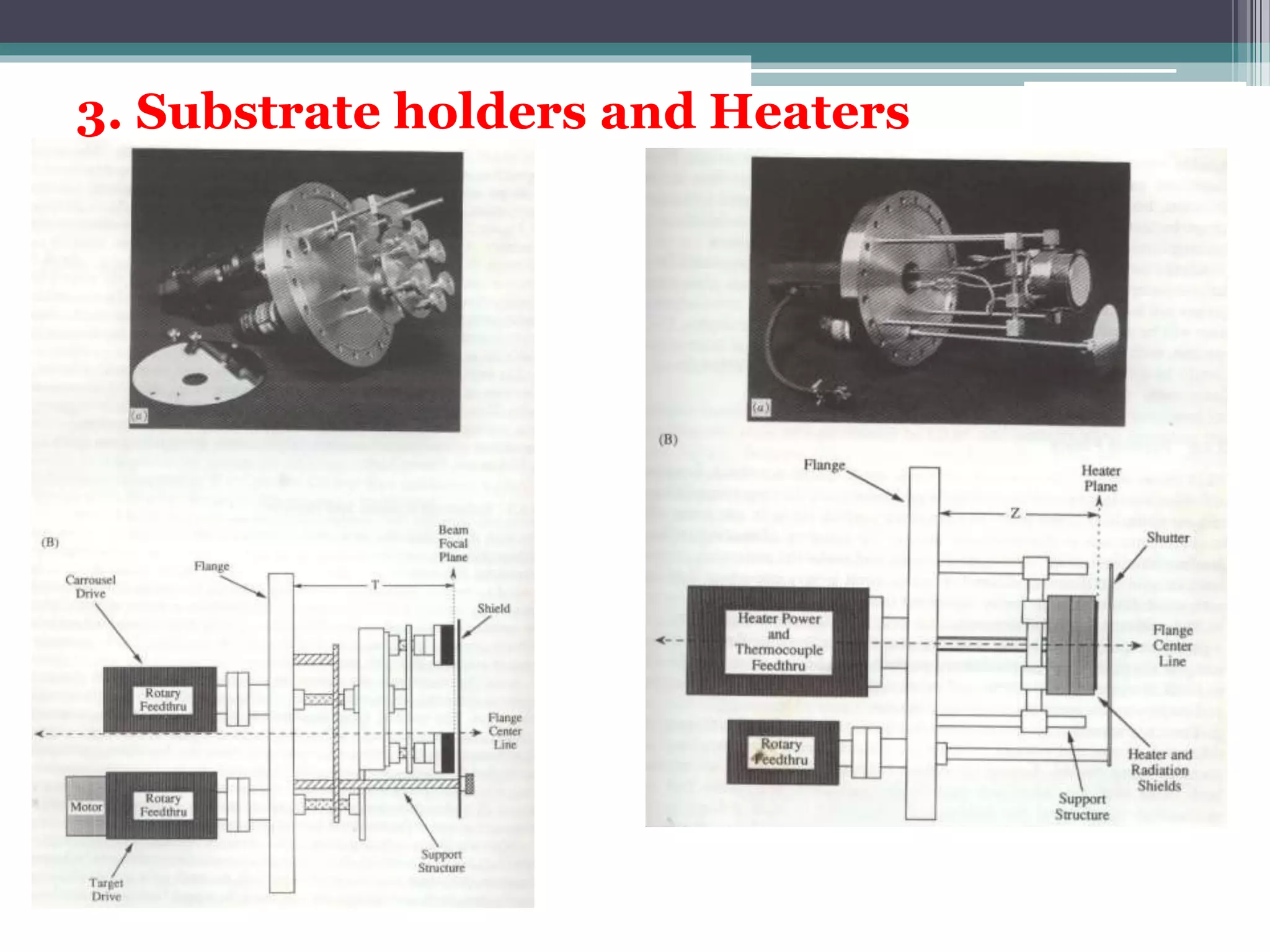
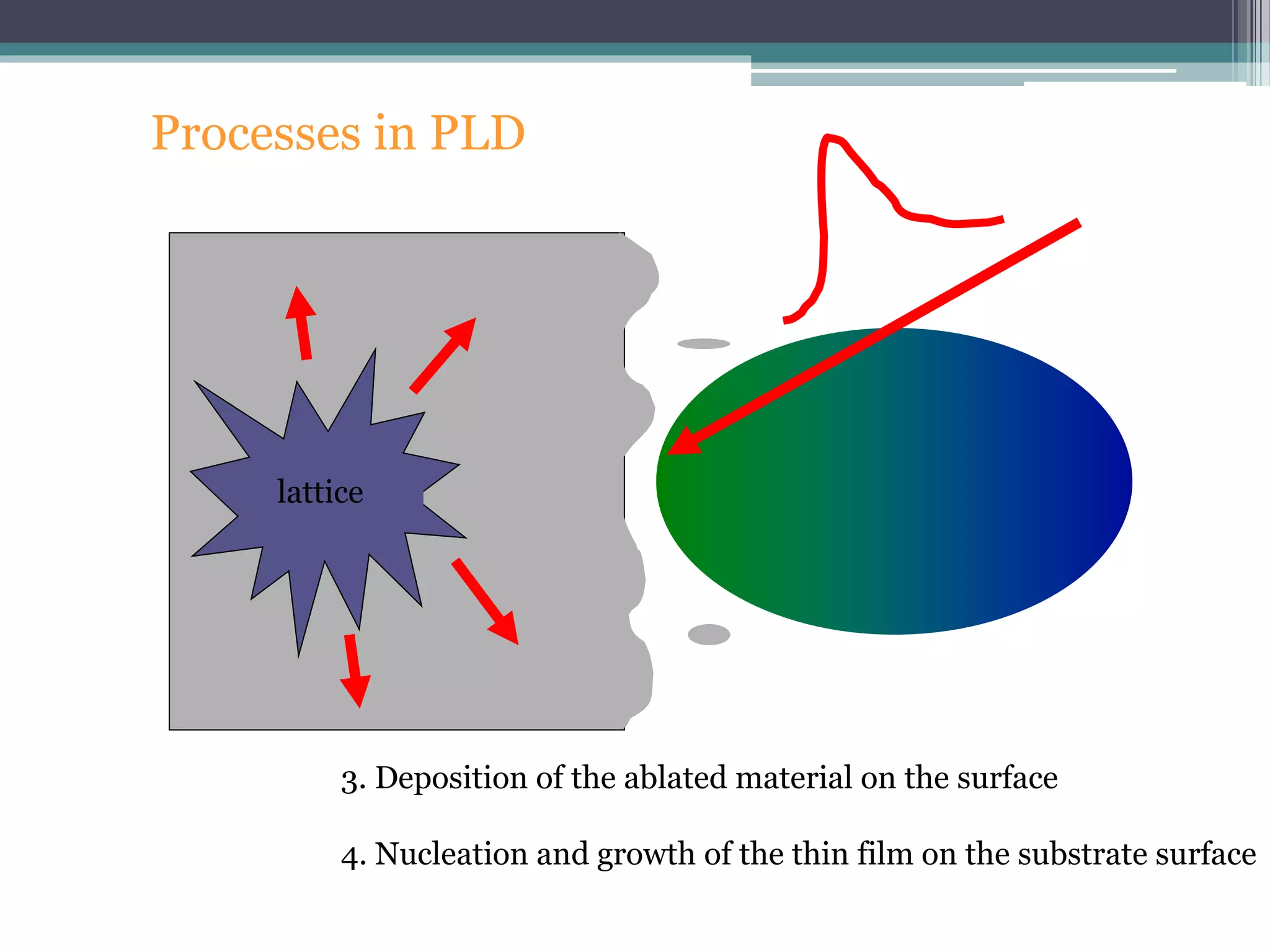
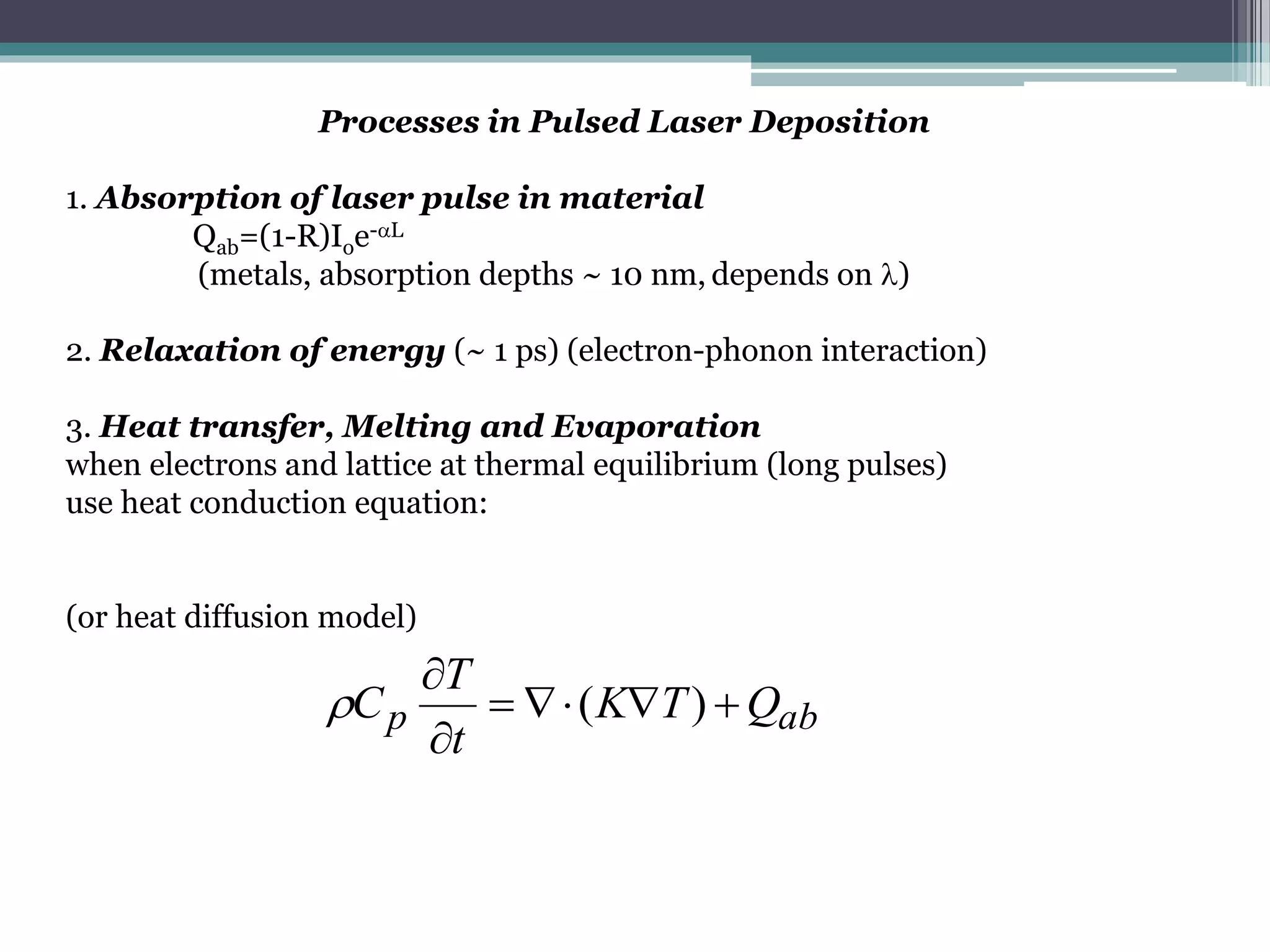
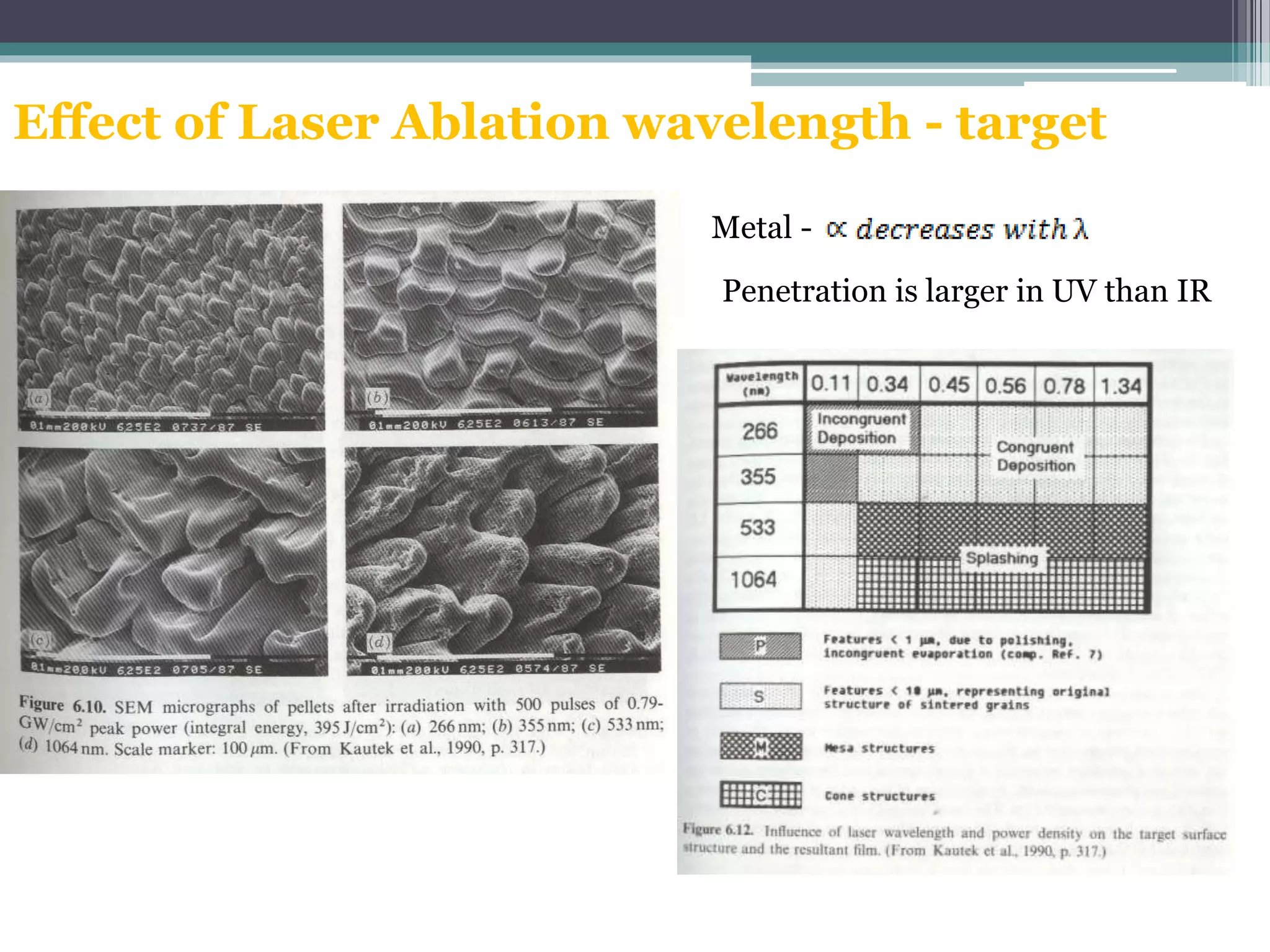
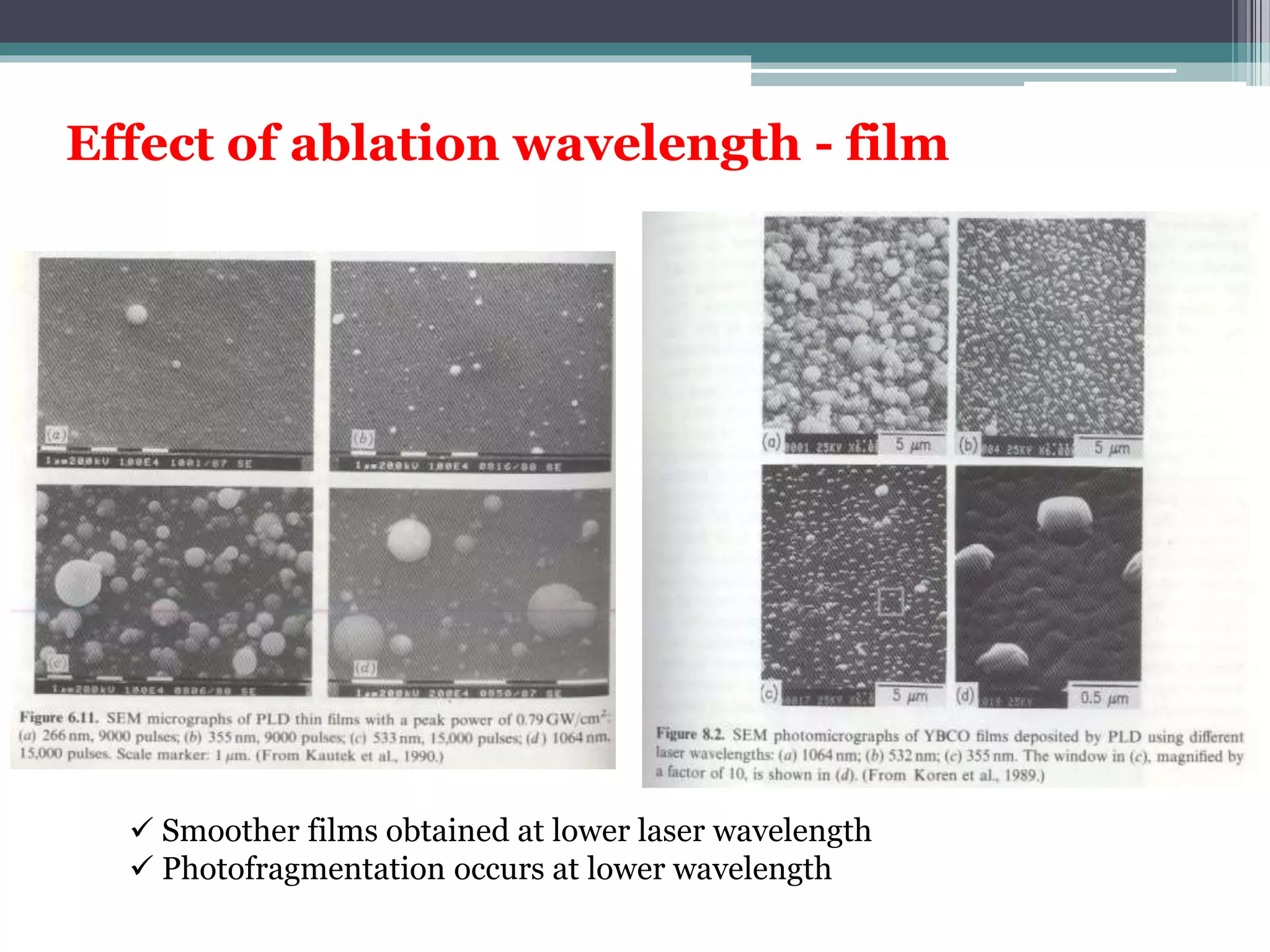
Pulsed laser deposition (PLD) involves using laser pulses to ablate material from a target that is deposited as a thin film on a substrate. PLD offers advantages like the ability to deposit complex oxide materials with precise stoichiometry. The first PLD system successfully deposited a high-temperature superconducting YBa2Cu3O7 thin film. PLD works by ablating material from a target using high-energy laser pulses to create a plasma plume that deposits on the substrate surface. Factors like laser wavelength and background gas are known to affect the film growth process in PLD. While PLD provides good control over film composition and properties, scaling it for large area deposition remains a challenge due to