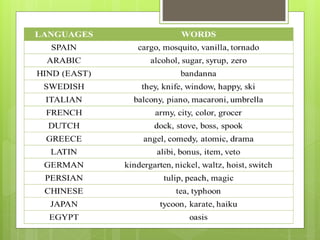
This document discusses the process of borrowing words from other languages. It defines borrowing as adopting words completely or partially from another language. Borrowings enter a language through either oral or written contact. Examples of borrowings include "television" from Greek and Latin, and "pizza" from Italian. There are two main types of borrowing: direct borrowing, which adopts words wholesale, and indirect borrowing, which involves loan translation, shifts in meaning, or blending elements of both languages. Direct borrowing includes cultural, core, and therapeutic borrowings, while indirect involves calques, loan shifts, and loan blends.