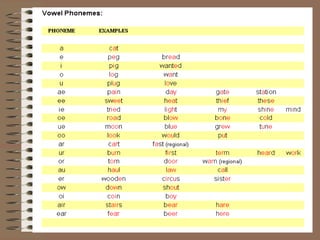
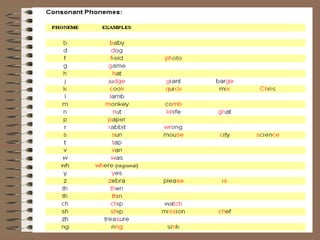
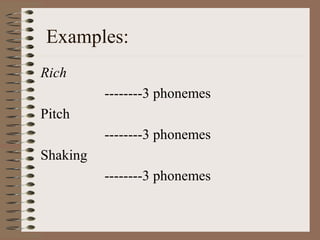
Phonology is the study of how sounds are organized and used in languages. It involves identifying the phonemes, or smallest units of sound, that make up words, and describing how combinations of phonemes are used to create meaning. Phonology also examines phonological processes like allophones, which are variations in pronunciation of the same phoneme, and rules that govern how phonemes are combined into syllables and words with correct stress patterns. The international phonetic alphabet is used to represent sounds in a standardized way across languages.







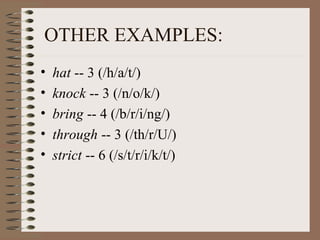




![• Examples (English) [p] and [pH] are
allophones of the phoneme /p/.
• [t] and [tH] are allophones of the phone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonemes-130725005751-phpapp02/85/Phonology-16-320.jpg)





![Transcription:
Ex.
Attend – [ə t n d ]ɛ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonemes-130725005751-phpapp02/85/Phonology-23-320.jpg)





