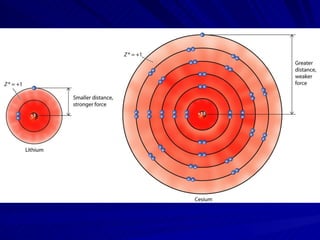
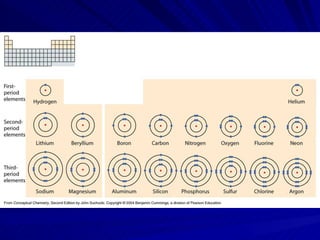
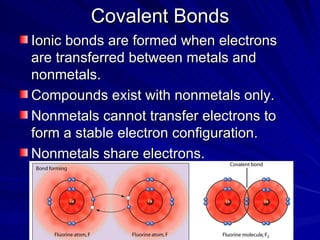
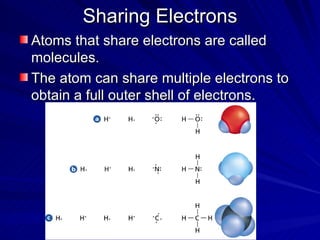
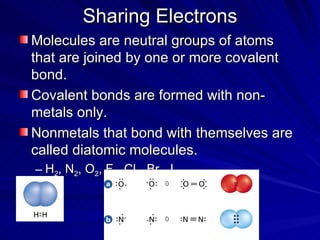
The document summarizes the key differences between ionic and covalent bonding. Ionic bonds form when a metal transfers electrons to a nonmetal, creating oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds form when nonmetals share electrons to obtain a full outer shell. Ionic compounds have high melting points, are brittle solids, and dissolve well in water, while covalent compounds have lower melting points, are soft and pliable, and are generally insoluble in water.