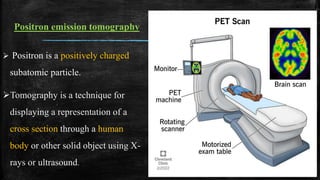
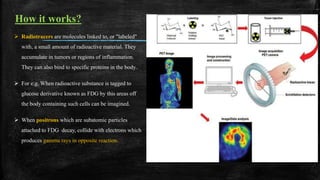
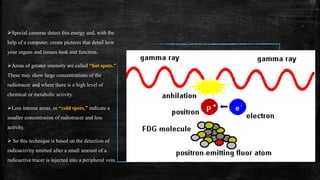
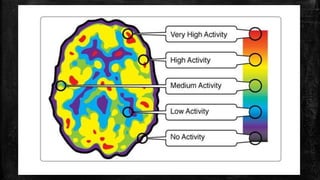
The document discusses positron emission tomography (PET), a nuclear medicine imaging technique that measures physiological functions by analyzing blood flow and metabolism using radiotracers like fluorine-18 for cancer detection and monitoring. It highlights the procedure of PET scans, advantages in diagnosing conditions in oncology and neurology, as well as the potential impact of dietary restrictions and patient factors on results. Additionally, it addresses safety concerns, complications, contraindications, and the significance of PET in various medical fields.









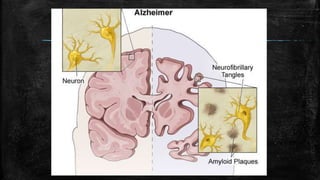

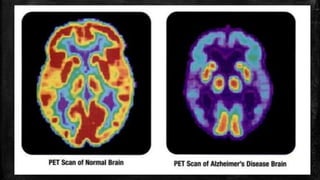
![▪ P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) has been thought to play a role in Aβ clearance
from the brain.
▪ The cholinergic deficit has been studied with PET, the radio-labelled analog of acetylcholine, such as N-
[(11) C]-methyl-4-piperidyl acetate (MP4A).
▪ PET scanning has resulted in improvement in the knowledge of the pathophysiology of atypical
Parkinsonism disorders and may be used as supportive criteria for differential diagnosis of these
conditions.
▪ Tracers that bind to presynaptic dopamine transporters, such as C-methylphenidate, and
dopamine terminal vesicle monoamine transporters, such as C-dihydrotetrabenazine, have been
developed as markers of presynaptic dopaminergic function. Dopaminergic neurons in these
regions project to the putamen and head of the caudate nucleus, respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/petscan1-230623170636-e31d1d80/85/PET-SCAN-1-pptx-17-320.jpg)




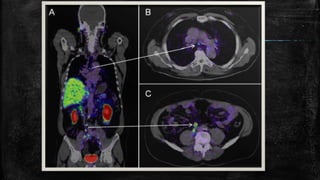
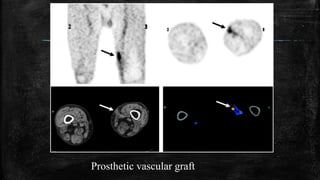
![Infectious Diseases
▪ PET can be used to image bacterial infections via 18F-FDG, by identifying infection-
associated inflammatory response.
▪ Agents include [18F]maltose,[18F]maltohexaose & [18F]2-fluorodeoxysorbitol (FDS).
▪ FDS importantly targets only Enterobacteriaceae.
▪ Applications include FUO, vascular graft infections, musculoskeletal infections
including osteomyelitis, joint prosthesis infections & diabetic foot infection.
▪ graft imaging, colonic inflammation & peritoneal tuberculosis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/petscan1-230623170636-e31d1d80/85/PET-SCAN-1-pptx-24-320.jpg)

![Musculoskeletal System Diseases
PET provides muscle activation data about deep-lying muscles compared with
techniques like electromyography, which is useful in superficial muscles only.
[18F]-NaF is used to measure regional bone metabolism and blood flow.
[18F]NaF is recently being used in studying bone metastasis also](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/petscan1-230623170636-e31d1d80/85/PET-SCAN-1-pptx-27-320.jpg)









