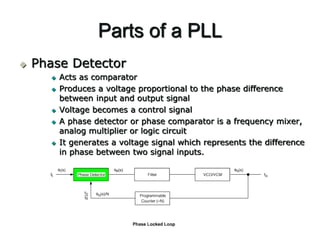
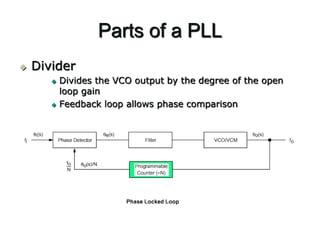
A PLL consists of a phase detector, filter, voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), and optional divider. The phase detector compares the phase of the input signal to the VCO output signal and generates an error voltage. The filter smooths the error voltage which is fed to the VCO. The VCO then adjusts its output frequency according to the error voltage to minimize the phase difference between its output and the input signal. An optional divider may be included to scale the VCO output frequency before feeding it back to the phase detector for comparison to the input signal. In this way, the PLL is able to lock its output phase to the input phase or some multiple of the input phase.