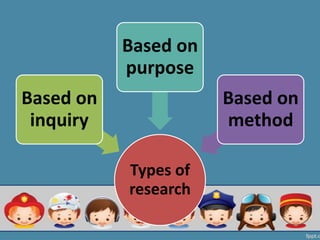
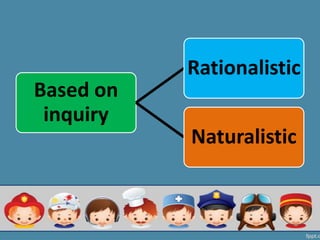
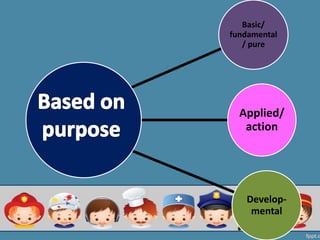
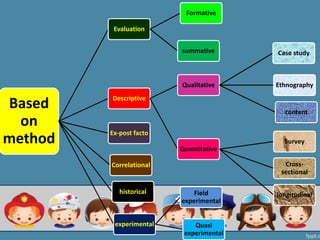
This document outlines different types of research categorized by inquiry, purpose, and method. There are two main types of inquiry: rationalistic, which begins with a theory and uses instruments to test relationships between variables, and naturalistic, which studies individuals' perceptions to understand behavior. Research can also be basic/fundamental, applied/action-oriented, or developmental. Methodologically, research can be qualitative (e.g. case studies, ethnography) or quantitative (e.g. surveys, experiments) and can examine populations descriptively, comparatively, or experimentally.