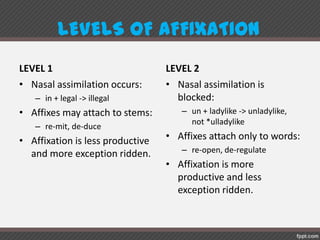
Phonology is the study of how sounds are organized and used in languages. It examines an inventory of sounds and rules for how they interact, and analyzes sound patterns to determine which sounds are significant for a language. Phonetics studies speech sound production, while phonology analyzes sound patterns and interpretations in a particular language. A phoneme is the smallest meaningful sound unit that distinguishes word meanings. Generative phonology assigns phonetic representations to utterances based on a speaker's internal grammar. Non-linear models like autosegmental and metrical phonology treat representations as multi-dimensional. Lexical phonology accounts for interactions of morphology and phonology in word formation through ordered levels.






![Differencebetween phoneand phoneme
PHONE
• One of many possible sounds
in the languages of the world.
• The smallest identifiable unit
found in a stream of speech.
• Pronounced in a defined way.
• Represented between brackets
by convention.
– Example:
• [b], [j], [o]
PHONEME
• One of many possible sounds
in the languages of the world.
• A minimal unit that serves to
distinguish between meanings
of words.
• Pronounced in one or more
ways, depending on the
number of allophones.
• Represented between slashes
by convention.
– Example:
• /b/, /j/, /o/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonology-121213062552-phpapp01/85/Phonology-8-320.jpg)