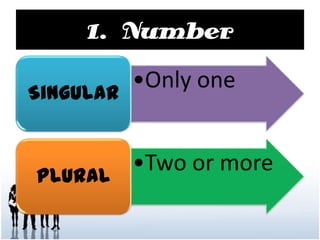
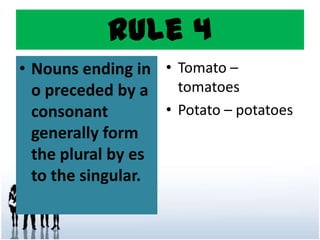
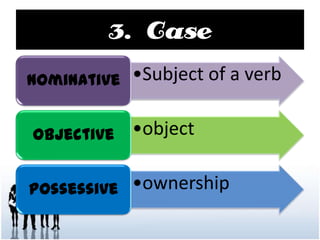
This document discusses the key properties of nouns including number, gender, and case. It provides 10 rules for forming the plural of nouns by changing word endings like adding "s" or "es" or changing the word entirely. It also outlines 7 rules for using nouns in the nominative, objective, and possessive cases based on their use as subjects, objects, in prepositional phrases, and to show ownership.