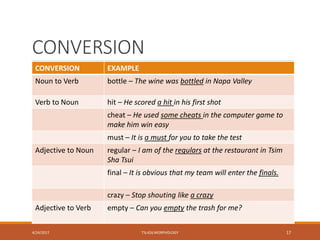
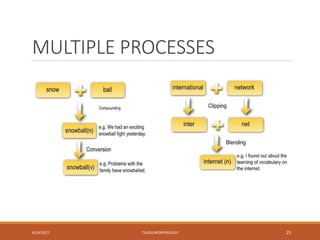
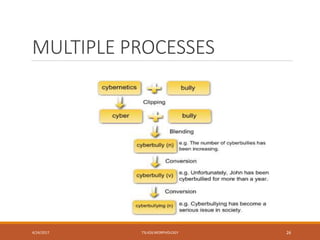
This document discusses various processes of word formation in morphology. It begins by introducing morphology and its focus on words and word formation. It then describes several word formation processes in detail, including coinage, borrowing, compounding, clipping, backformation, blending, conversion, acronyms, derivation, echoism/onomatopoeia, folk etymology, reduplication, and examples of multiple processes. The document provides definitions and examples for each word formation process.