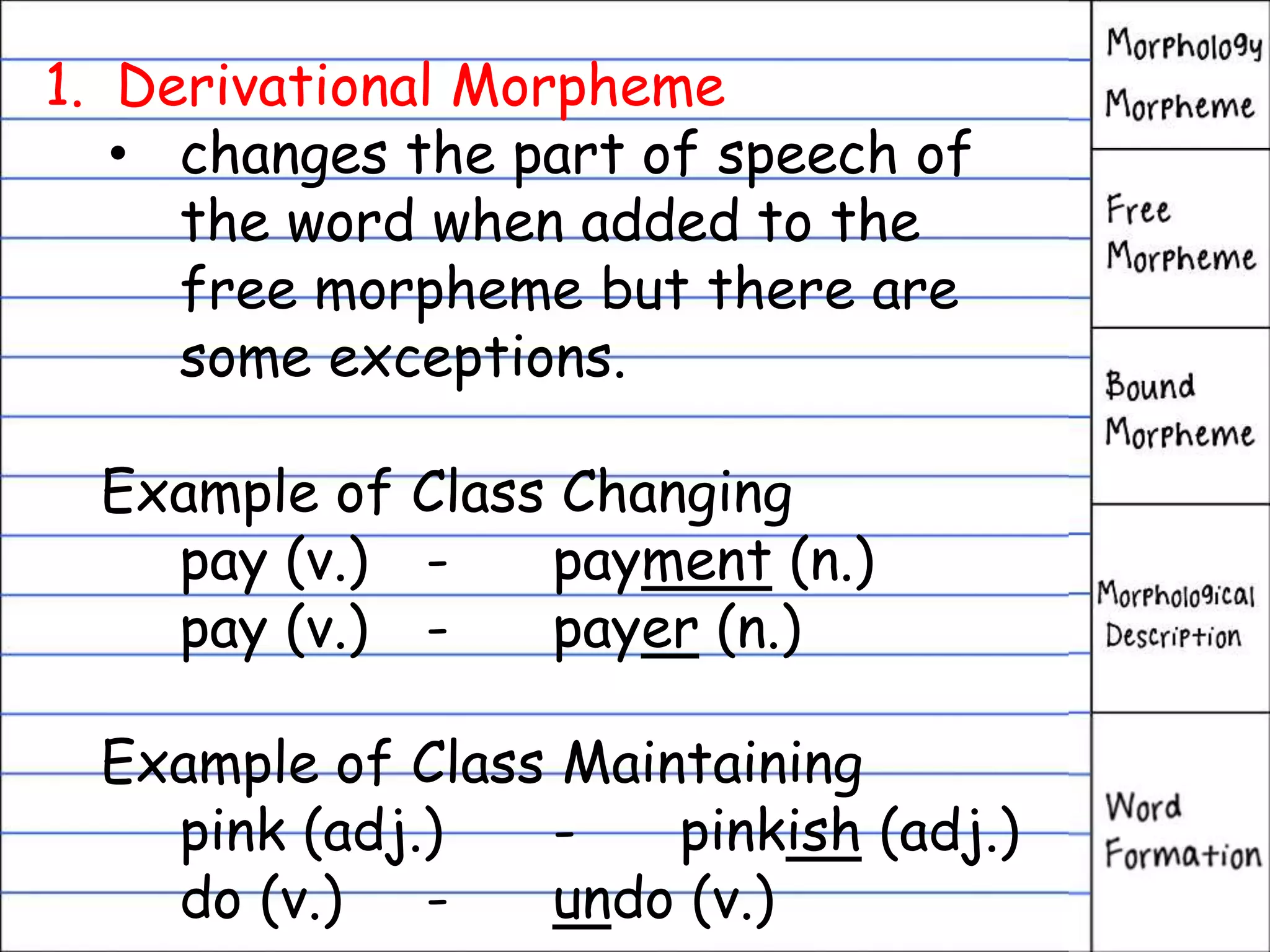
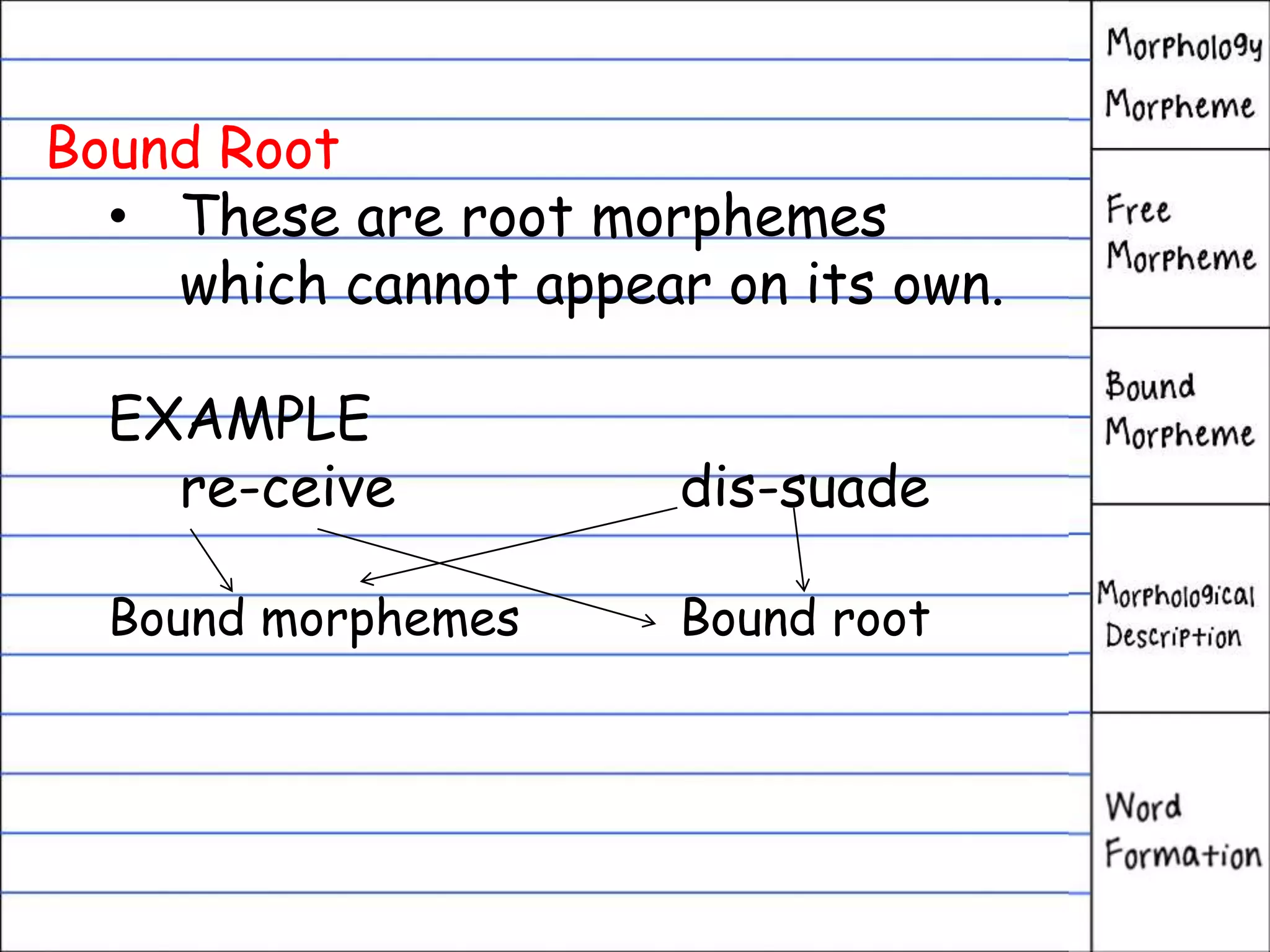
This document defines morphology and discusses the key concepts in word structure and formation. It explains that morphology studies the structure of words and how new words are derived. Morphemes are the smallest units of meaning, and can be free or bound. Free morphemes stand alone as words, while bound morphemes like prefixes and suffixes must be attached to other morphemes. The document also distinguishes between inflectional and derivational morphemes and their functions in language.