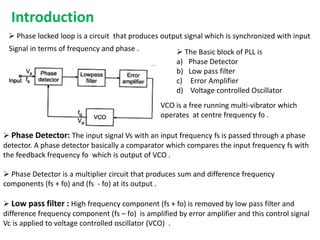
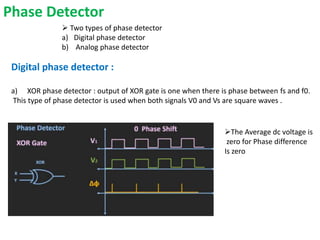
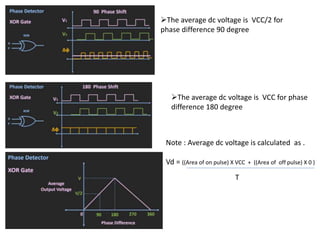
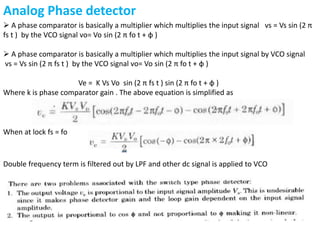
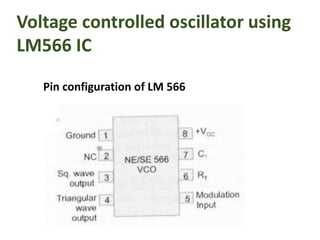
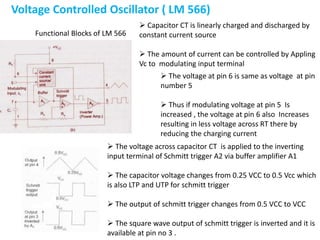
This document provides an overview of phase locked loops (PLL). It describes the basic blocks of a PLL including a phase detector, low pass filter, error amplifier, and voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). The phase detector compares the input and feedback signals and produces sum and difference frequencies. The low pass filter removes the sum frequency, and the error amplifier amplifies the difference frequency to control the VCO. The VCO then adjusts its frequency to reduce the difference between the input and feedback signals until they are locked. The document also discusses digital and analog phase detectors, VCO design using the LM566 IC, and formulas for output frequency.